This project solves the problem of task centralization. The effort of coding all tasks into a single project can be difficult. So let's think about decentralization networks!
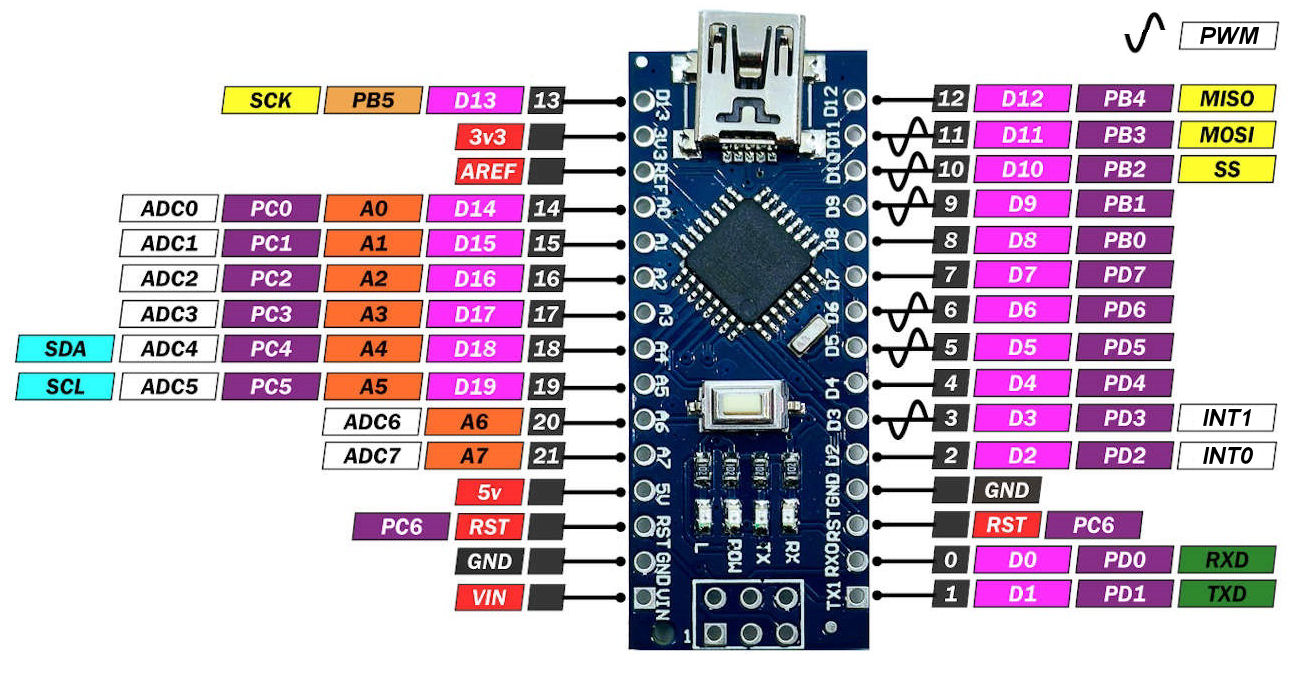
For modular programming you can use the Arduino I/O Extender. It acts as an I2C slave on an ATMega328P target.
Performing tasks in a decentralized way.
Supported: GPIO, PWM, ADC, COUNTER/TIMER
| Offset | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x00 |
0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Offset | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x07 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOIE1 | CS12 | CS11 | CS10 | ISC11 | ISC10 | ISC01 | ISC00 | |
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W |
** must be written before GPIO registers
| ISCx1 | ISCx0 | Interrupt Select |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Both edges |
| 1 | 0 | Falling edge |
| 1 | 1 | Rising edge |
| CS12 | CS11 | CS10 | Clock Select |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | OSC/1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | OSC/8 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | OSC/64 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | OSC/256 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | OSC/1024 |
| TOIE1 | Overflow Event |
|---|---|
| 0 | Disabled, keeps last value at 0x3C:3D |
| 1 | Enabled, writes 0xFFFF into 0x3C:3D on overflow |
| Offset | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x10 |
x | 0 | 0 | x | x | x | x | x |
| R/W | R | R | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | |
| !LOCK | CNT | PWM | PUR | DIR | PIN |
| Offset | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x26 |
x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W |
** 8-bit resulution on target ATMega328P
| Offset | Bit 15 | Bit 14 | Bit 13 | Bit 12 | Bit 11 | Bit 10 | Bit 9 | Bit 8 | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x2C:2D |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
** right-justified format
** 10-bit resulution on target ATMega328P
| Offset | Bit 15 | Bit 14 | Bit 13 | Bit 12 | Bit 11 | Bit 10 | Bit 9 | Bit 8 | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x3C:3D |
x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
** right-justified format
** 16-bit resulution on target ATMega328P
Note
Usable pins: 0-21
0 = LOW
1 = HIGH
Note
Usable pins: 0-21
Pin 13 aka LED_BUILTIN already mapped as output
0 = INPUT
1 = OUTPUT
Note
Usable pins: 0-21
0 = DISABLE
1 = ENABLE
Important
Usable pins only: 3, 5, 6, 9-11
0 = DISABLE
1 = ENABLE
Important
Usable pins only: 2, 3
0 = DISABLE
1 = ENABLE
I2C Master device code snippets
Setting GPIO 2 and 4 as input - GPIO 4 with enabled pull-up
Important
Each manipulation on bits 1-6 needs an active unlock bit.
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x12);
Wire.write(0x80);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x14);
Wire.write(0x84);
Wire.endTransmission();
Or in a sequential manner
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x12);
Wire.write(0x80);
Wire.write(0x00); // doesn't influence previous setting of pin 3
Wire.write(0x84);
Wire.endTransmission();
Reading GPIO 2 input
static uint8_t buffer[BUFFER_LENGTH], length;
uint8_t i = 0;
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x12);
Wire.endTransmission(false); // don't send stop
Wire.requestFrom(DEVICE_ADDRESS, 1, 1); // send stop after 1 byte rx
while(Wire.available()) {
buffer[i++] = Wire.read() & 1; // receive a byte, mask only position 0
length = i; // save length
}
Reading GPIO 14 aka ADC 0 input
static uint8_t buffer[BUFFER_LENGTH], length;
uint8_t i = 0;
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x1E);
Wire.write(0x80);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x2C);
Wire.endTransmission(false); // don't send stop
Wire.requestFrom(DEVICE_ADDRESS, 2, 1); // send stop after 2 byte rx
while(Wire.available()) {
buffer[i++] = Wire.read(); // receive a byte
length = i; // save length
}
Setting GPIO 0 and 1 as output
Important
Each manipulation on bits 1-6 needs an active unlock bit.
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x10);
Wire.write(0x82);
Wire.write(0x82);
Wire.endTransmission();
Changing GPIO 0 and 1 output status - GPIO 0 set Low - GPIO 1 set High
Tip
Each consequent write to an output pin doesn't need an unlock bit.
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x10);
Wire.write(0x00);
Wire.write(0x01);
Wire.endTransmission();
Setting PWM 1 and 2 value - PWM 1 to 50 - PWM 2 to 200
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x15);
Wire.write(0x8A);
Wire.write(0x8A);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x27);
Wire.write(0x32);
Wire.write(0xC8);
Wire.endTransmission();
Setting GPIO 2 as counter - Reading GPIO 2 input frequency - Using default settings of 0x07
static uint8_t buffer[BUFFER_LENGTH], length;
uint8_t i = 0;
uint16_t tcnt, freq;
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x12);
Wire.write(0x90);
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x3C);
Wire.endTransmission(false); // don't send stop
Wire.requestFrom(DEVICE_ADDRESS, 2, 1); // send stop after 2 byte rx
while(Wire.available()) {
buffer[i++] = Wire.read(); // receive a byte
length = i; // save length
}
tcnt = (buffer[0] << 8) | buffer[1]; // this value represents: MCU_CLOCK / CS1x * Δt
freq = 2000000 / tcnt; // convert to herz: (MCU_CLOCK / CS1x) / tcnt = 2e6 Hz / tcnt