Large Language Models (LLMs) offer significant potential for the development of cutting-edge recommender systems, particularly in terms of enhancing interactivity, explainability, and controllability. These are aspects that have traditionally posed challenges. However, the direct application of a general-purpose LLM for recommendation purposes is not viable due to the absence of specific domain knowledge.
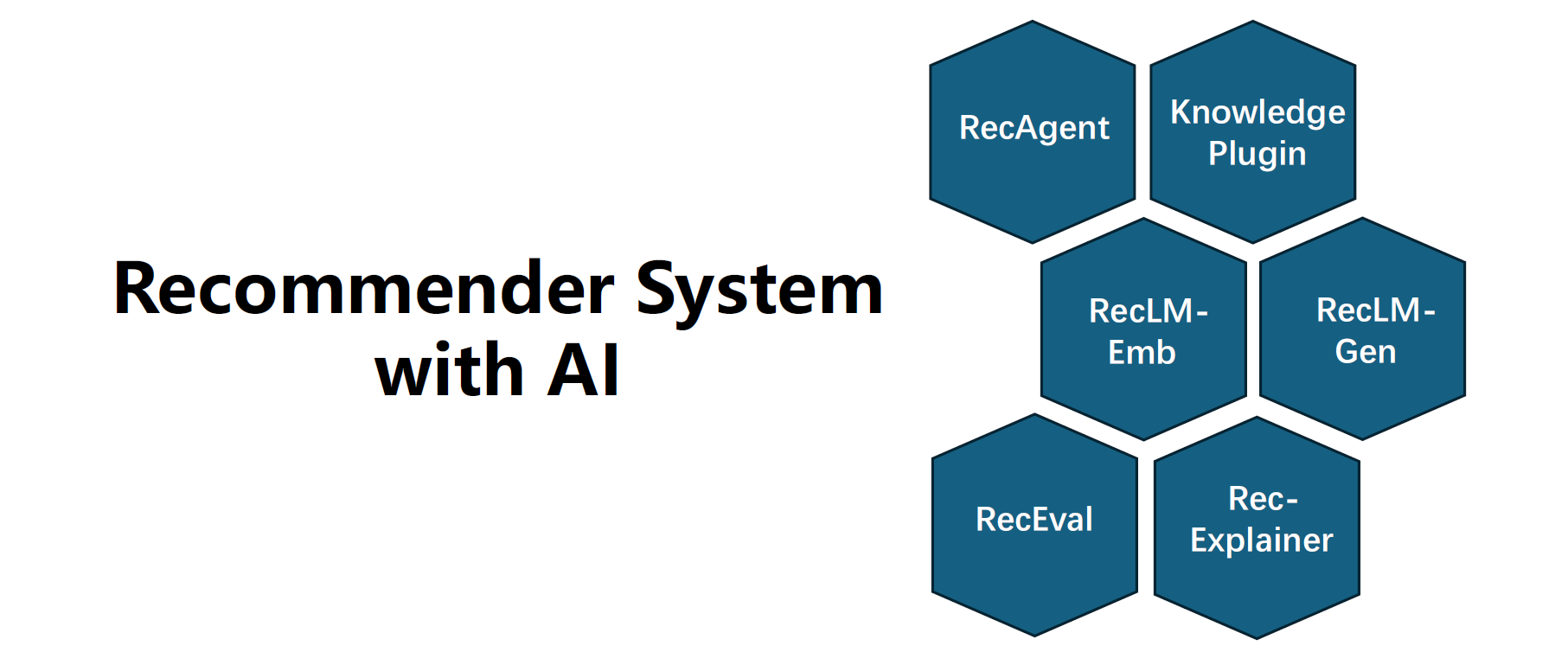
The RecAI project aims to bridge this gap by investigating various strategies to integrate LLMs into recommender systems, a concept people usually term as LLM4Rec. Our goal is to reflect the real-world needs of LLM4Rec through holistic views and methodologies.
We believe that by adopting a holistic perspective, we can incorporate the majority of practical requirements of LLM4Rec into one or more of the techniques explored in the RecAI project. These techniques include, but are not limited to, Recommender AI agents, the injection of knowledge through personalized prompting, fine-tuning language models as recommenders, evaluation, and LLMs as model explainers. The ultimate objective is to create a more sophisticated, interactive, and user-centric recommender system.
 |
Recommender AI Agent LLMs provide natural interactions and respond smartly to human instructions but lack domain-specific expertise. In contrast, traditional recommender systems excel with in-domain data training yet are constrained to structured data and lack interactivity. InteRecAgent introduces an AI agent that combines the strengths of both: it employs an LLM as the brain and traditional recommender models as tools. Consequently, traditional models like matrix factorization can be transformed into conversational, interactive, and explainable recommender systems.. |
 |
Selective Knowledge Plugin How can we enhance an LLM's domain-specific ability without finetuning the model? Then the prompt is the key. In this work, we introduce a method that augments LLMs with selective knowledge, so that large-scale, continuously evolving, and domain-specific data patterns can be injected by prompt. |
 |
Embedding RecLM Dense retrieval is a crucial component in a range of scenarios, including recommender systems and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). While generative language models such as GPTs are designed for sequential token generation, they are not optimized for retrieval-oriented embedding. This is where our project, RecLM-emb, comes into play. RecLM-emb aligns with text-embedding models like text-embedding-ada-002, but it is specifically optimized for item retrieval. The goal is to embed everything for item retrieval. Currently it only supports text modality, such as search query, item description, and user instructions. |
 |
Generative RecLM It's important to note that data patterns vary significantly across domains, meaning a general-purpose LLM may not deliver optimized performance within a specific domain. To adapt to specific domain data patterns, grounding to domain item catalogs, and enhance instruction-following capability, this project discusses the process of fine-tuning a generative Language Model for recommenders, referred to as RecLM-gen. Techniques include supervised finetuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL). Potential applications of this approach include rankers, conversational recommenders, and user simulators. |
 |
Model Explainer Deep learning-based recommender systems are widely used in various online services, thanks to their superiority in effectiveness and efficiency. However, these models often lack interpretability, making them less reliable and transparent for both users and developers. In this work, we propose a new model interpretation approach for recommender systems, call RecExplainer, by using LLMs as surrogate models and learn to mimic and comprehend target recommender models. |
 |
RecLM Evaluator Evaluation is crucial for assessing the true capabilities of models and identifying areas of weakness for further improvement. In the era of using language models as recommenders, which function in a human-like manner, the evaluation method has significantly deviated from traditional styles. This project intends to offer a comprehensive service for the evaluation of LM-based recommender systems. Whether provided with a trained LM or an API (such as Azure OpenAI API), it assesses the model's performance from various perspectives, including retrieval, ranking, explanation capability, and general AI ability. |
RecAI uses MIT license.
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.
This project may contain trademarks or logos for projects, products, or services. Authorized use of Microsoft trademarks or logos is subject to and must follow Microsoft's Trademark & Brand Guidelines. Use of Microsoft trademarks or logos in modified versions of this project must not cause confusion or imply Microsoft sponsorship. Any use of third-party trademarks or logos are subject to those third-party's policies.
Thanks to the open source codes of the following projects:
UniRec VisualChatGPT JARVIS LangChain guidance FlagEmbedding
Please refer to RecAI: Responsible AI FAQ for document on the purposes, capabilities, and limitations of the RecAI systems.
If this project aids your research, please cite our following paper and any related paper in the respective subfolder.
@article{lian2024recai,
title={RecAI: Leveraging Large Language Models for Next-Generation Recommender Systems},
author={Lian, Jianxun and Lei, Yuxuan and Huang, Xu and Yao, Jing and Xu, Wei and Xie, Xing},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.06465},
year={2024}
}