Thanks for visiting my GitHub account!
MongoDB is a document database. It stores data in a type of JSON format called BSON. Also, MongoDB is a source-available, cross-platform, document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database product, MongoDB utilizes JSON-like documents with optional schemas. see-more
- VS Code, Download ->https://code.visualstudio.com/download
- Node, Download-> https://nodejs.org/en/download
- MongoDB Shell(msi) , Download-> https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/shell
- MongoDB Compass (msi), Download-> https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/community
- Postman, Download-> https://www.postman.com/downloads/
Or Online Database (MongoDB Atlas)
- Register -> https://www.mongodb.com/cloud/atlas/register
-
Install Node.js
-
To verify installation into command form by node -v
-
For initialization npm write the query in the command window as npm init -y
-
Setup the opening file into the package.json and change the file with main:'server.js'
-
To create a server using the express package then write a query into the command window as npm install express. Write code in the server file for initialization const express = require("express"); const app = express(); app.listen(3000, () => { console.log("Server is running at http:https://localhost:3000"); });
-
Install the nodemon package for automatically running the server as- npm i --save-dev nodemon (For Developing purpose)
-
setup the package.json file in the scripts key, write "scripts": { "start": "node ./resources/backend/server.js", "dev": "nodemon ./resources/backend/server.js", "test": "echo "Error: no test specified" && exit 1" },
-
use the Morgan package for automatic restart. Hence install the morgan package as npm install --save-dev morgan (Development purpose) Write code in the server file for initialization const morgan = require("morgan"); app.use(morgan("dev")); --> Middlewire.
-
Install Postman software for API testing by the URL endpoint.
-
Install Mongobd + MongobdCompass and Mongoshell (For Database)
- Install Mondodb + Mongodb Compass and Mongodb Shell download from the google.
- Set up Environment Variable in drive:c/program file
- Create a directory in the base path of the c drive named data. Inside the data directory create another folder db.
- Write the command in the CMD window as Mongod. And write the other command in the other CMD window as mongosh.
- Then Check the version as mongod --version and mongosh --version.
- Install mongoose package as npm i mongoose
- Create an atlas account. In the atlas account create a cluster that have a user(as atlas admin) and network access with any access IP address.
- Connect the database using URL from the atlas cluster or local Mongodb compass using the mongoose package as mongoose. connect('mongodb:https://localhost:27017/database-name);
| Schema |
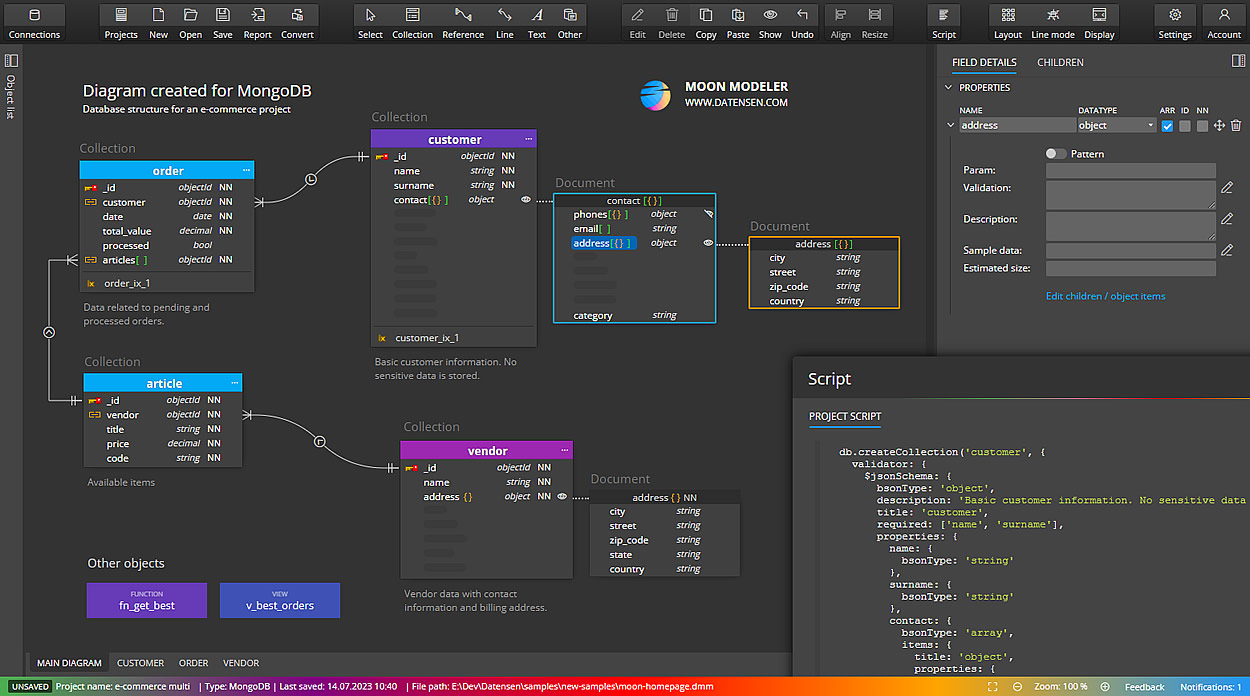 |
- SQL stands for Structured Query Language - MySQL Database
- It follows relational database management system
- store data as a form of table
- null possibility if we dont add value for column
- NoSQL stands for No Structured Query Language - MongoDB Database
- It follows documented oriented database management system
- store data as a form of document by using BSON structure
- no null possibility if we do not add add value for any field
- it uses BSON -> Binary JSON
- why BSON instead of JSON?
- JSON only supports limited number of data types such as String, Boolean, Number, Array (BSON added Date, Raw Binary, Number-Integer, Float, Long, Decimal to JSON)
- Speed - text based format is very slow to parse (BSON is fast to parse)
- Storage - JSON takes less compare to BSON
- Usage - JSON used for transmission data where BSON used for storage of data
- Encoding technique: JSON use UTF-8 string encoding where BSON use Binary encoding
- Security: JSON is Human and machine Readable where BSON in only machine Readable
-
What is MongoDB?
- Document Oriented Database system
- NoSQL
- Some important terms: Database, Table/Collection, Document/Row, Field/Column
// document example { id : '1', name: 'rahatul', languages: ['bangla', 'english'] }
-
Download & install MongoDB
-
MongoDB Compass
-
Check installation
mongod --version (mongodb server version) mongo --version (mongodb shell version)
-
database
- show databases:
show dbs - create / switch to a Database:
use databaseNameexample:use productsDB - check the Database you are in :
db + enter - drop database :
db.dropDatabase()
- show databases:
-
collections
- show collections:
show collections - create collection :
db.createCollection(name, option)exampledb.createCollection("products") - drop collection :
db.collectionName.drop()
- show collections:
-
database is collection of Documents
-
Field name regulations collected from MongoDB official website:
- The field name _id is reserved
- Field names cannot contain the null character.
-
insert documents command
db.collectionName.instertOne({})db.collectionName.instertMany([{},{}])db.collectionName.instert([{},{}])
-
Create data- inserting data to user collection example
{ title: "Fjallraven - Foldsack No. 1 Backpack, Fits 15 Laptops", price: 109.95, } // insertOne() db.products.insertOne({ title: "Fjallraven - Foldsack No. 1 Backpack, Fits 15 Laptops", price: 109.95, }) // insertMany() db.products.insertMany([ { title: "Fjallraven - Foldsack No. 1 Backpack, Fits 15 Laptops", price: 109.95, }, { title: "Mens Casual Premium Slim Fit T-Shirts ", price: 22.3, }, { title: "Mens Cotton Jacket", price: 55.99, } ])
-
Read / Find data
- read data syntax:
db.collectionName.find(query, projection) - read data in an easy way syntax:
db.collectionName.find().pretty() - read a specific data syntax:
db.collectionName.find({field: fieldValue})- example1:
db.products.find(ObjectId("633d183e09743587af26fb07")) - example2:
db.users.find({name: "anisul islam"})remember value is case sentitive
- example1:
- limit data syntax:
db.collectionName.find({field: fieldValue}).limit(NumberOfRows)- example:
db.users.find({age: 31}).limit(2)
- example:
- sorting: 1 for ascending, -1 for descending
- example:
db.products.find().sort({price: -1})
- example:
- less than and greater than
- example :
db.myCollection.find({field1: {$gt:25}})
- example :
- projection
- example :
db.students.find({name: "x"}, {name:0})get every field without name - example :
db.students.find({name: "x"}, {name:1})get only field - example :
db.students.find({name: "x"}, {_id:0, name:1})get only field even without mongodb _id
- example :
- read data syntax:
-
Update Data -> $set operator helps to set update value to a field
- update data syntax:
db.collectionName.update(selection_item, update_data) - update data syntax:
db.collectionName.updateOne(selection_item, update_data) - update data syntax:
db.collectionName.updateMany(selection_item, update_data) - find one and update data syntax:
db.collectionName.findOneAndUpdate(selection_item, update_data) - example:
db.products.update({id:"1"},{$set:{price:32}})
- update data syntax:
-
Delete data
- delete data syntax: `db.collectionName.deleteOne(selection)
- example:
db.users.deleteOne({name:"anisul islam"})
- example:
- delete data syntax: `db.collectionName.deleteOne()
- delete many data syntax: `db.collectionName.deleteMany({selected_item})
- delete many data syntax: `db.collectionName.deleteMany({})
- delete data syntax: `db.collectionName.deleteOne(selection)
- 2 ways to connect -> with mongoose package, with mongodb package
- method 1: with mongodb package
- install mongodb :
npm i mongodb
- install mongodb :
- method 2: with mongoose package
- mongoose in an ODM (Object data modeling) Library for MongoDB and node.js. It provides schema validation. node.js -> mongoose -> mongo driver -> mongoDB
const express = require("express");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const port = 3002;
const app = express();
const connectDB = async () => {
try {
await mongoose.connect("mongodb:https://localhost:27017/shop");
console.log("db is connected");
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
app.listen(port, async () => {
console.log(`server is running at http:https://localhost:${port}`);
await connectDB();
});- define structure of document with validation
- we can define default values of a field
- A model works as a wrapper for schema. It provides an interface for accessign database to create, update, delete, read from database.
const productSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
reuired: true,
},
description: {
type: String,
reuired: true,
},
price: {
type: Number,
reuired: true,
},
date: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now,
},
});
const Product = mongoose.model("Products", productSchema);const addProduct = async () => {
try {
const newProduct = new Product({
title: "iPhone 14",
description: "a nice cute product",
price: 1300,
});
const productData = await newProduct.save();
// insert many
// const productData = await Product.insertMany([newProduct1, newProduct2]);
console.log(productData);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
}
};
addProduct();- comparsion query operators: https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/operator/query-comparison/
- $eq, $ne, $gt, $lt, $gte, $lte, $in, $nin
const getProducts = async (req, res) => {
try {
const products = await Product.find();
const products = await Product.find().limit(1);
const products = await Product.find({ id: req.params.id });
const products = await Product.find({ isAvailable: true });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $eq: 1200 } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $in: [1200, 1300] } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $nin: [1200, 1300] } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $ne: 1200 } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $gt: 1200 } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $lt: 1200 } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $gte: 1200 } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $lte: 1200 } });
const products = await Product.find({ price: 1200 });
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $gt: 1200 } }).select({
title: 1,
});
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $gt: 1200 } }).select({
_id: 0,
title: 1,
});
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $gt: 1200 } }).select({
_id: 0,
title: 0,
});
console.log(products);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
getProducts();- $and, $or, $not, $nor
// {$and : [{},{}]}
const products = await Product.find({
$and: [{ price: { $lt: 1400 } }, { rating: { $gt: 4 } }],
});
const products = await Product.find({
$or: [{ price: { $lt: 1400 } }, { rating: { $gt: 4 } }],
});
// returns all that fail both clauses
const products = await Product.find({
$nor: [{ price: { $lt: 1400 } }, { rating: { $gt: 4 } }],
});
// $not
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $not: { $lt: 900 } } });- countDocuments() / count()
const products = await Product.find({ price: { $gt: 900 } }).countDocuments();
// ascending
const products = await Product.find().sort({ price: 1 });
// descending
const products = await Product.find().sort({ price: -1 });
// sort and select
const products = await Product.find()
.sort({ title: 1 })
.select({ title: 1, _id: 0 });
console.log(products);- update data syntax:
db.collectionName.updateOne(selection_item, update_data) - update data syntax:
db.collectionName.findByIdAndUpdate(selection_item, update_data, {new: true})
// updateOne
const products = await Product.updateOne({ _id }, { $set: { rating: 4.8 } });
console.log(products);
updateProduct("63432689c564aea397b3d210");
// findByIdAndUpdate it returns old data
const products = await Product.findByIdAndUpdate(
{ _id },
{ $set: { rating: 4.8 } }
);
console.log(products);
// findByIdAndUpdate it returns updated data
const products = await Product.findByIdAndUpdate(
{ _id },
{ $set: { rating: 4.7 } },
{ new: true }
);
console.log(products);- example:
db.users.deleteOne({name:"anisul islam"})
const products = await Product.deleteOne({ _id });
console.log(products);
// findByIdAndDelete return deleted data
const products = await Product.findByIdAndDelete({ _id });
console.log(products);- official documentation
- A common gotcha for beginners is that the unique option for schemas is not a validator.
- Numbers have: min, max validators
- Strings have: minlength, maxlength, trim, lowercase, enum
- validator error message can be provided using array syntax and object syntax
Array syntax: min: [6, 'Must be at least 6, got {VALUE}']
Object syntax: enum: { values: ['Coffee', 'Tea'], message: '{VALUE} is not supported' }// validation when creating schema
title: {
type: String,
required: [true, "product title is required"],
minlength: 3,
minlength: [3, "error message here"],
maxlength: 3,
lowercase: true,
uppercase: true,
trim: true // " iphone 7 ",
enum: ["iphone", "samsung", "motorola"] // no other value is allowed other than these,
enum: {
values: ['iphone', 'samsung', motorola"],
message: '{VALUE} is not supported'
}
},
price:{
type: String,
required: true,
min: 20,
max: 30
}
- for fulfilling own requirements based on certain situation we need to create custom validations.
- read about email vliadation
- create your own validation regular expression
price:{
type: String,
required: [true, "title is required"],
validate: {
validator: function (v) {
return v.length === 10;
},
message: (props) => `${props.value} is not a valid product title!`,
},
},
phone: {
type: String,
validate: {
validator: function(v) {
return /\d{3}-\d{3}-\d{4}/.test(v);
},
message: props => `${props.value} is not a valid phone number!`
},
required: [true, 'User phone number required']
}
email:{
// ^[\w-\.]+@([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]{2,4}$
type: String,
required: [true, 'User email is required'],
trim: true,
lowercase: true,
unique: true,
validate: {
validator: function(v) {
const emailRegex = /^([\w-\.]+@([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]{2,4})?$/;
return emailRegex.test(v);
},
message: props => `${props.value} is not a valid phone number!`
},
email: {
type: String,
trim: true,
lowercase: true,
unique: true,
required: 'Email address is required',
validate: [validateEmail, 'Please fill a valid email address'],
match: [/^\w+([\.-]?\w+)*@\w+([\.-]?\w+)*(\.\w{2,3})+$/, 'Please fill a valid email address']
}
}npm i validator
email: {
type: String,
unique: true,
required: [true, "email is required"],
trim: true,
lowercase: true,
validate: {
validator: validator.isEmail,
message: (props) => `${props.value} is not a valid email!`,
},
},const { page = 1, limit = 10 } = req.query;
const products = await Product.find()
.limit(limit)
.skip((page - 1) * limit);
console.log(products);
