- Jae Yoon Chung
- Mandy Yao
- Yunlu Deng
- Zifei Lu
This project aims to reimplement the baseline of VQA from Vahid Kazemi and Ali Elqursh’s paper, "Show, Ask, Attend, and Answer: A Strong Baseline For Visual Question Answering", by building upon the base code https://github.com/Cyanogenoid/pytorch-vqa and to advance the training model by using different modules such as Resnet on resnet50, Resnet on resnet101, Resnet on resnet152, retinanet on resnet101 and retinanet on resnet152. We were able to compare the graphical results in train_results folder and found that the most efficient model was retinanet on resnet101. We then used the weight of this trained model and tested samples of image and question. Overall, this project improved the base code with a greater accuracy model, made changes to the upstream code with Cuda and excluding deprecated packages in mind, and implementation testing.
We would like to give our sincere gratitute to:
- Vahid Kazemi and Ali Elqursh for their detailed paper
- Yan Zhang, Yangyang Guo, Peter Plantinga, Mantas Bandonis for their code base https://github.com/Cyanogenoid/pytorch-vqa
- Dan He, Duke Lin, Sneha Kondur and Tyler Farnan for their testing method https://github.com/dukelin95/vqa_pytorch
Please find more detailed citation at the end of this ReadMe. Moreover, this project aims to provide simple analysis of the results for future researchers to build on.
The following libraries are needed for the base model:
- torch
- torchvision
- h5py
- tqdm
- python3/3.8.10
- pytorch
- cuda
We recommend you to run our code on a VM or a large computer node with 8 cores, 4 gpus, and uninterrupted 15 hours running time for model training. Estimated run time should be no less than 8-10 hours as our project uses model that is not pre-trained.
To run the base model, you should follow these steps:
- Create a directory where you will save this project and create git by typing
git initin the terminal - Clone the repository to your computer by running
git clone -b master https://github.com/myaoo18/EC601-Visual-Question-Answering.git. Make sure that you clone the Master branch - Download the mscoco dataset, and set their paths in
config.py
- qa_path should contain the files
OpenEnded_mscoco_train2014_questions.json,OpenEnded_mscoco_val2014_questions.json,mscoco_train2014_annotations.json,mscoco_val2014_annotations.json. - train_path, val_path and test_path should contain the directory of training, validation and test images respectively. Please download them here: https://visualqa.org/vqa_v1_download.html using VQA 1.0
- Pre-process the images and vocabularies. (Before doing this, you can customize the number of layers of resnet. We used resnet152, resnet101, resnet50 respectively to test the performance of base model). You may modify line 18 to play around with the different resnet models.
python preprocess-images.py
python preprocess-vocab.py- Train the model with:
python train.pyThe default number of training epochs is 50 (indexed from 0 to 49). The result (*.pth file) will be saved to logs directory. You can plot diagram to visualize the result.
Our demo includes the function that the verbal input and output. For a given picture, customers can speak their question directly and our module would also output answer verbally. At the beginning, the demo shows that "I am listening". At this time, customer can speak question directly. After receiving and save question successfully, it will show "listening successfully". With the processing finished, the demo will output answer automatically.
Before successfully running the base model, we encountered several problems:
- At first we ran the model on BU SCC platform without GPU cores, thus making the training speed extremely slow. Therefore, we switched to Google Colab to run base model. However, the connection to Colab is unstable and has limited training time, so that we cannot get the time-consuming training job done. Finally, we solved this issue by asking for GPU cores in the BU SCC platform, so we can use cuda to speed up the training process.
- We encountered some permission issues when installing libraries and running the model on SCC platform, because the base model code involves a lot of reading and writing operations. We solved this by operating
chmodon all files to give permissions. - As some of the code of the base model is out of date, we modified these code when reimplementing it. Specifically, preprocess-images.py, config.py, data.py, train.py and utils.py.
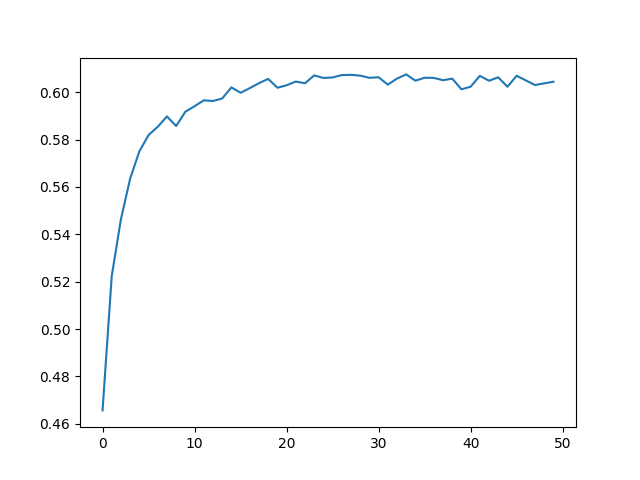
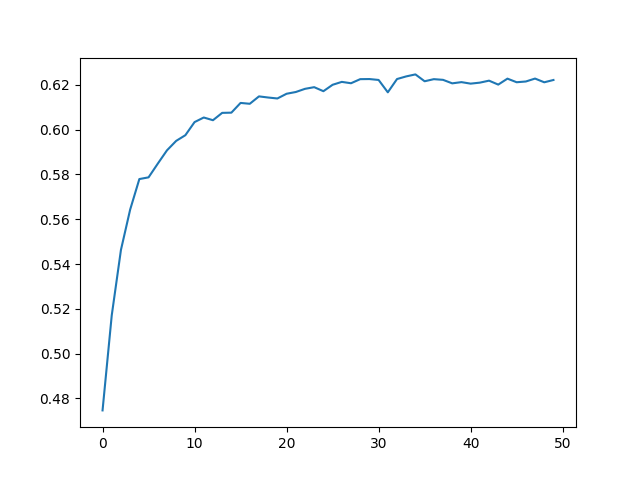
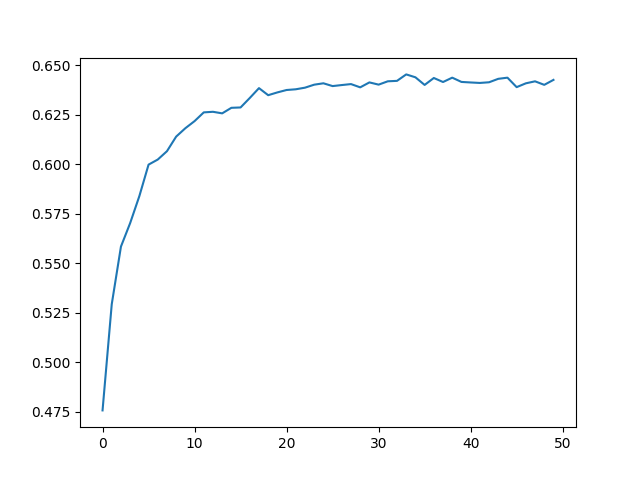
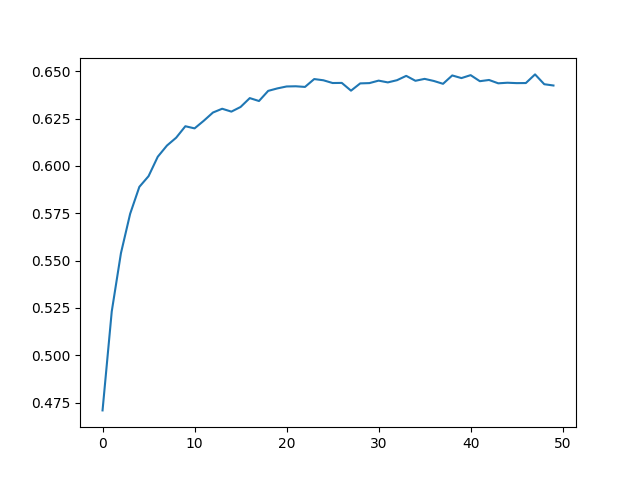
Overall result comparison:
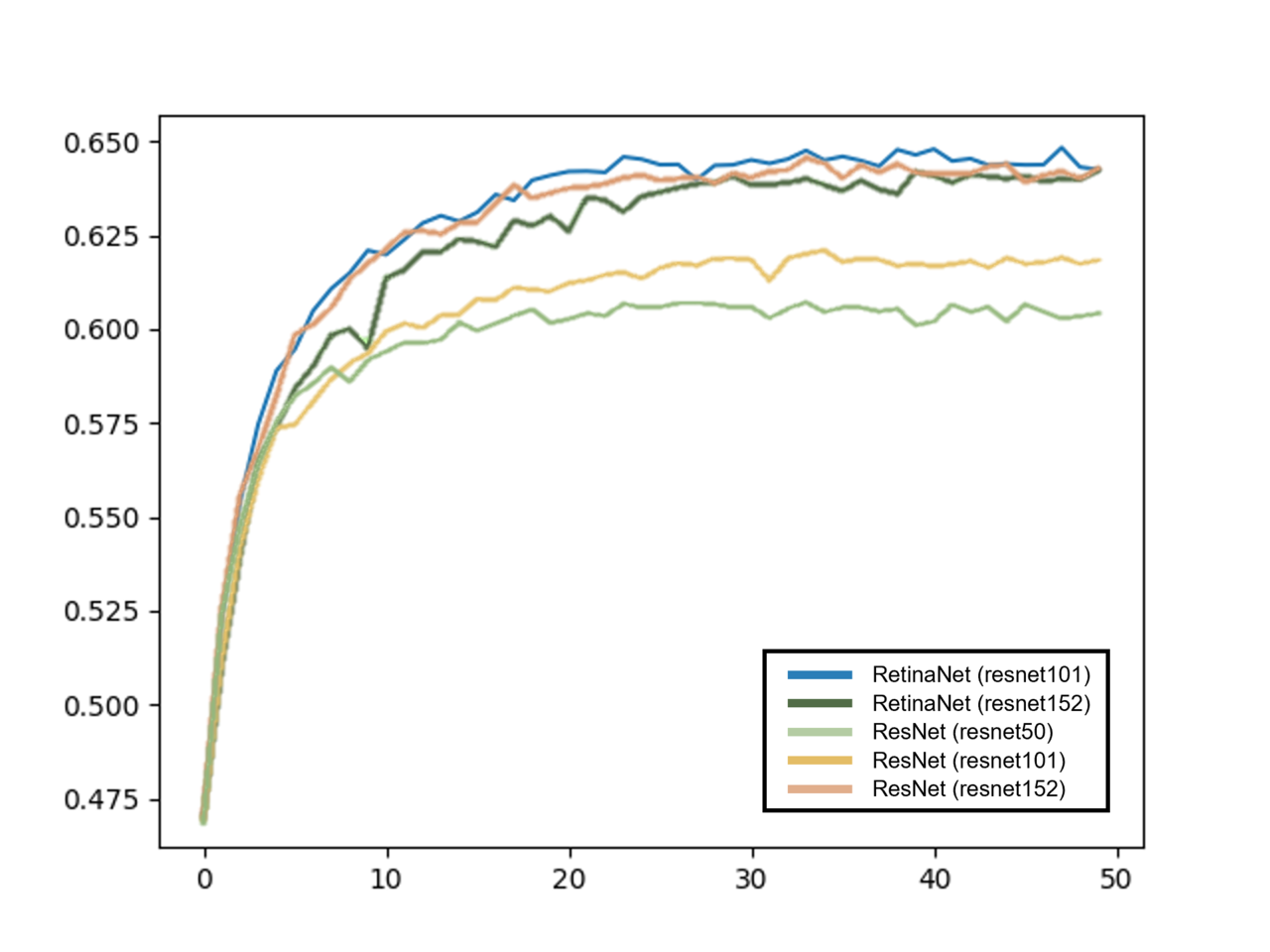 We successfully enhanced the accuracy of the base VQA model by modifying the Object Detection model Architecture.
We successfully enhanced the accuracy of the base VQA model by modifying the Object Detection model Architecture.
As shown in the graph above, RetinaNet with the backbone of resnet101 had a simular but higher accuaracy than the ResNet with the backbone of resnet152.
By using the RetinaNet as the object detection/classification model, we were able to achive a highter accuracy by using less layers than when using the Resnet.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.03162.pdf
https://github.com/Cyanogenoid/pytorch-vqa