This is a Jupyter Kernel for Swift, intended to make it possible to use Jupyter with the Swift for TensorFlow project.
This kernel is currently very barebones and experimental.
This kernel is implemented using LLDB's Python APIs.
Create a virtualenv and install jupyter in it.
virtualenv venv
. venv/bin/activate
pip2 install jupyter # Must use python2, because LLDB doesn't support python3.
Optionally install SourceKitten (this enables code completion).
Get a Swift toolchain. Here are a few options:
- Download a prebuilt Swift for TensorFlow toolchain.
- Download Swift for TensorFlow sources
and then build a toolchain using
SWIFT_PACKAGE=tensorflow_linux,no_test ./swift/utils/build-toolchain local.swiftorSWIFT_PACKAGE=tensorflow_osx,no_test ./swift/utils/build-toolchain local.swift.
- Use an XCode Swift toolchain.
Register the kernel with jupyter. The command depends on which toolchain you got:
# If you downloaded a prebuilt toolchain:
python2 register.py --sys-prefix --swift-toolchain <path to extracted swift toolchain directory>
# If you built a toolchain from sources:
python2 register.py --sys-prefix --swift-toolchain <path to "swift-nightly-install" directory>
# If you are using an XCode toolchain:
python2 register.py --sys-prefix --xcode-path <path to XCode Swift toolchain>
Optionally add --sourcekitten <path to sourcekitten binary> to the command if you installed
SourceKitten. This will give you code completion.
Now run jupyter notebook, and it should have a Swift kernel.
You can call Python libaries using Swift's Python interop to display rich output in your Swift notebooks. (Eventually, we'd like to support Swift libraries the produce rich output too!)
Prerequisites:
-
You must use a Swift toolchain that has Python interop. As of July 2018, only the [Swift for TensorFlow] toolchain has Python interop.
-
Install the
ipykernelPython library, and any other Python libraries that you want output from (such asmatplotliborpandas) on your system Python. (Do not install them on the virtualenv from the Swift-Jupyter installation instructions. Swift's Python interop talks to your system Python.)
After taking care of the prerequisites, run
%include "EnableIPythonDisplay.swift" in your Swift notebook. Now you should
be able to display rich output! For example:
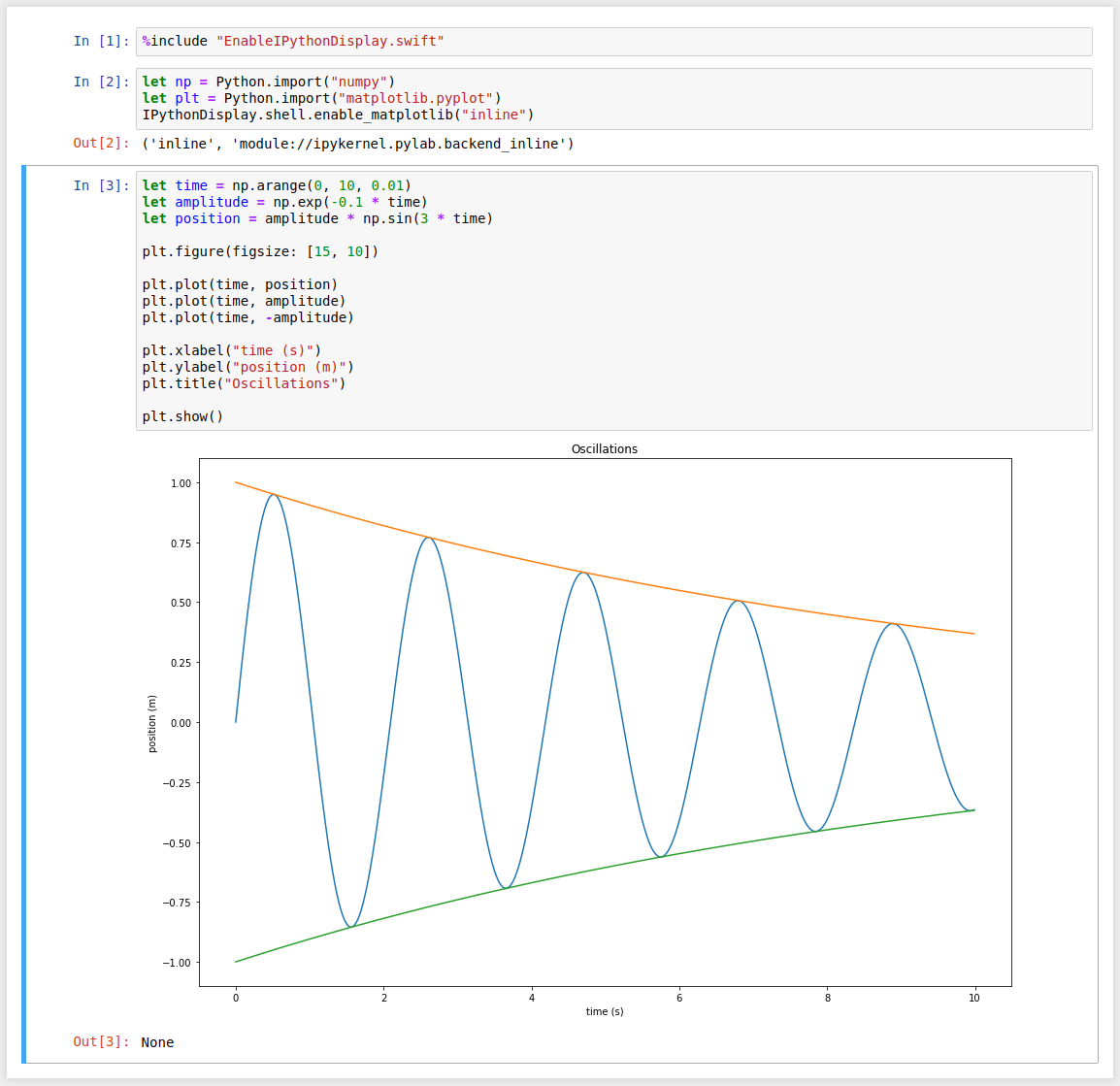
let np = Python.import("numpy")
let plt = Python.import("matplotlib.pyplot")
IPythonDisplay.shell.enable_matplotlib("inline")let time = np.arange(0, 10, 0.01)
let amplitude = np.exp(-0.1 * time)
let position = amplitude * np.sin(3 * time)
plt.figure(figsize: [15, 10])
plt.plot(time, position)
plt.plot(time, amplitude)
plt.plot(time, -amplitude)
plt.xlabel("time (s)")
plt.ylabel("position (m)")
plt.title("Oscillations")
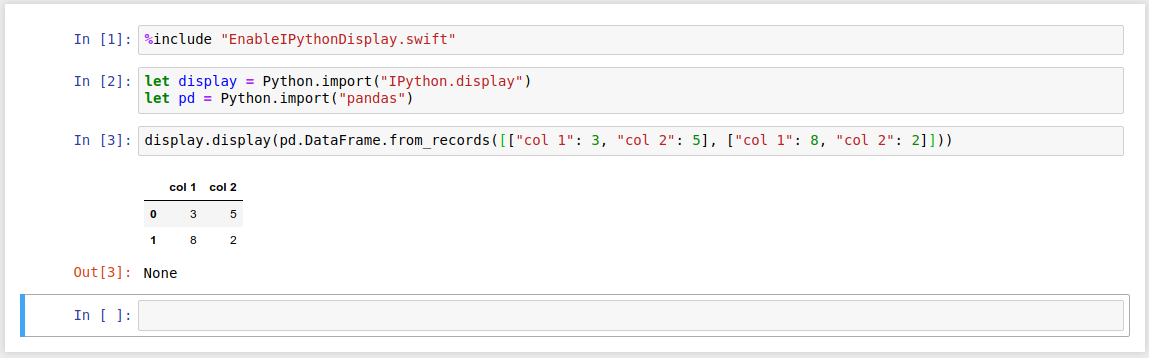
plt.show()let display = Python.import("IPython.display")
let pd = Python.import("pandas")display.display(pd.DataFrame.from_records([["col 1": 3, "col 2": 5], ["col 1": 8, "col 2": 2]]))%include directives let you include code from files. To use them, put a line
%include "<filename>" in your cell. The kernel will preprocess your cell and
replace the %include directive with the contents of the file before sending
your cell to the Swift interpreter.
<filename> must be relative to the directory containing swift_kernel.py.
We'll probably add more search paths later.