Access Control system using a cheap MFRC522, PN532 RFID readers or Wiegand RFID readers and Espressif's ESP8266 Microcontroller.
- Minimal effort for setting up your Access Control system, just flash and everything can be configured via Web UI
- Capable of managing up to 1.000 Users (even more is possible)
- Great for Maker Spaces, Labs, Schools, etc
- Cheap to build and easy to maintain
- Open Source (minimum amount of hardcoded variable, this means more freedom)
- Using WebSocket protocol to exchange data between Hardware and Web Browser
- Data is encoded as JSON object
- Records are Timestamped (Time synced from a NTP Server)
- MQTT enabled
- Bootstrap, jQuery, FooTables for beautiful Web Pages for both Mobile and Desktop Screens
- Thanks to ESPAsyncWebServer Library communication is Asyncronous
This project still in its development phase. New features (and also bugs) are introduced often and some functions may become deprecated. Please feel free to comment or give feedback.
- See Demo Here
- Get the latest release from here.
- See Known Issues before starting right away.
- See Security for your safety.
- See ChangeLog
- An ESP8266 module or a development board like WeMos D1 mini or NodeMcu 1.0 with at least 32Mbit Flash (equals to 4MBytes) (ESP32 does not supported for now)
- A MFRC522 RFID PCD Module or PN532 NFC Reader Module or Wiegand based RFID reader
- A Relay Module (or you can build your own circuit)
- n quantity of Mifare Classic 1KB (recommended due to available code base) PICCs (RFID Tags) equivalent to User Number
Compiled firmware binary and flasher tool for Windows PCs are available in directory /bin. On Windows you can use "flash.bat", it will ask you which COM port that ESP is connected and then flashes it. You can use any flashing tool and do the flashing manually. The flashing process itself has been described at numerous places on Internet.
The build enviroment is based on PlatformIO. Follow the instructions found here: https://platformio.org/#!/get-started for installing it but skip the platform init step as this has already been done, modified and it is included in this repository. In summary:
sudo pip install -U pip setuptools
sudo pip install -U platformio
git clone https://github.com/omersiar/esp-rfid.git
cd esp-rfid
platformio run
When you run platformio run for the first time, it will download the toolchains and all necessary libraries automatically.
platformio run- process/build all targetsplatformio run -e nodemcu -t upload- process/build and flash just the ESP12e target (the NodeMcu v2)platformio run -t clean- clean project (remove compiled files)
The resulting (built) image(s) can be found in the directory /bin created during the build process.
The following table shows the typical pin layout used for connecting MFRC522 hardware to ESP:
| Signal | PN532 | MFRC522 | WeMos D1 mini | NodeMcu | Generic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RST/Reset | RST | RST | N/C [1] | N/C [1] | N/C [1] |
| SPI SS | SS | SDA [3] | D8 [2] | D8 [2] | GPIO-15 [2] |
| SPI MOSI | MOSI | MOSI | D7 | D7 | GPIO-13 |
| SPI MISO | MISO | MISO | D6 | D6 | GPIO-12 |
| SPI SCK | SCK | SCK | D5 | D5 | GPIO-14 |
- Not Connected. Hard-reset no longer needed.
- Configurable via settings page.
- The SDA pin might be labeled SS on some/older MFRC522 boards.
For Wiegand based readers, you can configure D0 and D1 pins via settings page. By default, D0 is GPIO-4 and D1 is GPIO-5
- First, flash firmware (you can use /bin/flash.bat on Windows) to your ESP either using Arduino IDE or with your favourite flash tool
- (optional) Fire up your serial monitor to get informed
- Search for Wireless Network "esp-rfid-xxxxxx" and connect to it (It should be an open network and does not reqiure password)
- Open your browser and type either "https://192.168.4.1" or "https://esp-rfid.local" (.local needs Bonjour installed on your computer) on address bar.
- Log on to ESP, default password is "admin"
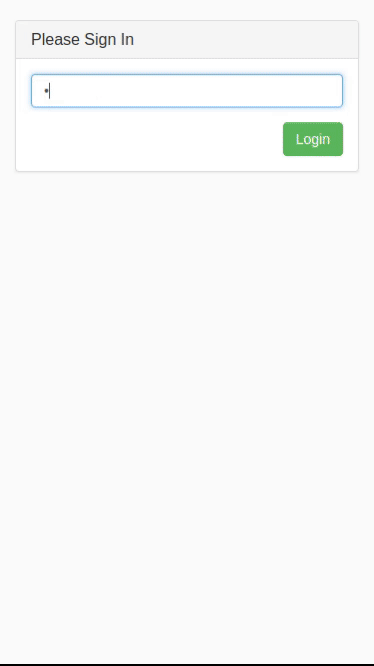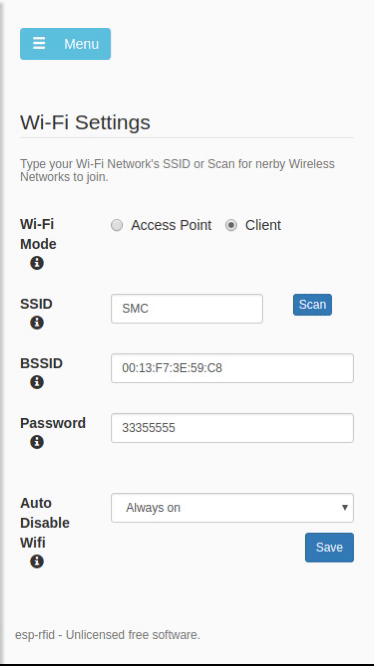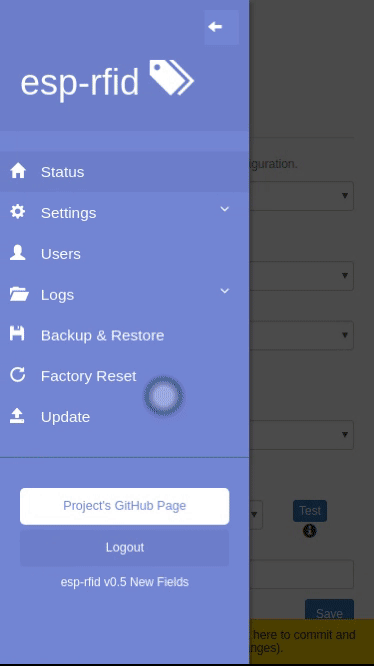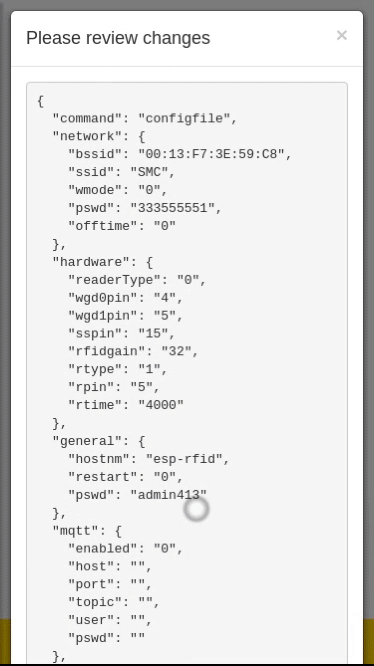
- Go to "Settings" page
- Configure your amazing access control device. Push "Scan" button to join your wireless network, configure RFID hardware, Relay Module.
- Save settings, when rebooted your ESP will try to join your wireless network.
- Check your new IP address from serial monitor and connect to your ESP again. (You can also connect to "https://esp-rfid.local")
- Go to "Users" page
- Scan a PICC (RFID Tag) then it should glimpse on your Browser's screen.
- Type "User Name" or "Label" for the PICC you scanned.
- Choose "Allow Access" if you want to
- Click "Add"
- Congratulations, everything went well, if you encounter any issue feel free to ask help on GitHub.
- MQTT functionality is not stable for now.
- See #99.
- Please also check GitHub issues.
We are syncing time from a NTP Server (in Client -aka infrastructure- Mode). This will require ESP to have an Internet connection. Additionaly your ESP can also work without Internet connection too (Access Point -aka Ad-Hoc- Mode), without giving up functionality. This will require you to do syncing manually. ESP can store and hold time for you approximately 51 days without a major issue, device time can drift from actual time depending on usage, temprature, etc. So you have to login to settings page and sync it in a timely fashion.
We assume ESP-RFID project -as a whole- does not offer strong security. There are PICCs available that their UID (Unique Identification Numbers) can be set manually (Currently esp-rfid relies only UID to identify its users). Also there may be a bug in the code that may result free access to your belongings. And also, like every other network connected device esp-rfid is vulnerable to many attacks including Man-in-the-middle, Brute-force, etc.
This is a simple, hobby grade project, do not use it where strong security is needed.
What can be done to increase security? (by you and by us)
- We are working on more secure ways to Authenticate RFID Tags.
- You can disable wireless network to reduce attack surface. (This can be configured in Web UI Settings page)
- Choose a strong password for the Web UI
Since we are limited on both flash and ram size things may get ugly at some point in the future. You can find out some test results below.
Restore some randomly generated user data on File System worth:
- 1000 seperate "userfile"
- random 4 Bytes long UID and
- random User Names and
- 4 bytes random Unix Time Stamp
- each have "access type" 1 byte integer "1" or "0".
Total 122,880 Bytes
At least 1000 unique User (RFID Tag) can be handled, the test were performed on WeMos D1 mini.
- Logging needs testing. How long should it need to log access? What if a Boss needs whole year log?
- Realiability on Flash (these NOR Flash have limited write cycle on their cells). It depends on manufacturer choice of Flash Chip and usage.
Thanks to the community, ESP-RFID come to alive with their great effort:
- @rneurink
- @thunderace
- @zeraien
- @nardev
- @romanzava
See ChangeLog
If this project helps you in a way, you can buy us a beer. You can make a donation to the ESP-RFID community with Bountysource
- 2017-10-03 steinar-t
- 2017-12-10 saschaludwig
Nothing says better thank you than a donation.
UNLICENSE