Simple and fast watershed delineation in python.
See examples/quickstart for more details.
Data available via the USGS HydroSHEDS project.
# Read elevation and flow direction rasters
# ----------------------------
from pysheds.grid import Grid
grid = Grid.from_raster('n30w100_con', data_name='dem')
grid.read_raster('n30w100_dir', data_name='dir')
grid.view('dem') # Delineate a catchment
# ---------------------
# Specify pour point
x, y = -97.294167, 32.73750
# Specify directional mapping
dirmap=(64, 128, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32)
# Delineate the catchment
grid.catchment(data='dir', x=x, y=y, dirmap=dirmap, out_name='catch',
recursionlimit=15000, xytype='label')
# Crop and plot the catchment
# ---------------------------
# Clip the bounding box to the catchment
grid.clip_to('catch')
grid.view('catch') # Calculate flow accumulation
# --------------------------
grid.accumulation(data='catch', dirmap=dirmap, out_name='acc')
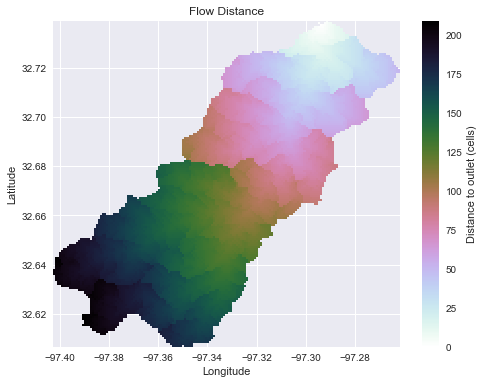
grid.view('acc') # Calculate distance to outlet from each cell
# -------------------------------------------
grid.flow_distance(data='catch', x=x, y=y, dirmap=dirmap,
out_name='dist', xytype='label')
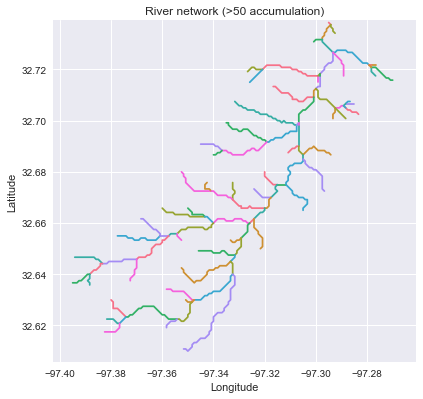
grid.view('dist') # Extract river network
# ---------------------
branches = grid.extract_river_network(fdir='catch', acc='acc',
threshold=50, dirmap=dirmap) # Combine with land cover data
# ---------------------
grid.read_raster('nlcd_2011_impervious_2011_edition_2014_10_10.img',
data_name='terrain', window=grid.bbox, window_crs=grid.crs)
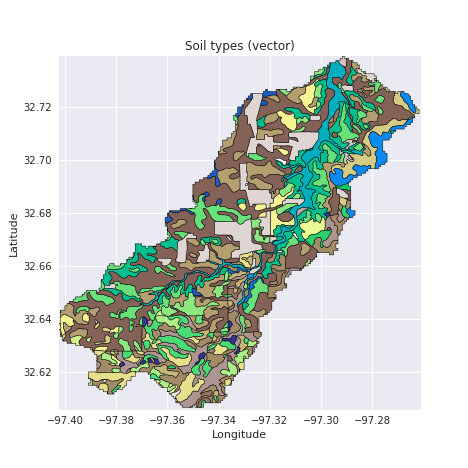
grid.view('terrain') # Convert catchment raster to vector and combine with soils shapefile
# ---------------------
# Read soils shapefile
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely import geometry, ops
soils = gpd.read_file('nrcs-soils-tarrant_439.shp')
# Convert catchment raster to vector geometry and find intersection
shapes = grid.polygonize()
catchment_polygon = ops.unary_union([geometry.shape(shape)
for shape, value in shapes])
soils = soils[soils.intersects(catchment_polygon)]
catchment_soils = soils.intersection(catchment_polygon) # Convert soils polygons to raster
# ---------------------
soil_polygons = zip(catchment_soils.geometry.values,
catchment_soils['soil_type'].values)
soil_raster = grid.rasterize(soil_polygons, fill=np.nan)- Hydrologic Functions:
flowdir: DEM to flow direction.catchment: Delineate catchment from flow direction.accumulation: Flow direction to flow accumulation.flow_distance: Compute flow distance to outlet.resolve_flats: Resolve flats in a DEM using the modified method of Garbrecht and Martz (1997).fraction: Compute fractional contributing area between differently-sized grids.extract_river_network: Extract river network at a given accumulation threshold.cell_area: Compute (projected) area of cells.cell_distances: Compute (projected) channel length within cells.cell_dh: Compute the elevation change between cells.cell_slopes: Compute the slopes of cells.
- Utilities:
view: Returns a view of a dataset at a given bounding box and resolution.clip_to: Clip the current view to the extent of nonzero values in a given dataset.resize: Resize a dataset to a new resolution.rasterize: Convert a vector dataset to a raster dataset.polygonize: Convert a raster dataset to a vector dataset.check_cycles: Check for cycles in a flow direction grid.set_nodata: Set nodata value for a dataset.
- I/O:
read_ascii: Reads ascii gridded data.read_raster: Reads raster gridded data.to_ascii: Write grids to ascii files.
pysheds currently only supports a d8 routing scheme
pysheds currently only supports Python 3
$ git clone https://github.com/mdbartos/pysheds.git
$ cd pysheds
$ python setup.py installPerformance benchmarks on a 2015 MacBook Pro:
- Flow Direction to Flow Accumulation: 36 million grid cells in 15 seconds.
- Flow Direction to Catchment: 9.8 million grid cells in 4.55 seconds.