Bat2Web: A Framework for Real-time Classification of Bat Species Echolocation Signals Using Audio Sensor Data
Bats play a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance, and studying their behaviors offers vital insights into environmental health and aids in conservation efforts. Determining the presence of various bat species in an environment is essential for many bat studies. Specialized audio sensors can be used to record bat echolocation calls that can then be used to identify bat species. However, the complexity of bat calls presents a significant challenge, necessitating expert analysis and extensive time for accurate interpretation. Recent advances in neural networks can help identify bat species automatically from their echolocation calls. Such neural networks can be integrated into a complete end-to-end system that leverages recent Internet of Things (IoT) technologies with long-range, low-powered communication protocols to implement automated acoustical monitoring. This paper presents the design and implementation of such a system that uses a tiny neural network for interpreting sensor data derived from bat echolocation signals. A highly compact Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model was developed that demonstrated excellent performance in bat species identification, achieving an F1-score of 0.9578 and an accuracy rate of 97.5%. The neural network was deployed, and the performance was evaluated on various alternative edge devices, including NVIDIA Jetson Nano and Google Coral.
To understand the project, you can view this video on YouTube: VIDEO
This system is characterized by the integration of edge devices, each outfitted with a microphone and an embedded computing unit for on-site deployment of a CNN model. Specifically, the system utilizes a high-fidelity 16-bit, 384 kHz analog-to-digital (A/D) Pettersson M500-384 USB Ultrasound microphone for audio signal acquisition.
We have elected to utilize the document-oriented MongoDB NoSQL database system for data management purposes. The interfacing with the database within the application server is facilitated through the use of the Mongoose library. This setup allows for efficient storage and retrieval of detection data, which is categorized according to three primary attributes: the geographic location of the detection (latitude and longitude coordinates); the timestamp of the detection (formatted according to the ISO 8601 standard); and the scientific name of the detected bat species.
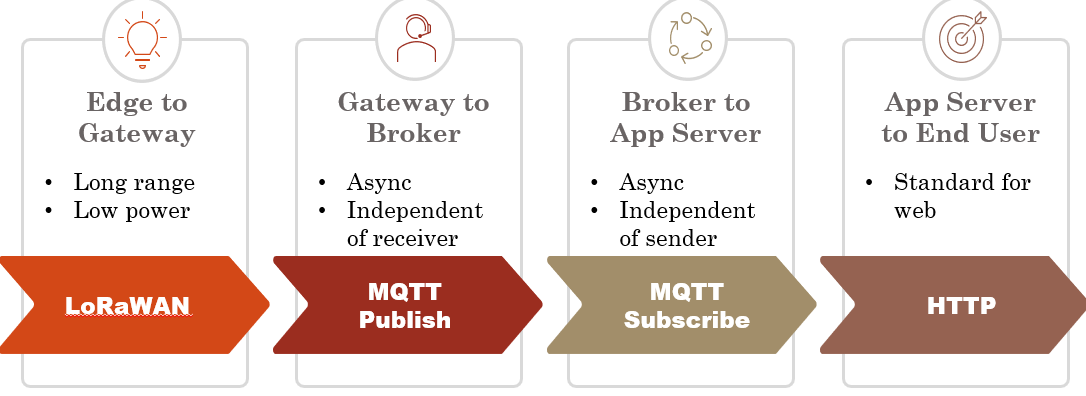
The LoRa Raspberry Pi Gateway serves as the middle-man during the communications, as it will receive the messages from the edge device over the LoRaWAN protocol, and forward them to The Things Network (TTN) broker. This gateway was configured to follow the relevant LoRa channel for our region (EU 863-870), and was registered in The Things Network web portal.
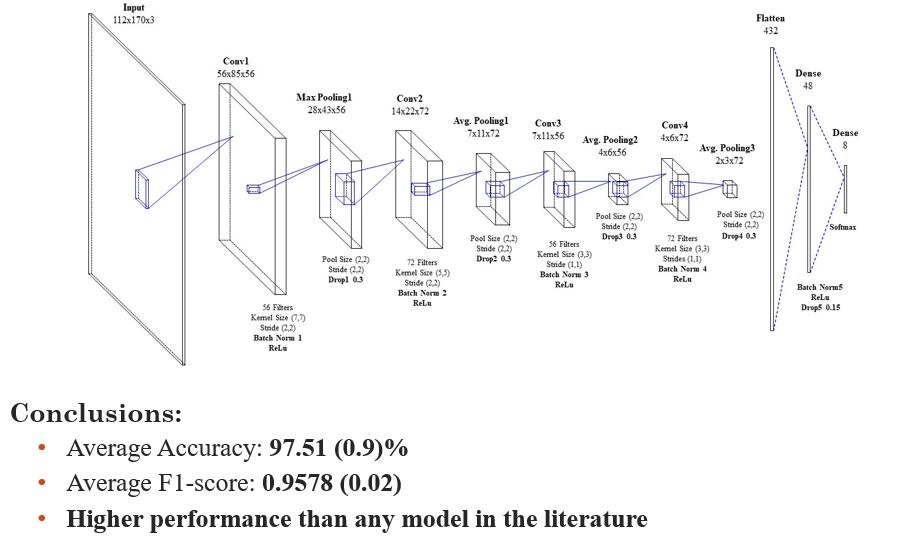
We developed a supervised Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model specifically tailored for classifying bat species in edge devices. This model utilizes the Mel-scaled Filter Bank (MSFB) representation of audio segments. Emphasizing the need for deployment on edge devices, the model was meticulously designed to be compact. The original CNN model was constructed using the TensorFlow framework, and its architecture is depicted in Figure below.
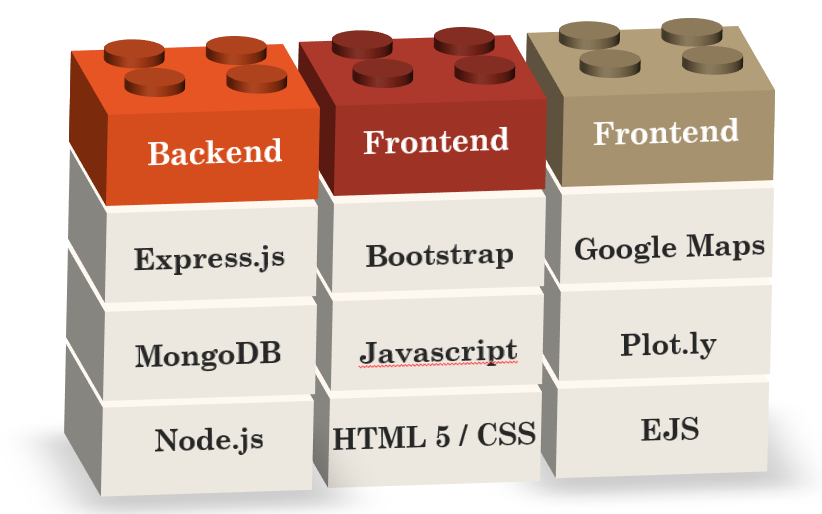
The development of the website's front-end was accomplished using a combination of JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and Bootstrap 4, ensuring a design that is both responsive and mobile-friendly, as depicted in Figure \ref{webapp_overall}. The backend features an ExpressJS based web server.
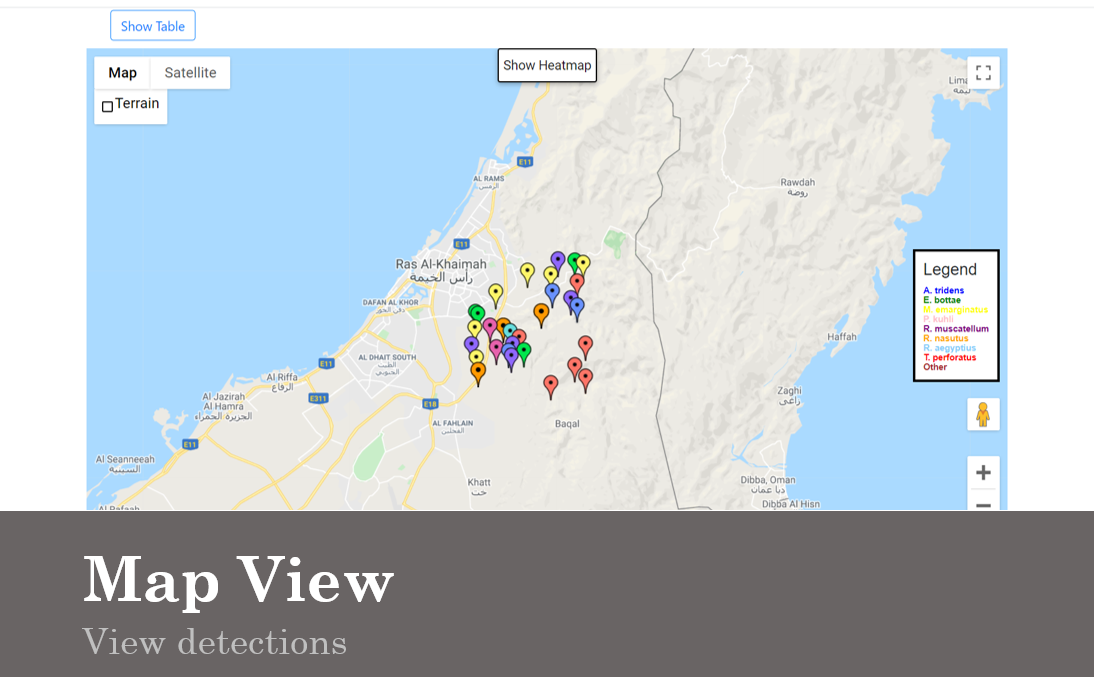
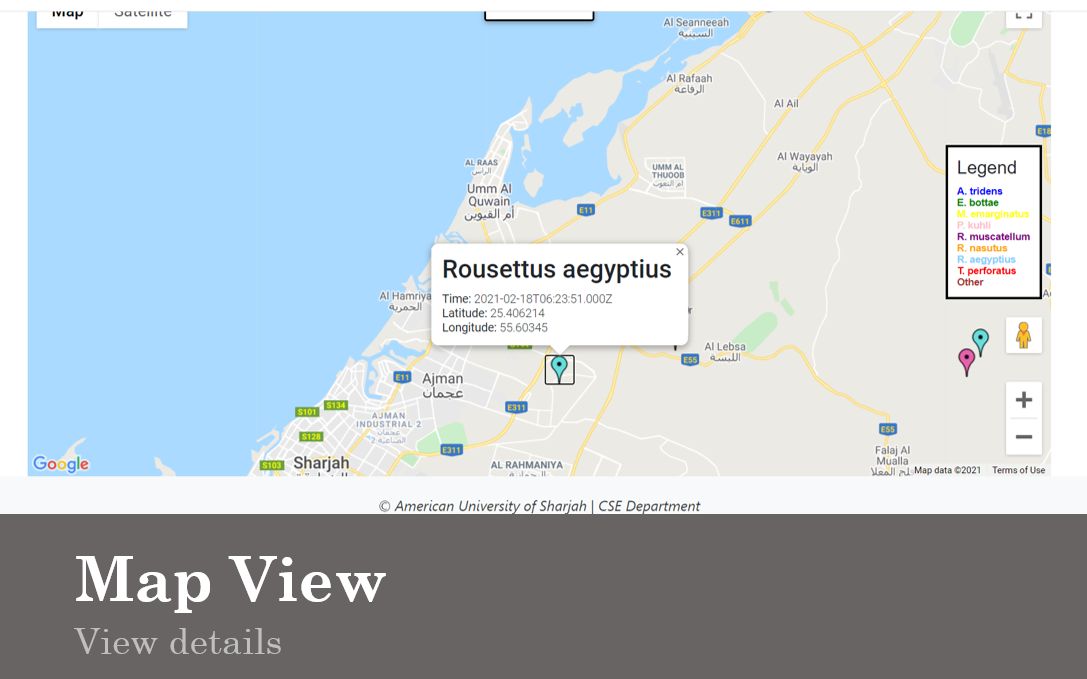
The web platform's homepage is characterized by a map interface, facilitated through the Google Maps API, which displays markers for each detection event. These markers are accompanied by a color-coded legend to aid in the visualization of data.
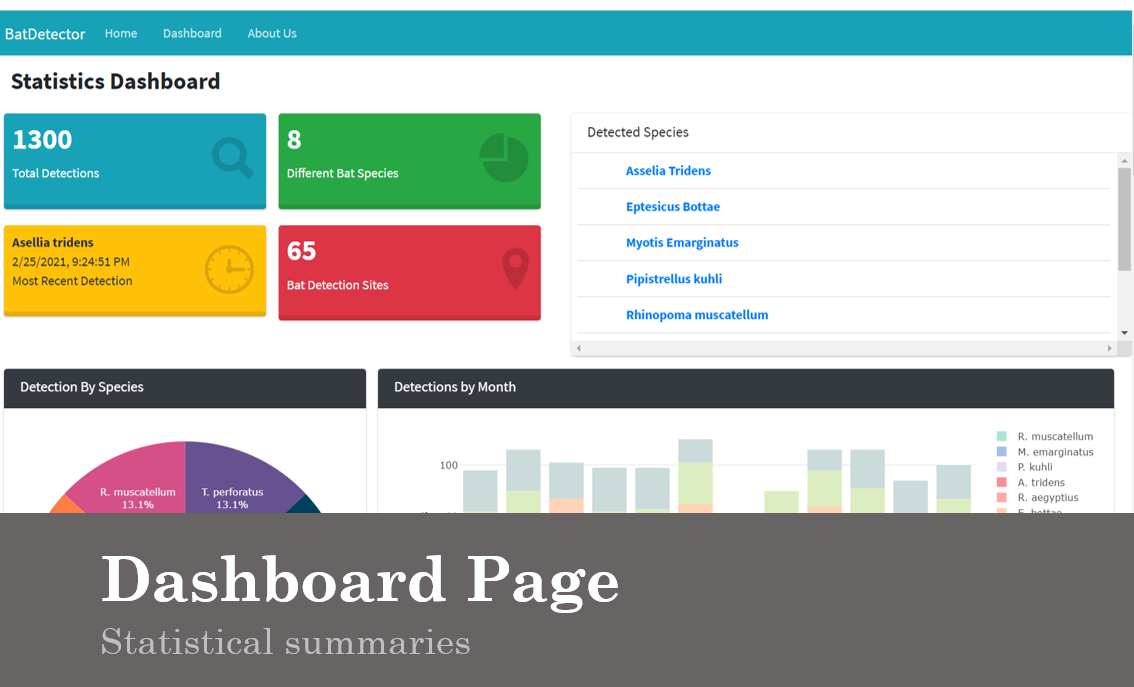
The Dashboard section of the web application is designed to present a comprehensive summary of the bat detections.
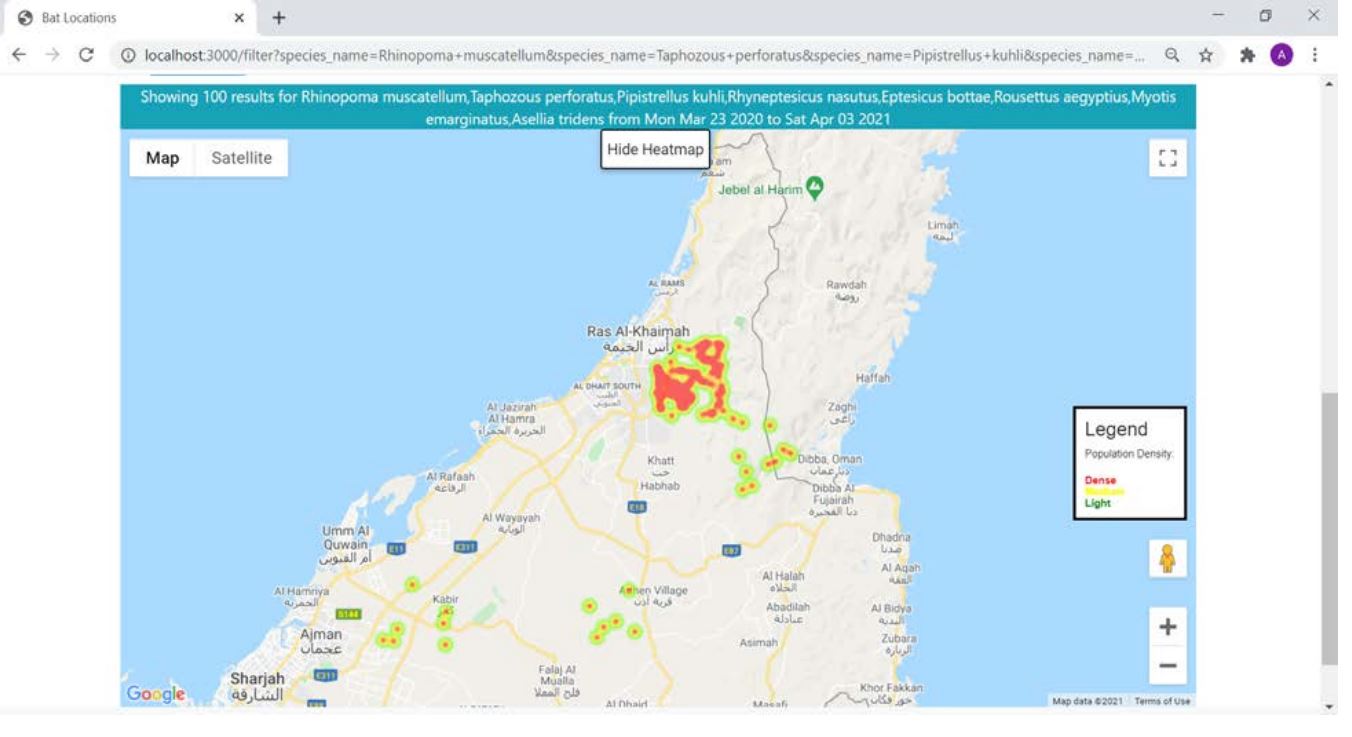
The website also shows a heatmap of detections on the Maps interface.
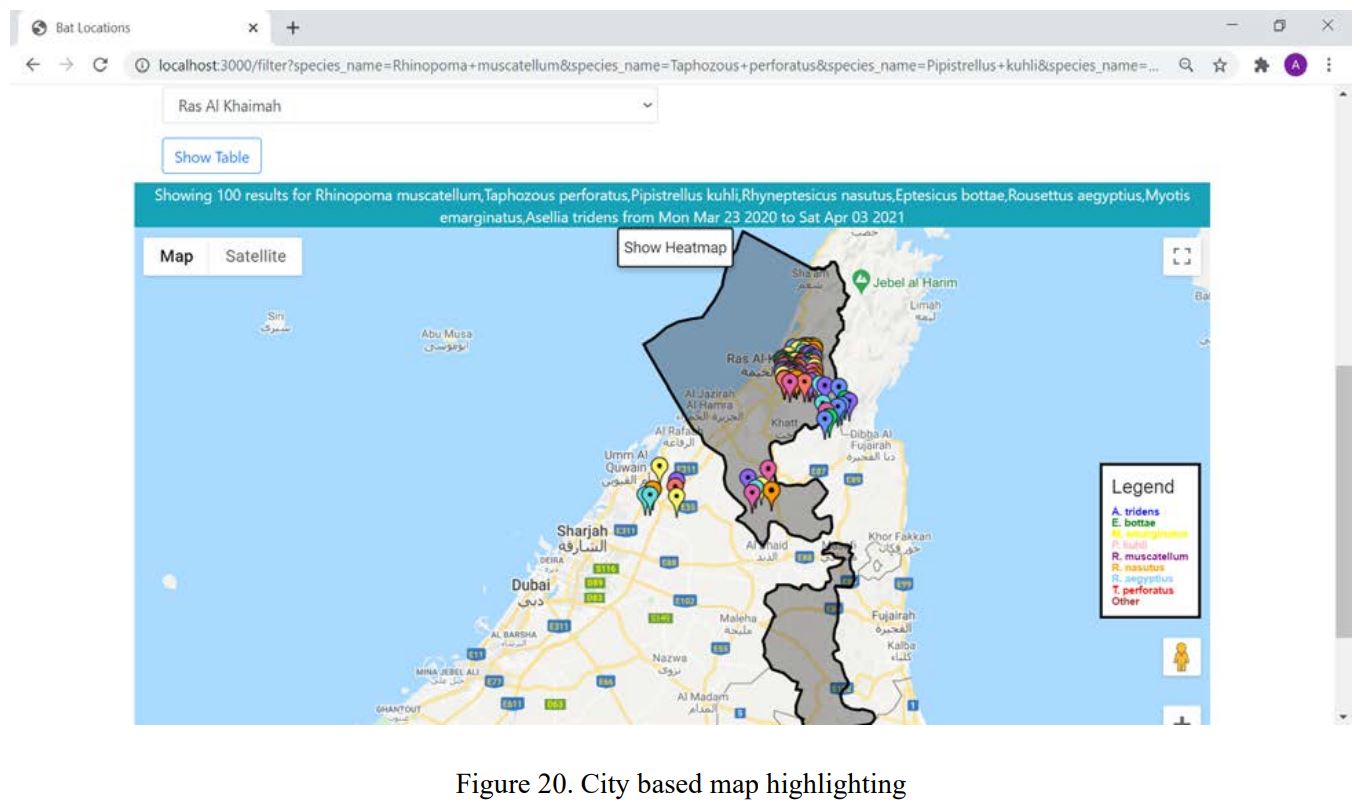
We can also select and filter detections within a city.
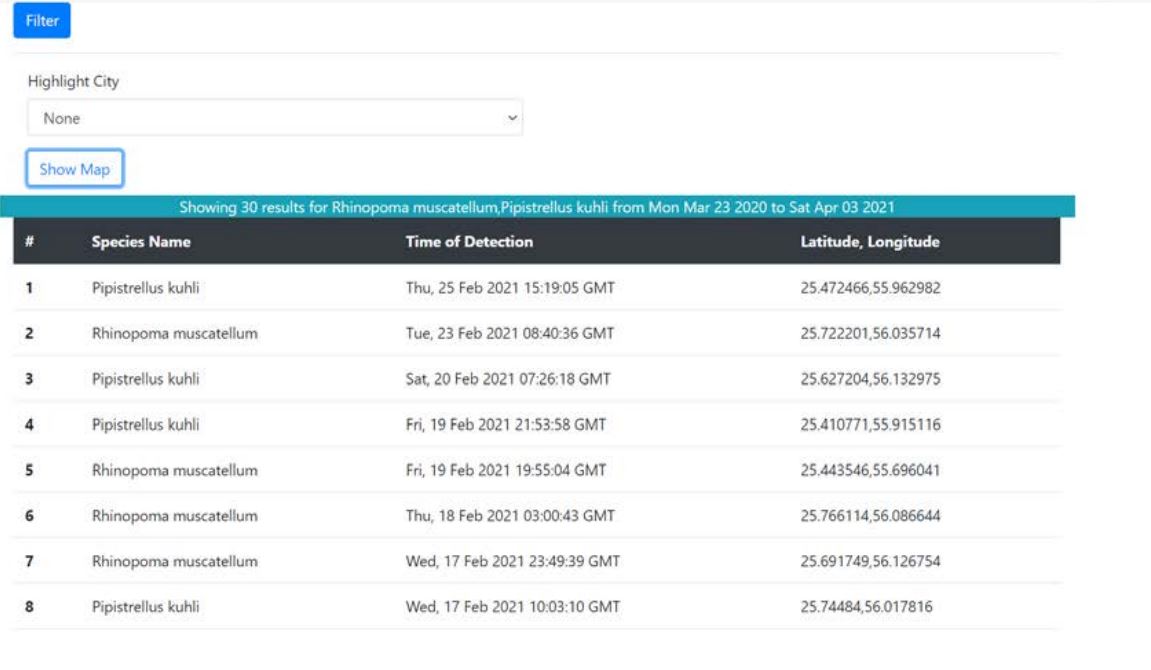
The alternate table view can provide raw details.
@article{,
title={Bat2Web: A Framework for Real-time Classification of Bat Species Echolocation Signals Using Audio Sensor Data.},
author={},
journal={},
volume={},
number={},
pages={},
year={},
publisher={MDPI}
}