Transactional non volatile storage for Arduino
Transactional non-volatile storage uses EEPROM for reliably storing client's data. It provides the following useful properties:
- client will not read the data it have never written
- client will not read the data corrupted for any reason
- the data update will succeed either entirely or not at all, in the latter case old data will be read
- the data is bound to the string tag and numerical instance id provided by the client so the data originally bound to the different tag or having different instance id will not be read to avoid erroneous interpretation of the semantically different data
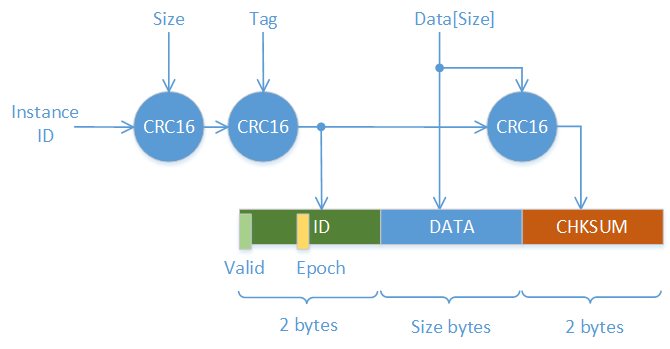
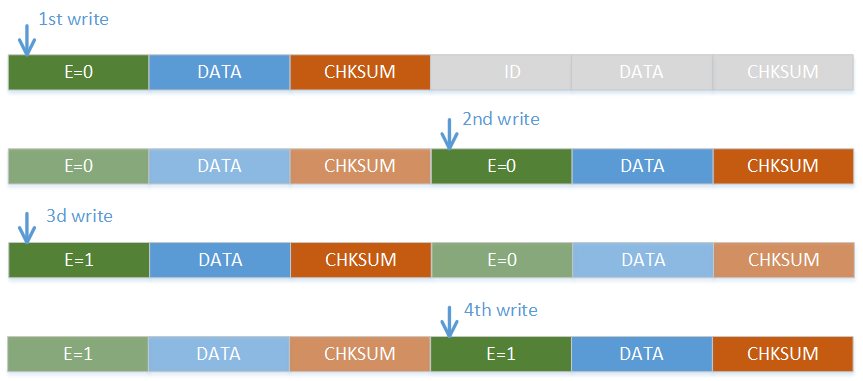
To provide the above guarantees the data is saved in 2 copies in 2 adjacent storage 'cells'. The first 2 bytes of the cell contains the value ID calculated as CRC16 of the size and tag with instance ID as initial value. The high order bit of the first ID byte serves as 'valid' bit and always set to 1 on writing new value. The low order bit of the first ID byte serves as 1bit 'epoch' number. So the are 14 bits left for value ID. The last 2 bytes of the cell contains the value checksum with value ID used as initial CRC value.
The cells are written in round robin manner with the epoch number updated every time we start writing the first cell.
The nv_tx_get call not only choose the latest value to read but also clear the valid bit in case the ID or checksum mismatch. So all subsequent nv_tx_put calls may just read the first byte of the cell to find out which cell should by written.
Oleg Volkov ([email protected])