This is an example repository for you to use to create a new blog site using Next.js and Contentful, using Contentful's GraphQL API.
Read more about the GraphQL API.
Click here to explore the demo site that uses this repository as its source code.
Fork the repository to your GitHub account and clone it to your local machine.
#using git
git clone [email protected]:whitep4nth3r/nextjs-contentful-blog-starter.git
#using the GitHub CLI
gh repo clone whitep4nth3r/nextjs-contentful-blog-starterIn a terminal window, navigate to the project directory and install dependencies with npm.
cd nextjs-contentful-blog-starter
npm installAt the root of the project, create a new .env.local file. Add the following environment variable names to the file:
CONTENTFUL_SPACE_ID=
CONTENTFUL_ACCESS_TOKEN=
You can choose to use your own Contentful account, or connect to the example space that we've provided.
If you'd like to view some example content in your development environment to get a feel for how it works, you can use the provided credentials in env.local.example which will connect your code to the example space provided by Contentful.
To get started with your own Contentful space, sign up for free.
Create a new space inside your Contentful account. Go to Settings > General Settings, and make a note of your space ID.
Generate a Content Delivery API access token for your Contentful space.
Add your space ID and access token to your .env.local file.
To get started quickly on your own version of the application, you can use the Contentful CLI to import the content model and the example content from the starter into your own Contentful space — without touching the Contentful UI!
#using homebrew
brew install contentful-cli
#using npm
npm install -g contentful-cli
#using yarn
yarn global add contentful-cliOpen a terminal and run:
contentful loginA browser window will open. Follow the instructions to log in to Contentful via the CLI.
The following command in your terminal, ensuring you switch out SPACE_ID for your new space ID.
cd nextjs-contentful-blog-starter/setup
contentful space import --space-id SPACE_ID --content-file content-export.jsonYou should see this output in the terminal. The import will take around 1 minute to complete.
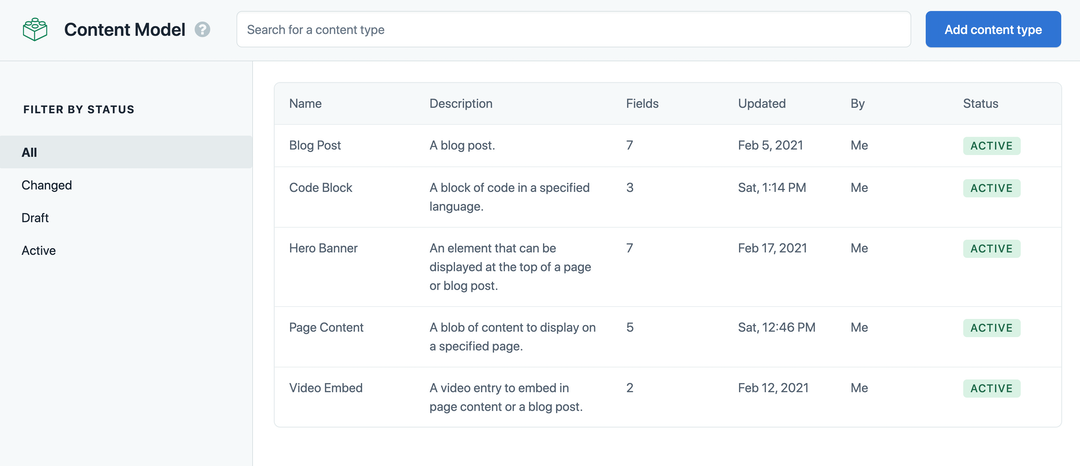
Refresh Contentful in your browser, navigate to the content model tab, and you'll find the content types have been imported into your space. You'll find the example content by clicking on the content tab.
Navigate to the project directory in a terminal window and run:
npm run devDuring the deploy process, add the following environment variables to Netlify. Use the same credentials as you set up in your local development environment.
CONTENTFUL_SPACE_ID
CONTENTFUL_ACCESS_TOKEN
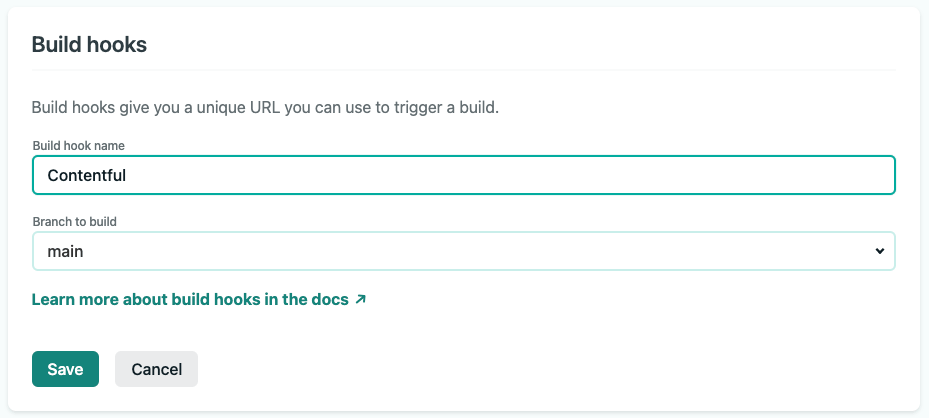
After you deploy the site to Netlify you can configure it to build whenever new a new entry is published in Contentful. To configure this navigate to your site settings on Netlify and go to the Build & Deploy tab. Find the Build hooks section and add a new build hook. Name the build hook something like Contentful and select your production branch.
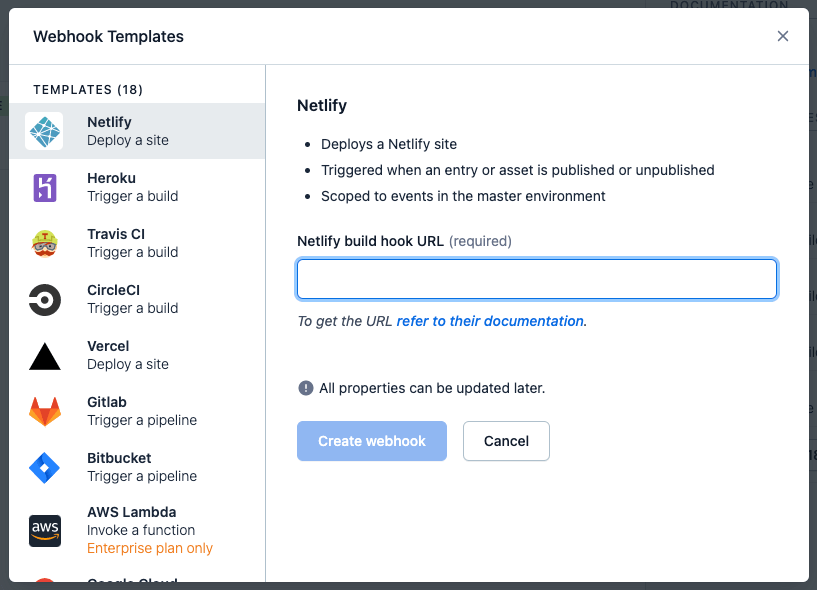
Copy the generated URL and navigate to Settings > Webhooks in your Contentful space. Under Webhook Templates click Add next to the Netlify template. Add the URL you just copied and click Create webhook.
Now when you publish an entry in your Contentful space it will trigger a build of your production branch on Netlify.
In your Contentful space, go to Settings > Content preview and add a new content preview. Under content preview URLs check Blog Post and add this URL
https://$NETLIFY_URL/api/preview?secret=$SECRET&slug={entry.fields.slug}&contentType=blogPost
Replacing $NETLIFY with the URL of your site deployed on Netlify and $SECRET which a secret value that you generate. Store this value as you will add to your Netlify environment variables in a moment.
Check Page Content and add this URL
https://$NETLIFY_URL/api/preview?secret=$SECRET&slug={entry.fields.slug}&contentType=pageContent
Replacing the variables with the same values you used above. Navigate to your site on Netlify and go to Site settings > Build & Deploy > Environment and add the following environment variables
CONTENTFUL_PREVIEW_SECRET
NEXT_PUBLIC_CONTENTFUL_PREVIEW_ACCESS_TOKEN
Set CONTENTFUL_PREVIEW_SECRET to the value you generated above and used for $SECRET in the preview URLs. Set NEXT_PUBLIC_CONTENTFUL_PREVIEW_ACCESS_TOKEN to your Contentful Content Preview API access token which can be found under Settings > API keys.
Trigger a new deploy of your site on Netlify so the new variables are applied and you should now be able to enter Preview mode by clicking the preview button on relevant content entries.