The Satellite Imagery Multiscale Rapid Detection with Windowed Networks (SIMRDWN) codebase combines some of the leading object detection algorithms into a unified framework designed to detect objects both large and small in overhead imagery. This work seeks to extend the YOLT modification of YOLO to include the TensorFlow Object Detection API. Therefore, one can train models and test on arbitrary image sizes with YOLO (versions 2 and 3), Faster R-CNN, SSD, or R-FCN.
-
Our arXiv paper: Satellite Imagery Multiscale Rapid Detection with Windowed Networks
-
Our original YOLT paper
-
The original YOLT repository (now deprecated)
SIMRDWN is built to execute within a docker container on a GPU-enabled machine. We use an Ubuntu 16.04 image with CUDA 9.0, python 3.6, and tensorflow-gpu version 1.13.1.
-
Clone this repository (e.g. to /simrdwn)
-
Install nvidia-docker
-
Build docker file
cd /simrdwn/docker nvidia-docker build --no-cache -t simrdwn . -
Spin up the docker container (see the docker docs for options)
nvidia-docker run -it -v /simrdwn:/simrdwn --name simrdwn_container0 simrdwn -
Compile the Darknet C program for both YOLT2 and YOLT3.
cd /simrdwn/yolt2 make cd /simrdwn/yolt3 make
Training data needs to be transformed to the YOLO format of training images in an "images" folder and bounding box labels in a "labels" folder. For example, an image "images/ex0.png" has a corresponding label "labels/ex0.txt". Labels are bounding boxes of the form
<object-class> <x> <y> <width> <height>
Where x, y, width, and height are relative to the image's width and height. Running a script such as /simrdwn/core/parse_cowc.py extracts training windows of reasonable size (usually 416 or 544 pixels in extent) from large labeleled images of the COWC dataset. The script then transforms the labels corresponding to these windows into the correct format and creates a list of all training input images in /simdwn/data/training_list.txt. Class integers are 0-indexex in YOLT, though they are 1-indexed in tensorflow; this can cause some confusion...
We also need to define the object classes with a .pbtxt file, such as /simrdwn/data/class_labels_car.pbtxt
If the tensorflow object detection API models are being run, we must transform the training data into the .tfrecord format. This is accomplished via the simrdwn/core/preprocess_tfrecords.py script.
python /simrdwn/core/preprocess_tfrecords.py \
--image_list_file /simrdwn/data/cowc_labels_car_list.txt \
--pbtxt_filename /simrdwn/data/class_labels_car.pbtxt \
--outfile /simrdwn/data/cowc_labels_car_train.tfrecord \
--outfile_val /simrdwn/data/cowc_labels_car_val.tfrecord \
--val_frac 0.1
We can train either YOLT models or tensorflow object detection API models. If we are using tensorflow, the config file may need to be updated in the /simrdwn/configs directory (further example config files reside here). Training can be run with commands such as:
# SSD vehicle search
python /simrdwn/core/simrdwn.py \
--framework ssd \
--mode train \
--outname inception_v2_3class_vehicles \
--label_map_path /simrdwn/data/class_labels_airplane_boat_car.pbtxt \
--tf_cfg_train_file /simrdwn/configs/_altered_v0/ssd_inception_v2_simrdwn.config \
--train_tf_record /simrdwn/data/labels_airplane_boat_car_train.tfrecord \
--max_batches 30000 \
--batch_size 16 \
--gpu 0
# YOLT vechicle search
python /simrdwn/core/simrdwn.py \
--framework yolt2 \
--mode train \
--outname dense_3class_vehicles \
--yolt_cfg_file ave_dense.cfg \
--weight_dir /simrdwn/yolt2/input_weights \
--weight_file yolo.weights \
--yolt_train_images_list_file labels_airplane_boat_car_list.txt \
--label_map_path /simrdwn/data/class_labels_airplane_boat_car.pbtxt \
--nbands 3 \
--max_batches 30000 \
--batch_size 64 \
--subdivisions 16 \
--gpu 0
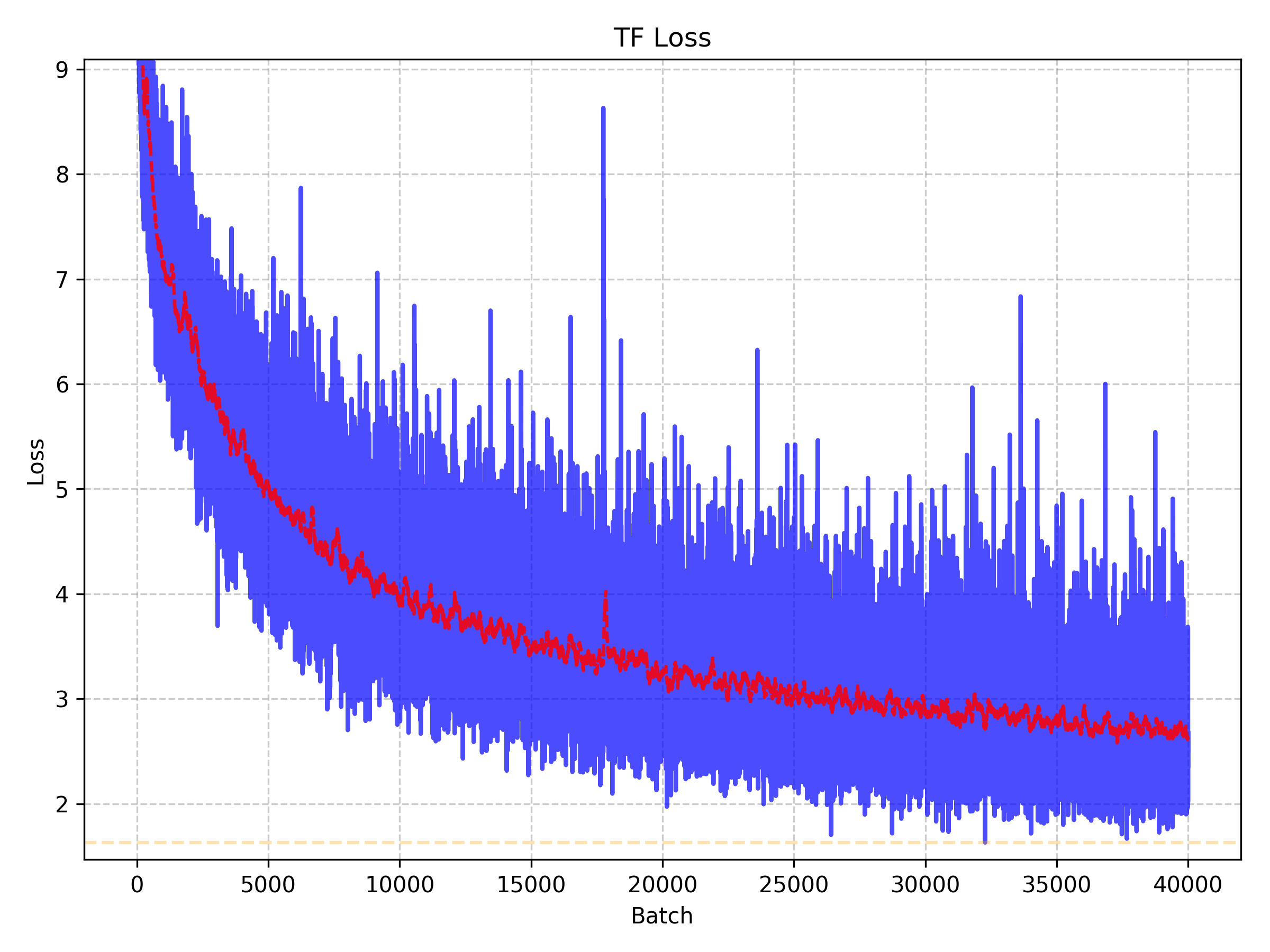
The training script will create a results directory in /simrdwn/results with the filename [framework] + [outname] + [date]. Since one cannot run TensorBoard with YOLT, we include scripts /simrdwn/core/yolt_plot_loss.py and /simrdwn/core/tf_plot_loss.py thatcan be called during training to inspect model convergence. An example convergence plot is shown below.
During the test phase, input images of arbitrary size are processed.
-
Slice test images into the window size used in training.
-
Run inference on windows with the desired model
-
Stitch windows back together to create original test image
-
Run non-max suppression on overlapping predictions
-
Make plots of predictions (optional)
# SSD vehicle search python /simrdwn/src/simrdwn.py \ --framework ssd \ --mode test \ --outname inception_v2_3class_vehicles \ --label_map_path '/simrdwn/train_data/class_labels_car.pbtxt' \ --train_model_path '/simrdwn/results/ssd_train_path' \ --tf_cfg_train_file ssd_inception_v2_simrdwn_orig.config \ --use_tfrecords=1 \ --testims_dir 'vechicle_test' \ --keep_test_slices 0 \ --test_slice_sep __ \ --test_make_legend_and_title 0 \ --edge_buffer_test 1 \ --test_box_rescale_frac 1 \ --plot_thresh_str 0.2 \ --slice_sizes_str 416 \ --slice_overlap 0.2 \ --alpha_scaling 1 \ --show_labels 0 # YOLT vehicle search python /simrdwn/core/simrdwn.py \ --framework yolt \ --mode test \ --outname dense_3class_vehicles \ --label_map_path '/simrdwn/train_data/class_labels_car.pbtxt' \ --train_model_path '/simrdwn/results/yolt2_train_path' \ --weight_file ave_dense_final.weights \ --yolt_cfg_file ave_dense.cfg \ --testims_dir 'vechicle_test' \ --keep_test_slices 0 \ --test_slice_sep __ \ --test_make_legend_and_title 0 \ --edge_buffer_test 1 \ --test_box_rescale_frac 1 \ --plot_thresh_str 0.2 \ --slice_sizes_str 416 \ --slice_overlap 0.2 \ --alpha_scaling 1 \ --show_labels 1Outputs will be something akin to the images below. The alpha_scaling flag makes the bounding box opacity proportional to prediction confidence, and the show_labels flag prints the object class at the top of the bounding box.


If you plan on using SIMRDWN in your work, please consider citing YOLO, the TensorFlow Object Detection API, YOLT, and SIMRDWN.
