This project aims to generate an analytical business report from a sales database.
The Northwind database contains sales data from a company called Northwind Traders, which imports and exports specialty foods from around the world. In this report, we will primarily focus on extracting insights from revenue, product, and customer data using SQL operations in a PostgreSQL database.
The analyses provided here can benefit companies of all sizes looking to enhance their analytical capabilities. Through these reports, organizations can strategically position themselves in the market, leveraging data-driven decisions to improve their future results.
It is possible to run this project using only Docker, as it builds both the PostgreSQL database and the client pgAdmin. All instructions are provided in How to run this project section.
The query below aggregates the operational revenue by year and calculates the cumulative operational revenue over the same years. It is useful for obtaining an overall trend of the results.
CREATE VIEW annual_revenues_analysis AS
WITH annual_revenues AS (
SELECT
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date) AS year,
ROUND(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))::numeric, 2) as revenue
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
orders AS o
ON od.order_id = o.order_id
GROUP BY
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date)
)
SELECT
year,
revenue,
SUM(revenue) OVER (ORDER BY year) AS cumulative_revenue
FROM annual_revenues;| year | revenue | cumulative_revenue |
|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 208083.97 | 208083.97 |
| 1997 | 617085.20 | 825169.17 |
| 1998 | 440623.87 | 1265793.04 |
By using a similar approach to the previous query, we can aggregate the operational revenue by month, calculate the cumulative operational revenue by year (year-to-date), and obtain the total and relative difference between each month. This can be useful for observing trends in small time windows and identifying patterns specific to the business, such as certain parts of the year yielding better results than others.
CREATE VIEW ytd_revenue_analysis AS
WITH monthly_revenue_table AS (
SELECT
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date) AS year,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM o.order_date) AS month,
ROUND(SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1.0 - od.discount))::numeric,2) AS monthly_revenue
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
orders AS o
ON od.order_id = o.order_id
GROUP BY
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date),
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM o.order_date)
),
cumulative_revenue_table AS (
SELECT
year,
month,
monthly_revenue,
SUM(monthly_revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month) AS ytd_revenue
FROM
monthly_revenue_table
)
SELECT
year,
month,
monthly_revenue,
ytd_revenue,
monthly_revenue - LAG(monthly_revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month) AS monthly_difference,
ROUND((monthly_revenue - LAG(monthly_revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month)) / LAG(monthly_revenue) OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY month) * 100::numeric,2) AS percentage_monthly_difference
FROM
cumulative_revenue_table
ORDER BY
year, month;| year | month | monthly_revenue | ytd_revenue | monthly_difference | percentage_monthly_difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 7 | 27861.90 | 27861.90 | ||
| 1996 | 8 | 25485.28 | 53347.18 | -2376.62 | -8.53 |
| 1996 | 9 | 26381.40 | 79728.58 | 896.12 | 3.52 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1998 | 3 | 104854.16 | 298491.56 | 5438.87 | 5.47 |
| 1998 | 4 | 123798.68 | 422290.24 | 18944.52 | 18.07 |
| 1998 | 5 | 18333.63 | 440623.87 | -105465.05 | -85.19 |
The query below orders the customers by the total and relative operational revenue they were responsible for over the total time. This is very useful for understanding the concentration of operational revenue and forecasting future results.
CREATE VIEW customers_analysis AS
SELECT
c.company_name,
ROUND(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))::numeric, 2) AS total_revenue,
ROUND((SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount)) / SUM(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))) OVER() * 100)::numeric, 2) AS percentage_of_total_revenue
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
orders AS o
ON od.order_id = o.order_id
LEFT JOIN
customers AS c
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY
c.company_name
ORDER BY
total_revenue DESC| company_name | total_revenue | percentage_of_total_revenue |
|---|---|---|
| QUICK-Stop | 110277.31 | 8.71 |
| Ernst Handel | 104874.98 | 8.29 |
| Save-a-lot Markets | 104361.95 | 8.24 |
| Rattlesnake Canyon Grocery | 51097.80 | 4.04 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| Lazy K Kountry Store | 357.00 | 0.03 |
| Centro comercial Moctezuma | 100.80 | 0.01 |
After classifying customers based on operational revenue, we can categorize them by executing the following query.
CREATE VIEW revenue_groups AS
SELECT
c.company_name,
ROUND(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))::numeric, 2) AS total_revenue,
ROUND((SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount)) / SUM(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))) OVER() * 100)::numeric, 2) AS percentage_of_total_revenue,
NTILE(5) OVER (ORDER BY SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount)) DESC) AS revenue_group
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
orders AS o
ON od.order_id = o.order_id
LEFT JOIN
customers AS c
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY
c.company_name
ORDER BY
total_revenue DESC| company_name | total_revenue | percentage_of_total_revenue | revenue_group |
|---|---|---|---|
| QUICK-Stop | 110277.31 | 8.71 | 1 |
| Ernst Handel | 104874.98 | 8.29 | 1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Lazy K Kountry Store | 357.00 | 0.03 | 5 |
| Centro comercial Moctezuma | 100.80 | 0.01 | 5 |
Now only the customers who are in groups 3, 4, and 5 will be selected for a special marketing analysis with them, for example.
CREATE VIEW revenue_groups_filtered AS
WITH companies_revenue_groups AS (
SELECT
c.company_name,
ROUND(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))::numeric, 2) AS total_revenue,
ROUND((SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount)) / SUM(SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount))) OVER() * 100)::numeric, 2) AS percentage_of_total_revenue,
NTILE(5) OVER (ORDER BY SUM((od.unit_price * od.quantity) * (1 - od.discount)) DESC) AS revenue_group
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
orders AS o
ON od.order_id = o.order_id
LEFT JOIN
customers AS c
ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY
c.company_name
ORDER BY
total_revenue DESC
)
SELECT
*
FROM
companies_revenue_groups
WHERE
revenue_group IN (3,4,5);| company_name | total_revenue | percentage_of_total_revenue | revenue_group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Split Rail Beer & Ale | 11441.63 | 0.90 | 3 |
| Tortuga Restaurante | 10812.15 | 0.85 | 3 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Lazy K Kountry Store | 357.00 | 0.03 | 5 |
| Centro comercial Moctezuma | 100.80 | 0.01 | 5 |
We can also filter customers by specific criteria, like filtering for only UK customers who paid more than 1000 dollars, for example.
CREATE VIEW uk_customers_who_payed_more_than_1000 AS
SELECT
c.company_name,
ROUND(SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1.0 - od.discount))::numeric, 2) AS revenue
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
orders AS o
ON od.order_id = o.order_id
LEFT JOIN
customers AS c
ON o.customer_id = c.customer_id
WHERE
LOWER(c.country) = 'uk'
GROUP BY
c.company_name
HAVING
SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1.0 - od.discount)) > 1000
ORDER BY
revenue DESC;| company_name | revenue |
|---|---|
| Seven Seas Imports | 16215.33 |
| Eastern Connection | 14761.03 |
| Around the Horn | 13390.65 |
| Island Trading | 6146.30 |
| B's Beverages | 6089.90 |
| Consolidated Holdings | 1719.10 |
The query below orders the products responsible for generating more operational revenue, as well as their total quantity sold.
CREATE VIEW products_analysis AS
SELECT
DISTINCT p.product_name,
ROUND((SUM(od.unit_price * od.quantity * (1.0 - od.discount)) OVER (PARTITION BY p.product_name))::numeric, 2) AS revenue,
SUM(od.quantity) OVER (PARTITION BY p.product_name) AS quantity_sold
FROM
order_details AS od
LEFT JOIN
products AS p
ON od.product_id = p.product_id
ORDER BY
revenue DESC;| product_name | revenue | quantity_sold |
|---|---|---|
| Côte de Blaye | 141396.74 | 623 |
| Thüringer Rostbratwurst | 80368.67 | 746 |
| Raclette Courdavault | 71155.70 | 1496 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| Genen Shouyu | 1784.82 | 122 |
| Geitost | 1648.12 | 755 |
| Chocolade | 1368.71 | 138 |
In this report, we performed some queries to obtain specific business insights to assist the business. There are always more filters and approaches we can explore, as well as extending the monthly analysis conducted on operational revenue to include customers and products.
The Northwind database contains sales data for a company called Northwind Traders, which imports and exports specialty foods from around the world.
The Northwind database is an ERP with data on customers, orders, inventory, purchases, suppliers, shipments, employees, and accounting.
The Northwind dataset includes sample data for the following:
- Suppliers: Northwind's suppliers and vendors
- Customers: Customers who purchase products from Northwind
- Employees: Details of Northwind Traders' employees
- Products: Product information
- Shippers: Details of carriers that ship the traders' products to end customers
- Orders and Order Details: Sales order transactions occurring between customers and the company
The Northwind database includes 14 tables, and the relationships between the tables are shown in the following entity relationship diagram.
After connecting to your own database, use the northwind.sql file to populate the database by copying the script, pasting it into the query tool, and running it.
Its is required to have docker and docker compose intalled to be able to run this project.
Once we have docker avaiable, we do the following steps:
- Clone the repository locally.
git clone https://github.com/lealre/northwind-analytics-sql.git- Access the project folder.
cd northwind-analytics-sql- Build the Docker container.
docker compose up -dThe -d flag is used to run the container detached from the terminal.
-
Access pgAdmin at http:https://localhost:5050/
-
Set the master password (when accessing for the first time).
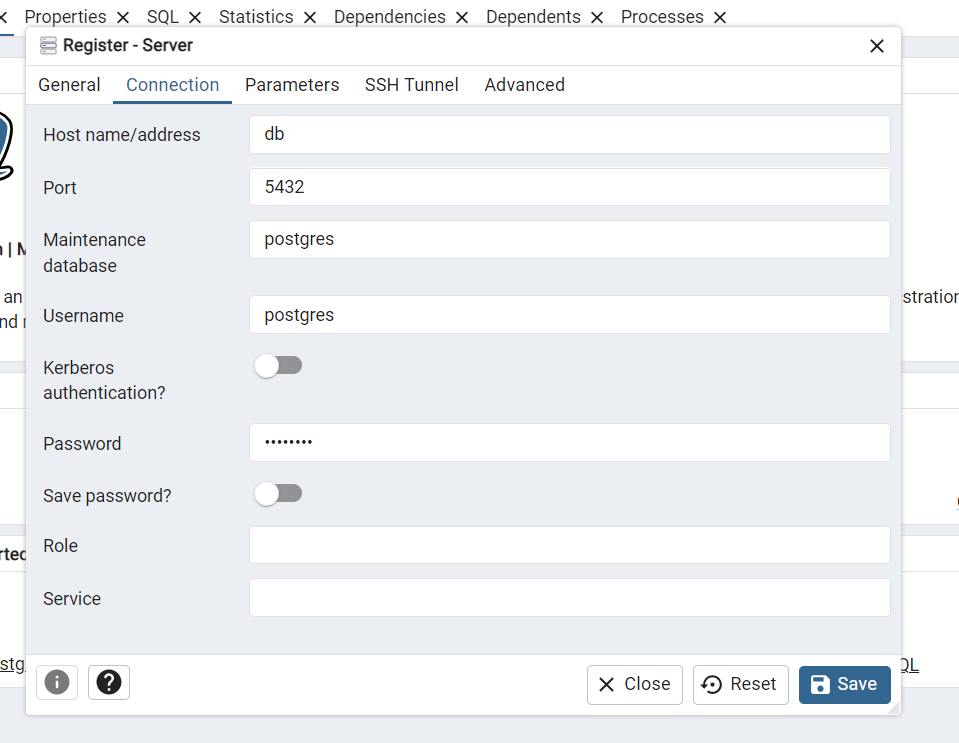
- Right-click on the server to connect pgAdmin to the database.
- Set the server name (it can be any name you want).
- Connect to the database using the credentials we set in the
docker-compose.yamlfile.
Host name: db
Password: postgres
After completing this final step, you will be able to access the Northwind database, as well as the views created in the report.