KVA is a simple key-value-artifact store designed to log and retrieve data. It is like wandb, but not so shitty. At its heart, it is a append-only JSON store with some helpers to easily retrieve data and handle files.
from kva import kva
kva.init(run_id="some-run")
kva.log(config={'foo': 'bar'})
# Oups there was something missing in the config
kva.log(config={'hello': 'world'})
kva.log(step=1, loss=42)
kva.log(step=2)
kva.log(loss=4.2)
print(kva.get(run_id="some-run").latest('config'))
# {'foo': 'bar', 'hello': 'world'}
print(kva.get(run_id="some-run").latest('config', deep_merge=False))
# {'hello': 'world'}
print(kva.get(run_id="some-run").latest('loss'))
# 4.2
print(kva.get(run_id="some-run").latest(['loss', 'step']))
# {'loss': 4.2, 'step': 1}
print(kva.get(run_id="some-run").latest('loss', index='step')) # Identical to: .latest(['loss'], index=['step'])
# step loss
# 0 1.0 42.0
# 1 2.0 4.2pip install git+https://github.com/nielsrolf/kva
For local storage, set:
export KVA_STORAGE='~/.kva' # Default
When configured to stora data locally, kva stores data in a git friendly way:
data.jsonl
artifacts/{filehash}/filename.extension
Appends dict(**data, **init_data) to the append-only database.
Every value that is a kva.File (or a subclass thereof) is additionally saved.
Filters the rows of the database for exact matches and returns a kva.DB object.
Returns a view of the data in the db:
kva.DB().latest(
columns, # Which values to get
index=None, # If set, returns a dataframe of latest values in the db for each value of the index
deep_merge=True # Wether or not to merge data of different rows or only select the latest row
)
Adds data to subsequent calls of kva.log.
A wrapper for kva.filter(f) where the f checks if all values of a row are identical to values in keys.
Basically another way of calling with kva.context(**data):
- starts a run that remains active until
kva.finish()is called. - subsequent calls to
kva.log(**other_data)also log**data - therefore you can use it like this:
Start the UI via:
python server.py --view path/to/view/config.yaml
A view config looks like this:
index:
- project # This is just an example to show that index may consist of multiple columns
- run_id # this has the effect that for each unique index (i.e. fo each run_id), we see one link on the main UI
# Once we click on a link, we see a details page on <url>/{project}/{run_id} with multiple panels
panels:
- name: summary # Title of the panel
columns: '*' # The data of each panel is corresponds to: kva.get(project=..., run_id=...).latest(columns=<specified in the panel>, index=<specified in the panel>)
type: data # This means: we simply see a foldable yaml or table, depending on whether an index is selected or not
- name: Loss # Title
columns: ['loss', 'square']
index: step
type: lineplot # Plot the data - use index as x-axis and in this case 'loss' on the y-axis. This only works when the datatype of all columns if numerical
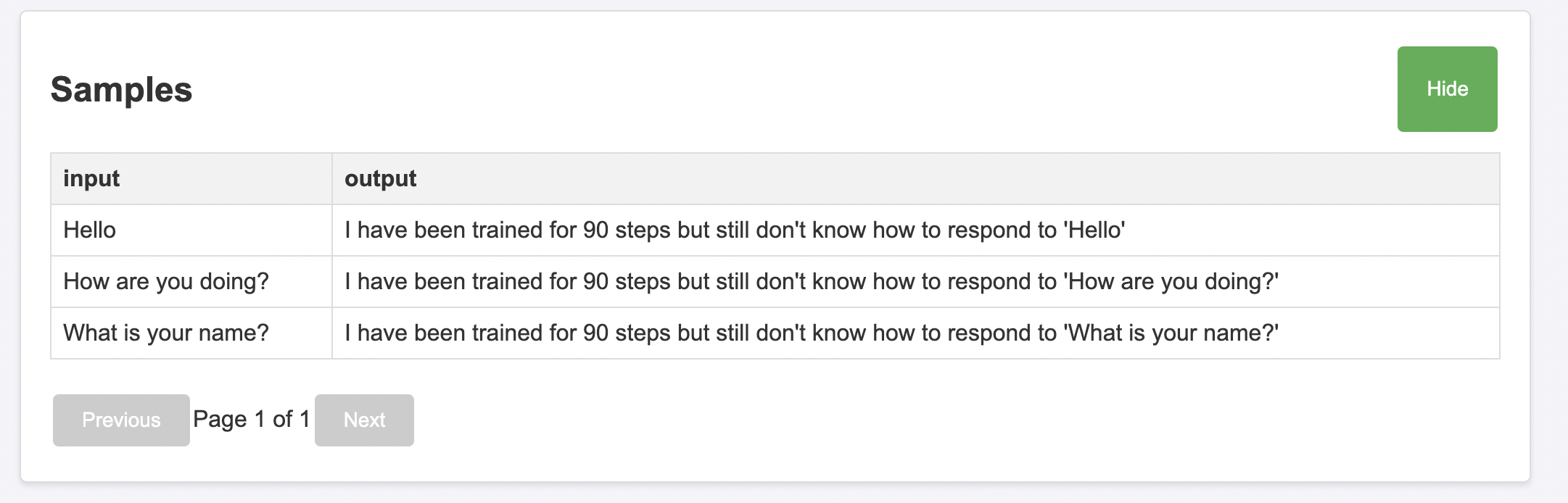
- name: samples # View for examples/llm_sampling.py
columns: ['output']
index: ['input']
type: data # Display the data as a table
- name: image-example
columns: ['output'] # We assume that an image was logged as kva.log(output=File('image.png'))
type: data # Data displays images / audios / videos directly when a value is of type File
- name: images-over-training
columns: ['image'] # We assume that an image was logged as kva.log(output=File('image.png'))
type: data
slider: 'step' # Slider selects the step, at each step we display with the standard data displayer