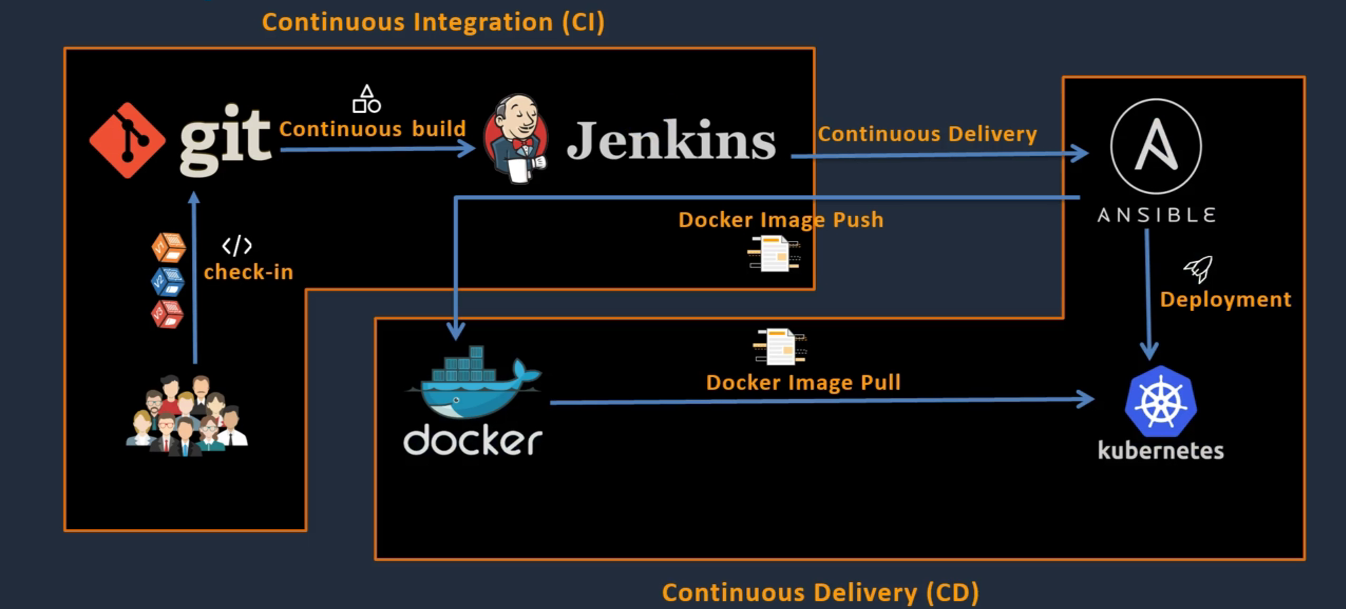
Continuous integration(CI), continuous delivery/deployment(CD) are DevOps practices that aim to speed the software delivery without compromising on quality. By automating as many steps in the process as possible, CI/CD provides rapid feedback builds to shorten the time it takes to release software to users.
- CI/CD (DevOps flow)
- Table of Contents
- Run Amazon Linux 2023 on Docker
- Run Amazon Linux 2 as a virtual machine on premises
- Setup Kubernetes (K8s)
- Installing Docker on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- Set up and install Docker Engine from Docker’s apt repository
- Install Docker manually and manage upgrades manually.
- Docker Hub Quickstart
- What is the different between "run" and "exec"
- Configure the Docker client
- Kubernetes Cluster installation using minikube
- Kubernetes Cluster installation using kubeadm
- Installing Helm
- Installing Jenkins
- Installing Ansible
- Installing Skaffold
- Installing Go
Amazon Linux 2023 (AL2023) was released to general availability in all AWS regions on March 15, 2023.
docker pull amazonlinux:latest
docker run -it amazonlinux:latest /bin/bashUse the Amazon Linux 2 virtual machine (VM) images for on-premises development and testing. Run Amazon Linux 2 on premises
The seed.iso boot image includes the initial configuration information that is needed to boot your new VM, such as the network configuration, host name, and user data.
- meta-data> – This file includes the hostname and static network settings for the VM.
- user-data – This file configures user accounts, and specifies their passwords, key pairs, and access mechanisms.
The key generation utility – PuTTYgen can create various public-key cryptosystems including Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA), Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA), Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), and Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA) keys.Although PuTTYgen collects keys in its native file format i.e. .ppk files, the keys can easily be converted to any file format. For more details you can see "Essential Shell scripting for developers"
The steps vary depending on your chosen VM platform. e.g. VMware: In the Navigator panel, right-click the new virtual machine and choose Edit Settings. for New CD/DVD Drive, choose seed.iso File.
Kubernetes, also known as K8s, is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Install and Set Up kubectl on Linux
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl.sha256"
echo "$(cat kubectl.sha256) kubectl" | sha256sum --check
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
kubectl version --client --output=yaml
chmod u+w,g+r,o-r file.txt
chmod u=rwx,g=rw,o=rwx file.txt
chmod 754 file.txt
chmod -R 777 dir1
ls -al *.(txt|pdf)
sudo ln -s /home/user1/bin/myscript.sh /bin
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | sh
# OR
yum install docker -y
docker -v# start docker services
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
service docker status
useradd dockeradmin
passwd dockeradmin
usermod -aG docker dockeradmin
Install Docker Engine on Ubuntu :
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo \
"deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
"$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
sudo docker run hello-worldmkdir docker && cd docker
cat <<EOF | tee ./urls.txt >/dev/null
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/dists/jammy/pool/stable/amd64/containerd.io_1.6.9-1_amd64.deb
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/dists/jammy/pool/stable/amd64/docker-ce_23.0.5-1~ubuntu.22.04~jammy_amd64.deb
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/dists/jammy/pool/stable/amd64/docker-ce-cli_23.0.5-1~ubuntu.22.04~jammy_amd64.deb
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/dists/jammy/pool/stable/amd64/docker-buildx-plugin_0.10.4-1~ubuntu.22.04~jammy_amd64.deb
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/dists/jammy/pool/stable/amd64/docker-compose-plugin_2.6.0~ubuntu-jammy_amd64.deb
EOF
wget -i ./urls.txt
sudo dpkg -i ./containerd.io_1.6.9-1_amd64.deb \
./docker-ce_23.0.5-1~ubuntu.22.04~jammy_amd64.deb \
./docker-ce-cli_23.0.5-1~ubuntu.22.04~jammy_amd64.deb \
./docker-buildx-plugin_0.10.4-1~ubuntu.22.04~jammy_amd64.deb \
./docker-compose-plugin_2.6.0~ubuntu-jammy_amd64.deb
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo docker run hello-world
# unisatall
sudo apt remove docker-compose-plugin \
docker-buildx-plugin \
docker-ce-cli \
docker-ce \
containerd.io
# check
sudo apt list --installed | grep -i docker
sudo apt list --installed | grep -i containerd
Docker Hub is a service provided by Docker for finding and sharing container images with your team. It is the world’s largest repository of container images with an array of content sources including container community developers, open source projects and independent software vendors (ISV) building and distributing their code in containers.
docker pull alpine:latest
mkdir /home/demo && touch /home/demo/Dockerfile
cd /home/demo
cat > Dockerfile <<EOF
FROM alpine:latest
CMD echo "Hello world!"
EOF
docker build -t <your_username>/my-hello .
docker image ls
rm -rf /home/demo
docker run <your_username>/my-hello
docker login
docker push <your_username>/my-hello
"docker run" has its target as docker images and "docker exec" is targeting pre-existing docker containers.
docker run #{image} -it /bin/bash
docker exec -it #{container} /bin/bash~/.docker/config.json
{
"proxies": {
"default": {
"httpProxy": "http:https://proxy.example.com:3128",
"httpsProxy": "https://proxy.example.com:3129",
"allProxy": "socks5:https://proxy.example.com:3130",
"noProxy": "*.test.example.com,.example.org,127.0.0.0/8"
}
}
}OR manually set proxy in container:
#set
export all_proxy=socks5:https://127.0.0.1:1089/ && export ALL_PROXY=socks5:https://127.0.0.1:1089/
export http_proxy=http:https://127.0.0.1:8889/ && export HTTP_PROXY=http:https://127.0.0.1:8889/
export https_proxy=http:https://127.0.0.1:8889/ && export HTTPS_PROXY=http:https://127.0.0.1:8889/
export NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,172.17.0.1,172.17.0.2 && export no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.1,172.17.0.1,172.17.0.2
# unset
unset all_proxy && unset ALL_PROXY && unset http_proxy && unset HTTP_PROXY && unset https_proxy && unset HTTPS_PROXY && unset NO_PROXY && unset no_proxyminikube is local Kubernetes, focusing on making it easy to learn and develop for Kubernetes. to install the latest minikube stable release:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
#Start a cluster using the docker driver
minikube start --driver=docker
# minikube config set driver docker
minikube status
minikube ip
kubectl get po -A
minikube dashboard
# To access the dashboard remotely, run the following command:
minikube dashboard --url=true
kubectl proxy --address='0.0.0.0' --disable-filter=true
minikube pause
minikube unpause
minikube stop
Kubeadm is a tool built to provide kubeadm init and kubeadm join as best-practice "fast paths" for creating Kubernetes clusters. kubeadm performs the actions necessary to get a minimum viable cluster up and running. By design, it cares only about bootstrapping, not about provisioning machines. More details: Kubernetes Cluster installation using kubeadm
Helm is the package manager for Kubernetes, Helm Charts help you define, install, and upgrade even the most complex Kubernetes application.
This guide shows how to install the Helm CLI.
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.10.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf helm-v3.10.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm search repo bitnami
helm repo update # Make sure we get the latest list of charts
Jenkins is a self-contained, open source automation server which can be used to automate all sorts of tasks related to building, testing, and delivering or deploying software. More details: Installing Jenkins(LTS)
Ansible automates the management of remote systems and controls their desired state. more details Automation with Ansible.
Skaffold handles the workflow for building, pushing and deploying your application, allowing you to focus on what matters most: writing code.
# For Linux x86_64 (amd64)
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/v2.0.0/skaffold-linux-amd64 && \
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/wget https://dl.google.com/go/go1.20.4.linux-amd64.tar.gz
rm -rf /usr/local/go && tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.20.4.linux-amd64.tar.gz
vi ~/.bash_profile
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
source ~/.bash_profile
echo $PATH
go version
mkdir -p ~/go/src/hello
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Printf("Hello, World\n")
}cd ~/go/src/hello
go build
./hello