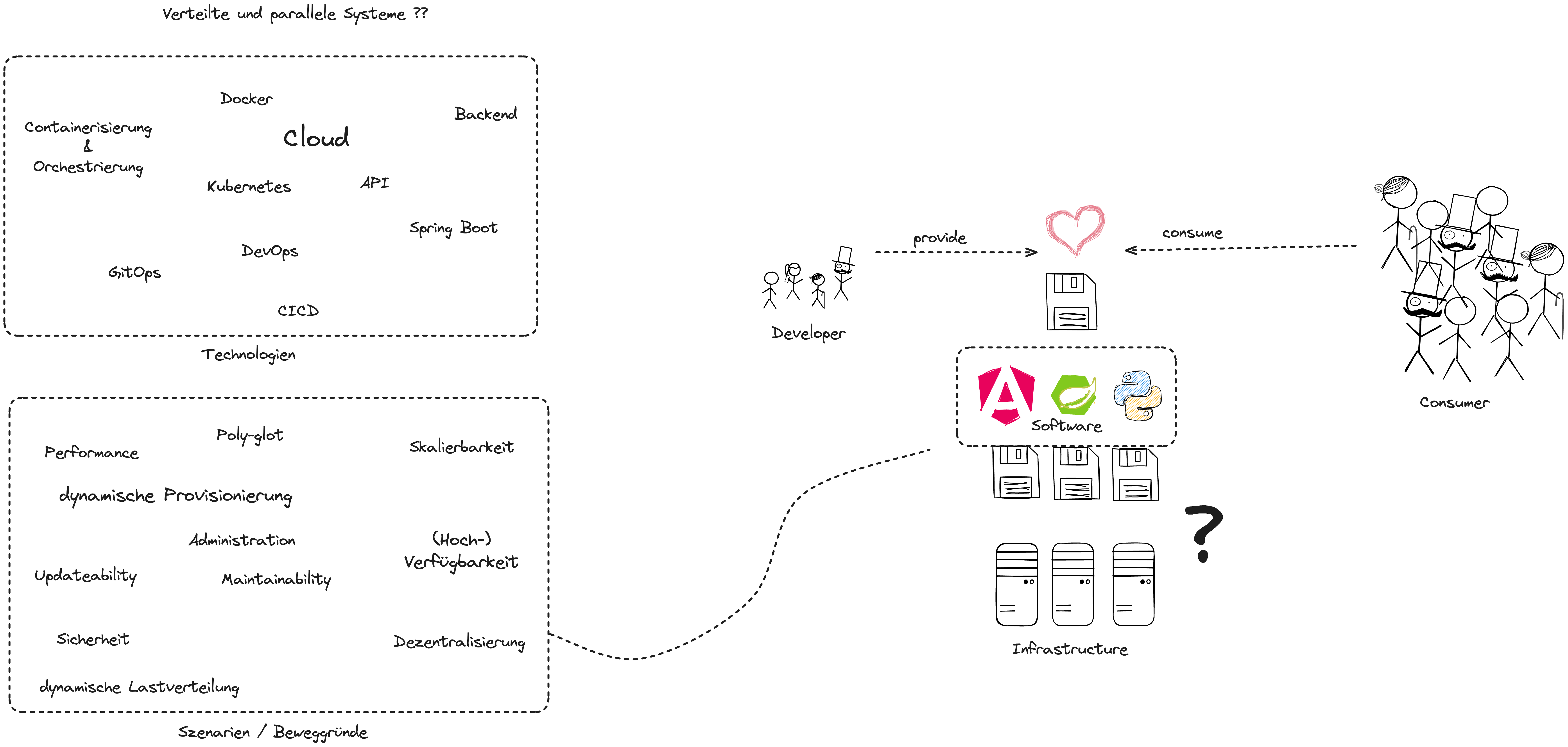
- Why distributed systems, why container, why modern software?
- What is Cloud Computing? Encounters in everyday life and history
- Characteristic, advantages & challenges
- Terminology - public, private, hybrid, dedicated
- Abstraction layers - IaaS, PaaS, FaaS, SaaS
- Overview - Hypervisors, virtual machines, containers and orchestration
The student is able to describe the reasons for distributed systems and cloud computing in own words and list examples for offerings, topologies and technologies. Includes ability to differentiate between different abstraction layers and knowledge how those layers and according technologies interact with each other. No exercises in this module
- What is Polyglot Software Development?
- What did the role of containers change for polyglot software?
- Security and Cloud - is it safe? :-)
- Differentiate between distributed systems and cloud. What are the overlaps and what are the differences?
- List 3 reasons for adopting a distributed architecture?
- List 3 challenges when adopting?
- List 3 real-world examples of cloud services we have used?
- Explain on the example of Gitpod/Codespaces/DockerHub/GitHub/Spring Initializr what a cloud service is (and it what it's not) and in which categorie would you put it? And why?
- Distributed app
- Polyglot implementation
- Containerisation
- Kubernetes
- DevOps/CICD/Observability (optional)
- Get a public GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket account
- Play around with GitHub codespaces and/or Gitpod
-
Why do we need Containers?
-
Challenges for (polyglot) distributed systems in traditional IT:
- Each environment has to be configured manually: Servers as well as local dev environments
- Configuration has to be as identical as possible: minor configuration drifts can lead to errors and the "it runs on my machine" problem
- Polyglot Server Environments are a huge challenge as for each programing language a separate configuration has to be managed on all systems.
- Changing Versions is tedious for local dev environment
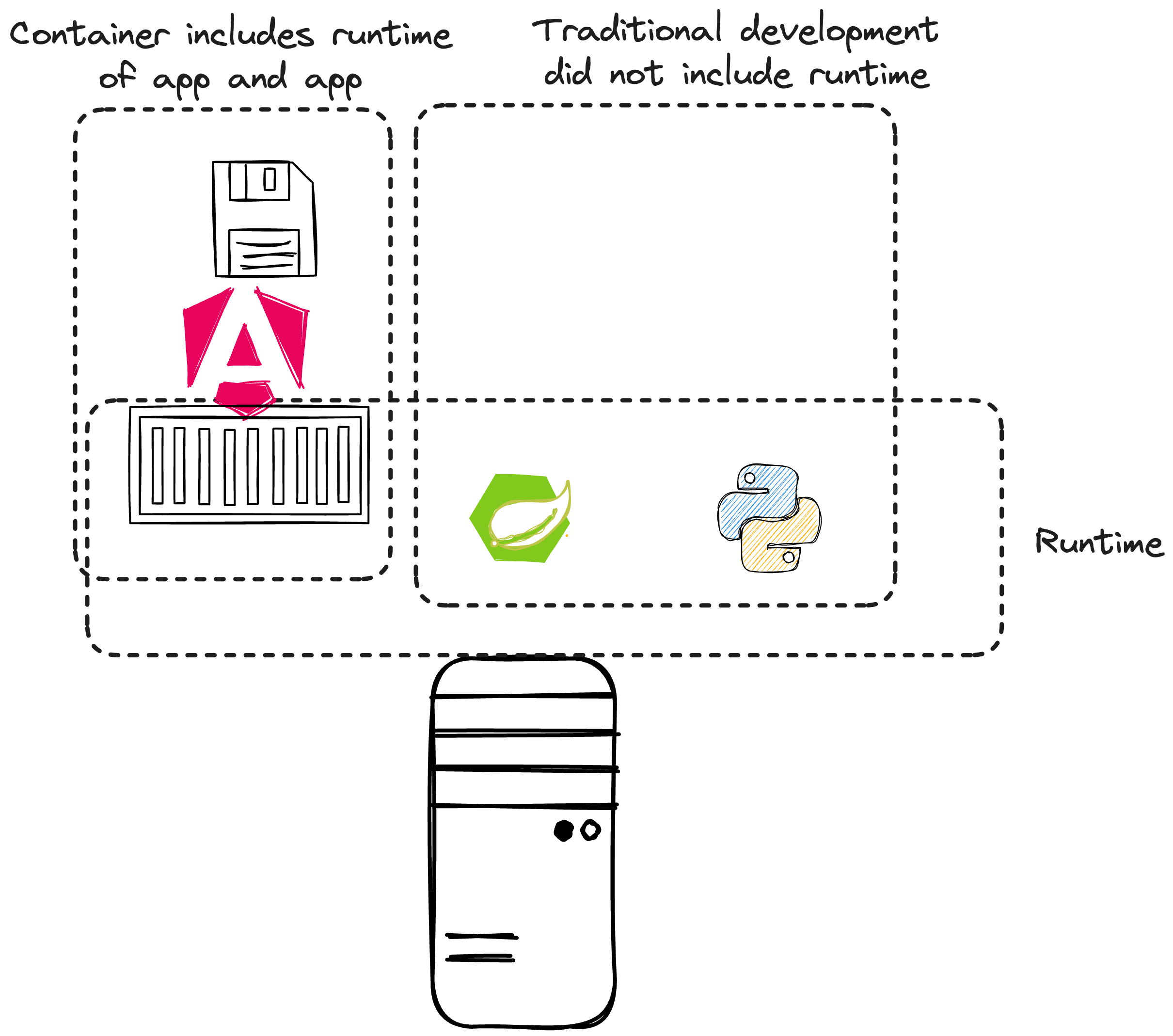
- Whereas containerized Applications bring their own Environment and Configuration
- No need to preconfigure the local environment per programming language or application.
- Only the container engine is required to run all kinds of containers.
- How does the container engine work?
- Layer-based setup of containers
- Container vs Container Image
- How to create a container from application to dockerfile to image to running container
-
Do I have to set up, build, and run the dockerfile for each container? With the dockerfile you need to create the image once. From the given you can run as many container instances as you want without re-executing the dockerfile.
-
Can I run multiple applications inside a container? (Reason about your answer) Yes, it's possible. (But) 12-factor nummer? single process is violated, no independent scaling of internal apps possible.
-
Make an example where a multi-process container might make sense? (Real-world example) Single process containers make a lot of sense when the container is about one certain application (frontend, backend, db ...) Multi process containers can make sense when there is no main running process and only the isolation factor is important. z.B. gitpod/devcontainer etc.
Exercises can be found here
- Background: Spring Framework - History & components
- Spring ← → Spring Boot
- Spring Initializr (start.spring.io) & starter dependencies
- Basic project structure (folders, configuration ..)
- "Hello, World!" example explained
- Using Actuator
The student is able to build and configure an own Spring Boot application from scratch with the IDE of choice. The exercise is to build an own "Hello, World!" application that exposes various - endpoints and is able to execute CRUD operations on the state of the application. Optional: Add logging and testing, configure Actuator.
- "WHY Spring Boot?" Provide 3 advantages of this framework
- Describe Spring Boot to somebody not familiar with it in own words ()
- How do you start building a Spring Boot app? Initializr & Dependencies
- List 4 different starter dependencies and explain briefly what they do (old question) (4P) "I did not do my lab task with Spring Boot. I implemented using Python and I can tell you how it works there ..."
- https://start.spring.io
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-requestmapping
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-actuator-enable-endpoints
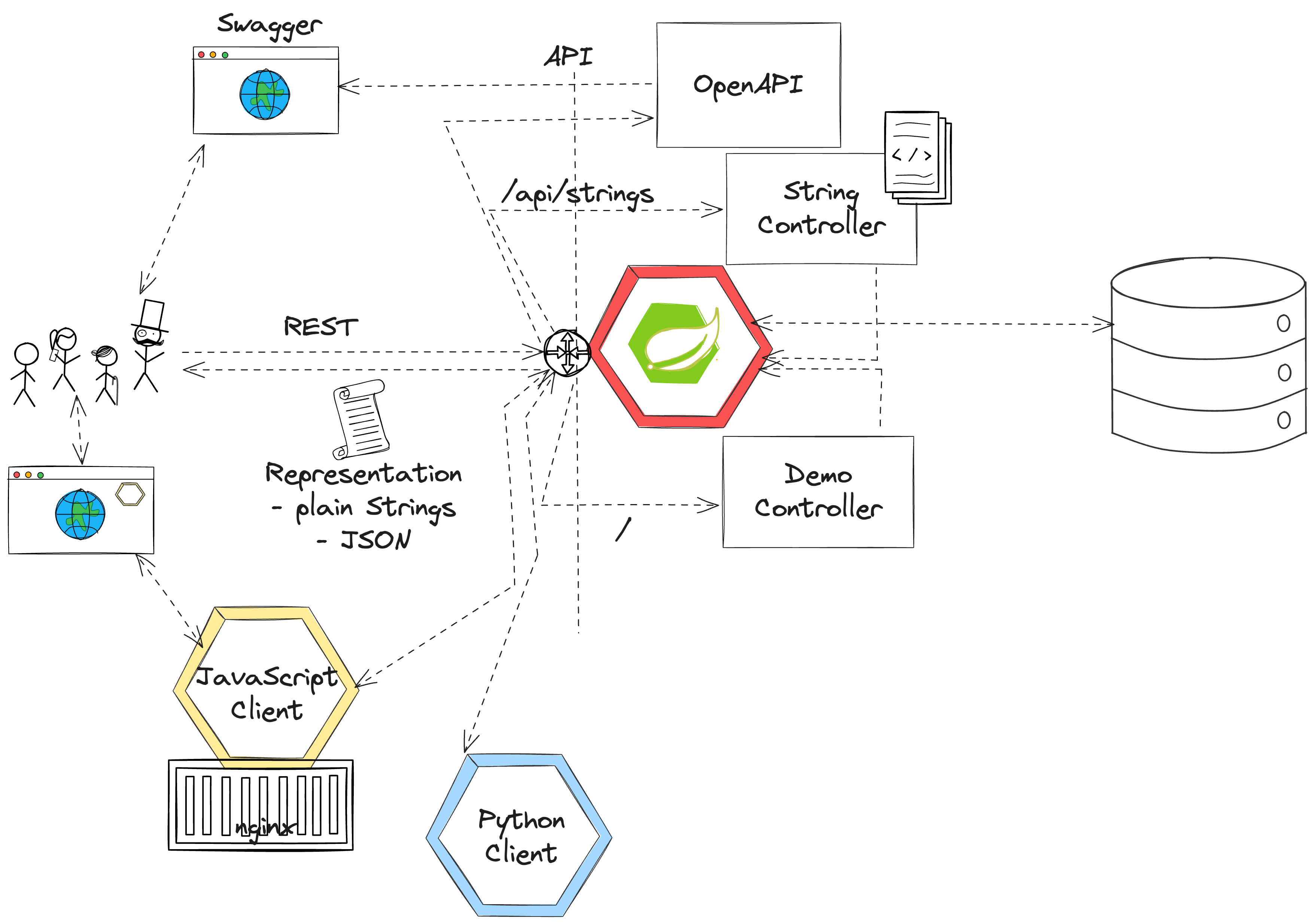
- Synchronous communication
- HTTP and REST
- Verbs, Resources, Nouns
- Evolution, Richardson Maturity Model
- CRUD Operations
- Building a REST API with Spring (Boot)
- Building a data model with REST
- Identify good and bad API examples and explain why - also categorize within the Richardson's Maturity Model
- Describe the concepts of Verbs and Nouns
- When is an invocation idempotent and safe? What does it mean? Provide examples
- Describe in your own words the mapping of REST calls to database (SQL) and CRUD calls
- Be aware of Richardson's maturity model and explain it
The student understands the concepts of an API and synchronous communication in distributed systems and can explain it in own words.
Docker Advanced Topics:
- Storage through Docker Volumes
- Connectivity through Docker Networks
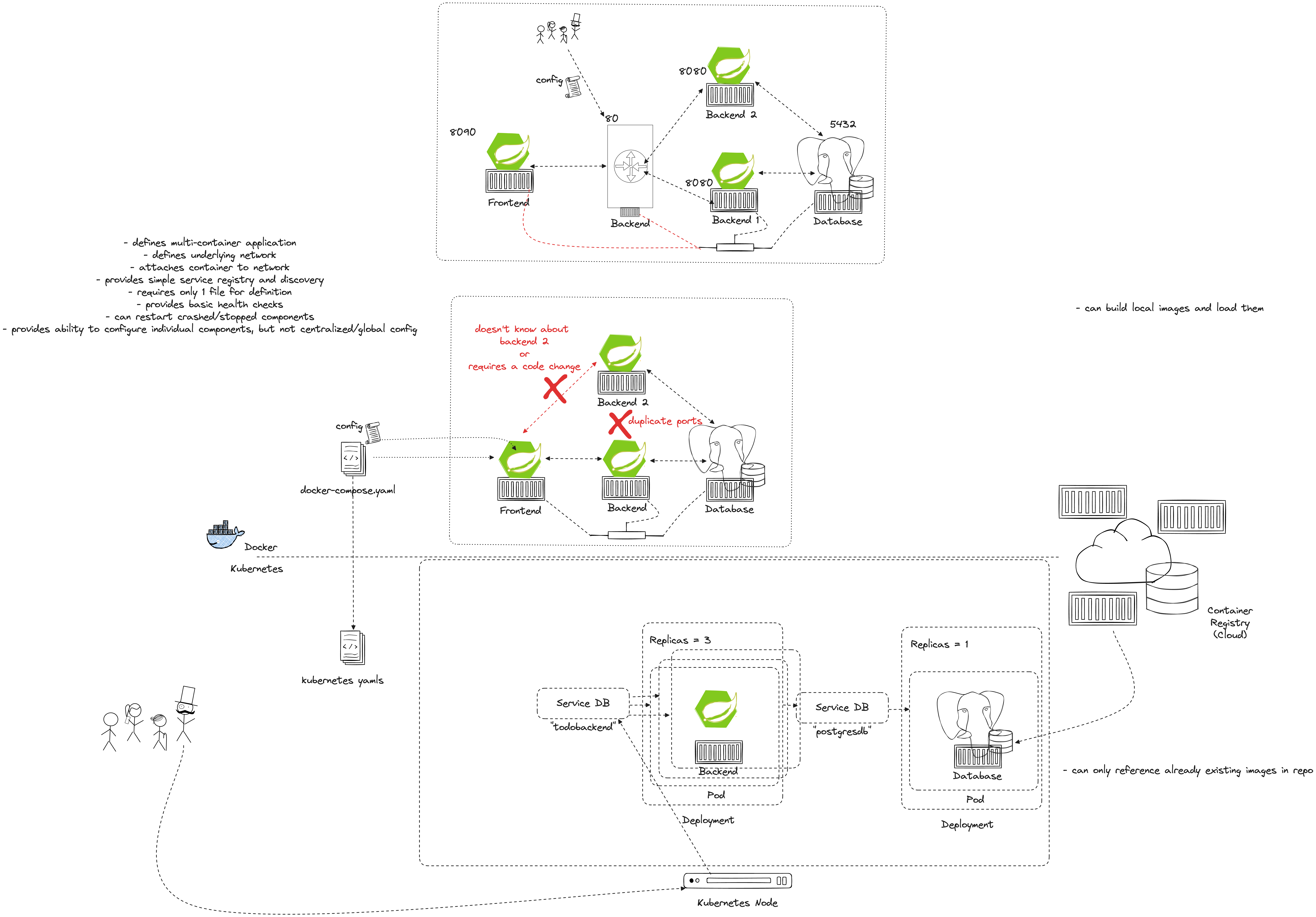
- Multi Container Setup through Docker Compose
The student understands how storage and connectivity are handled per default in containers and knows the purpose and implementation of volumes, networks, and docker-compose files. Exercises can be found in the later chapters of the docker exercise website.
- How does data persistence behave by default in containers for files newly created in a running container?
- What is the difference between Bind Mounts and Volumes?
- When to use volumes for my containers?
- How to share a file or directory with multiple containers?
- Why do i need a network for containers? When do i not need it?
- The results created by a docker-compose file could also be created manually: entering necessary cli commands one after another. What commands would be used?
Cloud-native Software development - Theory part
Theory lecture - Cloud-Native Software
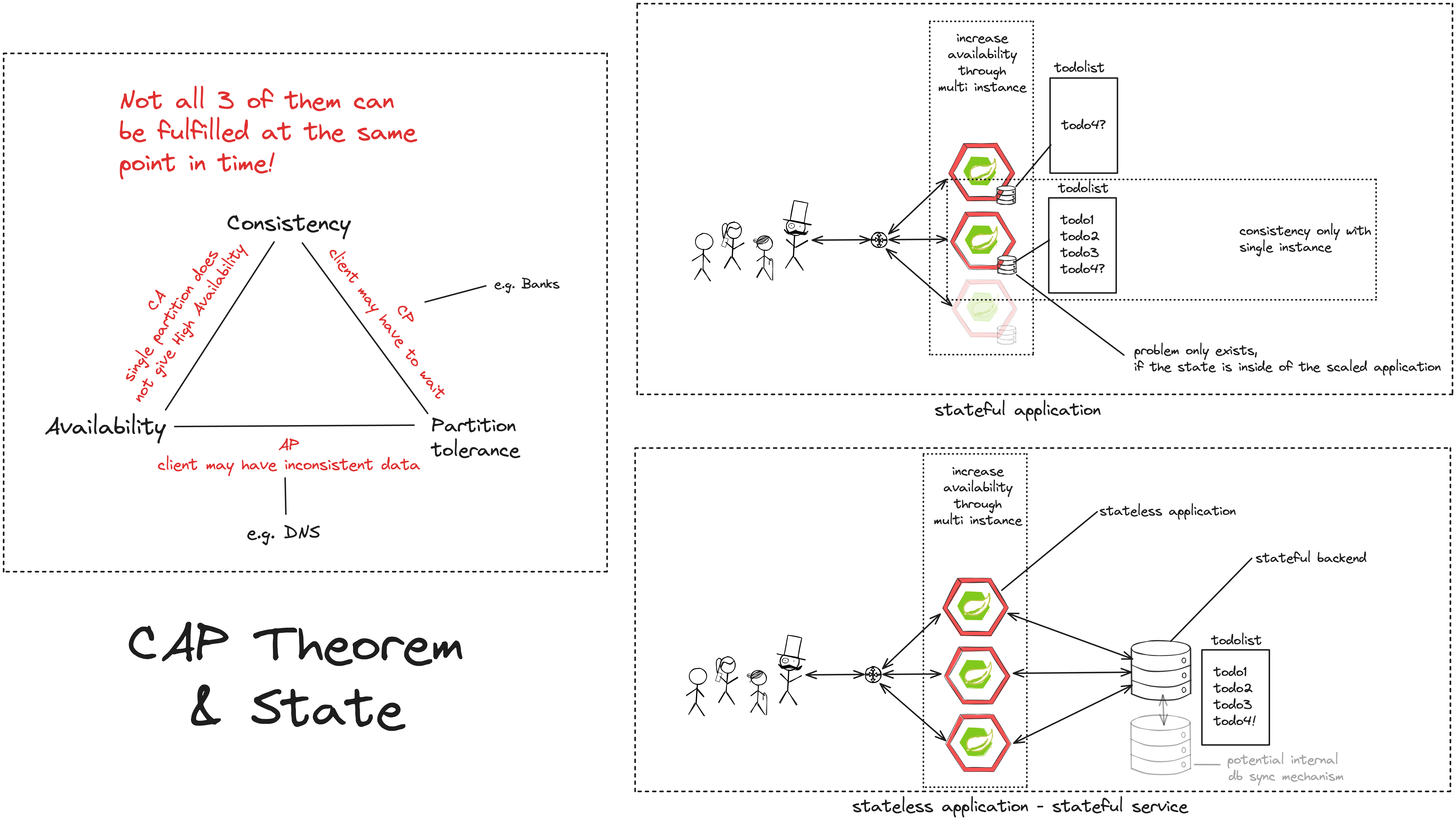
- CAP Theorem
- Conway's Law
- Fallacies of distributed computing
- Domain-Driven Design basics (not relevant for exam)
- 12-factor application
- Evolution of applications and deployments: Monolithic -> Service-Oriented Architecture -> Microservices
- Introduction to serverless and FaaS terminology
The student knows about the evolution of distributed systems (and middleware) and the drivers towards state-of-the-art implementation and deployment. She/he can explain the underlying concepts and theories and put it into practical context. No dedicated exercises for this module. Recap of basics: Spring Boot, Docker, configuration.
- "WHY" Cloud-Native Software? What IS Cloud-Native Software?
- Why "evolution" from a monolithic approach to a distributed approach?
- How does the CAP Theorem/Conway's Law relate to this?
- (NO Domain-Driven Design questions)
- How do the 12-factor application "methodology" relate to the technologies that we covered in this semester? (important)
- "WHY" is external configuration important in cloud-native software?
- Where did you see aspects of external configuration in the technologies we used? Provide examples
- What is the advantage of polyglot applications? Why in particular for cloud-native software? What kind of disadvantages do you see?
- Spring Data
- Concept of entities and repositories
- Running databases based on Docker images as containers
The student is able to build a Spring Boot application (or extend an existing one) with Spring Data configuration. The exercise is to create an application, which performs CRUD operations on a database backend. Other technologies than Spring Boot ar just as good. Provide a docker-compose file to stand up a multi-container environment with application and database.
- "WHY" persistence? "WHY" persistence frameworks like JPA?
- Describe the necessary components to build an application with Spring Data or your technology of choice? Potentially sketch
- How can docker compose help if you have a persistence-based application?
- What is Resilience
- Resilience in Distributed Systems
- Typical Problems in distributed Systems
- Patterns towards Resilience
- Retry
- Fallback
- Timeout
- Loadbalancer
- Circuit Breaker
- Monitoring
The student understands what errors distributed systems typically face and how to design a more resilient systems through various design patterns. No exercise for this module.
- Explain Resilience in distributed systems
- How to classify the error types a service might be facing
- Which errors did you/we encounter during the labs that are prone to distributed systems?
- Outline the concept of different resilience patterns
- List 3 resilience patterns of your choice, describe briefly how they work and provide a real-world example (e.g. automatic restarts, the process of an app is observed and the app is restarted in case of downtime, e.g. docker-compose, Kubernetes)
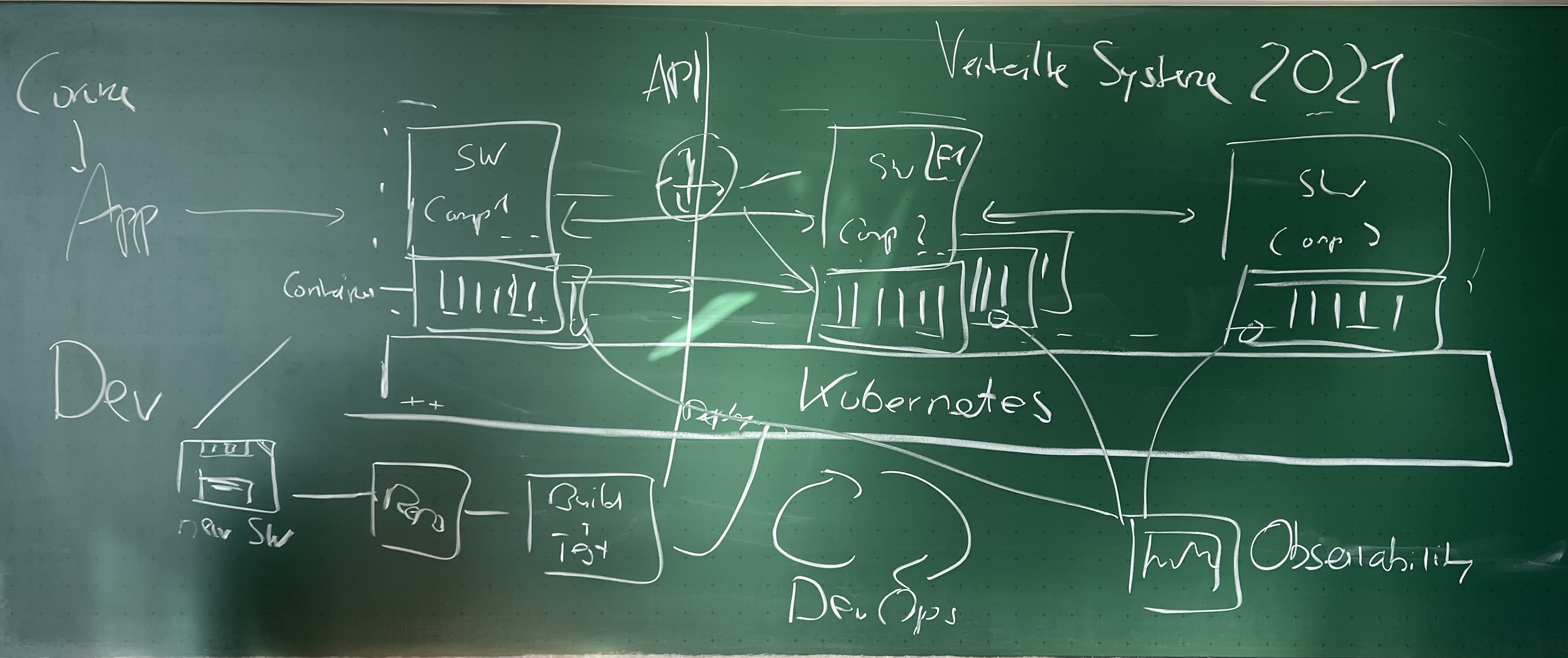
Kubernetes Topics:
- The Kubernetes Cluster
- The Contol Plane
- Worker Nodes
- Pods
- Deployments
- Services
- Desired State Management
The Student understands the core principle of Kubernetes, the key characteristics and the basic API objects to interact with k8s. The Student can explain the differences between these objects and their purpose. As exercises we have added a chapter to the lecture exercises website.
- What are the core ideas/principles of kubernetes?
- What could be a valid scenario for a multi cluster setup?
- How does Kubernets achieve and maintain the desired state?
- Why do we use pods instead of using containers directly?
- Why do we (preferably) use deployments instead of just pods?
- What exactly happens when a node fails and how does the recovery procedure look like?
- Explain the limitations of Docker as opposed to Kubernetes on the aspect of scaling? How can it be achieved in both technologies?
- Concept of probes and health checks in Kubernetes
- "WHY?" - Necessity of these checks. Especially in the context of container based applications
- See documenation and comments in code
Link:
- Motivation: drawbacks of k8s workflow
- helm templating
- helm charts
- helm dependencies
- What is the core principal of helm and what can it be compared to?
- How does it simplify the kubernetes workflow
- What is a possible scenario where helm can be utilized?