Build a Traffic Sign Recognition Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Load the data set (see below for links to the project data set)
- Explore, summarize and visualize the data set
- Design, train and test a model architecture
- Use the model to make predictions on new images
- Analyze the softmax probabilities of the new images
- Summarize the results with a written report
Here I will consider the rubric points individually and describe how I addressed each point in my implementation.
1. Provide a Writeup / README that includes all the rubric points and how you addressed each one. You can submit your writeup as markdown or pdf. You can use this template as a guide for writing the report. The submission includes the project code.
You're reading it! and here is a link to my project code
1. Provide a basic summary of the data set. In the code, the analysis should be done using python, numpy and/or pandas methods rather than hardcoding results manually.
I used the Python and NumPy libraries to calculate summary statistics of the traffic signs data set:
- The size of training set is
34799 - The size of the validation set is
4410 - The size of test set is
12630 - The shape of a traffic sign image is
(32, 32, 3) - The number of unique classes/labels in the data set is
43
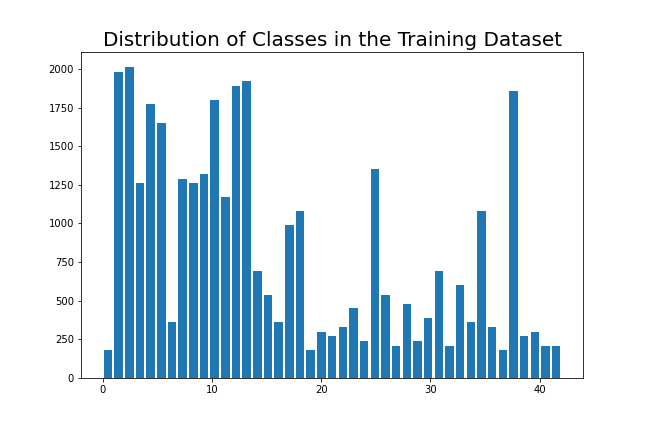
Here is an exploratory visualization of the data set. It is a histogram showing the distribution of image labels in the training set.
1. Describe how you preprocessed the image data. What techniques were chosen and why did you choose these techniques? Consider including images showing the output of each preprocessing technique. Pre-processing refers to techniques such as converting to grayscale, normalization, etc.
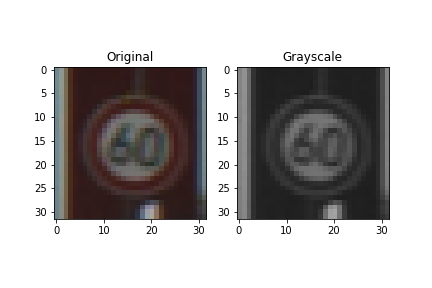
As a first step, I decided to convert the images to grayscale to eliminate the possible color distortion in various images.
Grayscaling also yields better accuracy by previous experimentations.
Here is an example of a traffic sign image before and after grayscaling.
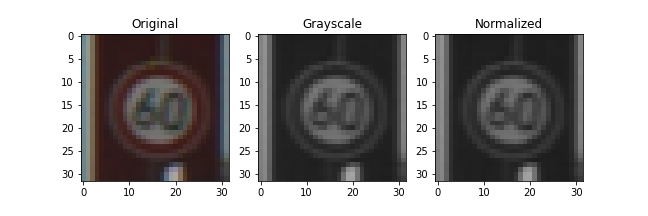
Then, I normalized the image data to values between [-1,1] in order for the mean to be zero. The difference between the normalized and grayscale images is not visually significant.
2. Describe what your final model architecture looks like including model type, layers, layer sizes, connectivity, etc.) Consider including a diagram and/or table describing the final model.
My final model, which is a LeNet architecture, consisted of the following layers:
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x3 RGB image |
| Convolution 3x3 | 1x1 stride, valid padding, outputs 28x28x6 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, outputs 14x14x6 |
| Convolution 3x3 | 1x1 stride, valid padding, outputs 10x10x16 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling | 2x2 stride, outputs 5x5x16 |
| Flatten | Flattens 3D into 1D output |
| Fully connected | 120 outputs |
| RELU | |
| Fully connected | 84 outputs |
| RELU | |
| Fully connected | 43 outputs (logits) |
3. Describe how you trained your model. The discussion can include the type of optimizer, the batch size, number of epochs and any hyperparameters such as learning rate.
To train the model, I used 100 epochs, batch size of 128, and learning rate of 0.001. However, the training accuracy starts hitting 1.000 at epoch 29, and stabilizes at 1.000 around the 40th epoch. So, using 100 epochs is simply an overkill, and 40 should be good to go with our batch size and learning rate.
The training pipeline involves minimizing the loss function using Adam optimizer.
4. Describe the approach taken for finding a solution and getting the validation set accuracy to be at least 0.93. Include in the discussion the results on the training, validation and test sets and where in the code these were calculated. Your approach may have been an iterative process, in which case, outline the steps you took to get to the final solution and why you chose those steps. Perhaps your solution involved an already well known implementation or architecture. In this case, discuss why you think the architecture is suitable for the current problem.
My final model results were:
- training set accuracy of
1.000 - validation set accuracy of
0.942 - test set accuracy of
0.931
If a well known architecture was chosen:
- What architecture was chosen?
- Why did you believe it would be relevant to the traffic sign application?
- How does the final model's accuracy on the training, validation and test set provide evidence that the model is working well?
In this project, the LeNet architecture was chosen as it has already been well-implemented, and also yields great accuracy.
The accuracy on the training set starts off pretty well, reaching 0.940 accuracy at only 2nd epoch. Similarly, the model also yields great accuracy with the validation and test sets, which are above 0.93.
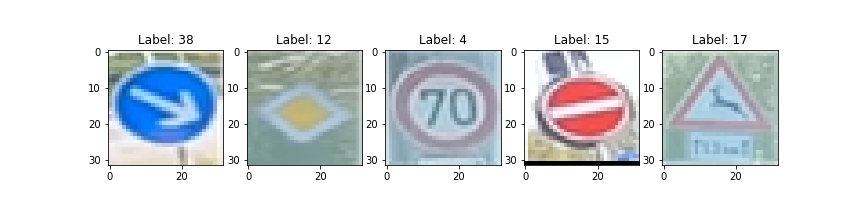
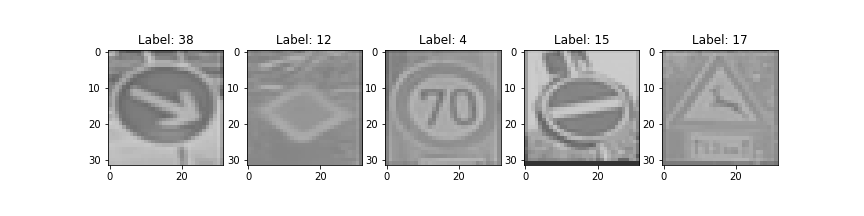
1. Choose five German traffic signs found on the web and provide them in the report. For each image, discuss what quality or qualities might be difficult to classify.
The extra testing images were screen-captured from various parts of AutoTopNL's Video of the German Autobahn.
Here are five German traffic signs that I found on the web:
After pre-processing the images, these are the results:
Since the images are somehow loaded as RGB-A images, the usual method of grayscaling by averaging the RGB-A values did not make the image as clear as RGB images, as you can see the images are slightly brighter and have less contrast than they are supposed to.
Adding that to the fact that these images are taken under direct sunlight through the front windshield, the contrast of each image is reduced, and each grayscale image (especially the 2nd and the 5th) are quite hard to see.
2. Discuss the model's predictions on these new traffic signs and compare the results to predicting on the test set. At a minimum, discuss what the predictions were, the accuracy on these new predictions, and compare the accuracy to the accuracy on the test set (OPTIONAL: Discuss the results in more detail as described in the "Stand Out Suggestions" part of the rubric).
Here are the results of the prediction:
| Image | Prediction |
|---|---|
| Keep right | Keep right |
| Priority road | Priority road |
| Speed limit (70km/h) | Speed limit (70km/h) |
| No entry | No entry |
| Wild animals crossing | No entry |
The model was able to correctly guess 4 of the 5 traffic signs, which gives an accuracy of 80%. This compares favorably to the accuracies on previous validation and test sets, which were 0.942 and 0.931, respectively.
3. Describe how certain the model is when predicting on each of the five new images by looking at the softmax probabilities for each prediction. Provide the top 5 softmax probabilities for each image along with the sign type of each probability. (OPTIONAL: as described in the "Stand Out Suggestions" part of the rubric, visualizations can also be provided such as bar charts)
For the first image, the model is almost absolutely sure that this is a keep right sign (probability of 0.99999976), and the image does contain a keep right sign. The top five softmax probabilities were
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .999 999 8 | Keep right |
| .000 000 141 | Turn left ahead |
| .000 000 129 | Roundabout mandatory |
| .000 000 006 28 | No entry |
| .000 000 004 05 | Road work |
For the second image, the model is also very certain that it is a priority road sign (probability of 0.99995995), which turns out the image actually contains a priority road sign. These are the top five softmax probabilities:
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .999 96 | Priority road |
| .000 016 3 | Roundabout mandatory |
| .000 004 69 | Speed limit (50km/h) |
| .000 004 42 | Speed limit (100km/h) |
| .000 003 33 | No vehicles |
For the third image, the model is slightly less certain that it is a Speed limit (70km/h) sign (probability of 0.99989915), but the image actually is a sign for Speed limit (70km/h). These are the top five softmax probabilities:
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .999 9 | Speed limit (70km/h) |
| .000 099 1 | Speed limit (20km/h) |
| .000 000 737 | Speed limit (30km/h) |
| .000 000 375 | General caution |
| .000 000 276 | Bicycles crossing |
For the fourth image, the model is very certain that it is a no entry sign (probability of 0.99996662), and the image actually is a no entry sign. The top five softmax probabilities were
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .999 97 | No entry |
| .000 033 2 | Priority road |
| .000 000 066 5 | Turn right ahead |
| .000 000 046 6 | Turn left ahead |
| .000 000 025 0 | No passing for vehicles over 3.5 metric tons |
For the last image, the model is not so sure that it found another no entry sign (probability of 0.42036515), and the image does not contain a no entry sign as expected, but a wild animals crossing sign. In fact, none of the top 5 probabilities were correct. Here we see the top five softmax probabilities:
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .420 | No entry |
| .237 | Roundabout mandatory |
| .1467 | Speed limit (20km/h) |
| .0446 | Ahead only |
| .0396 | Speed limit (30km/h) |
The probabilities by the model above shows that the model is extremely confident in areas where the correct predictions are made. However, the model's attempt at the last image was all incorrect for the top 5 softmax probabilities. This shows that the model is mostly reliable, but will also rarely terribly fail to recognize other signs.