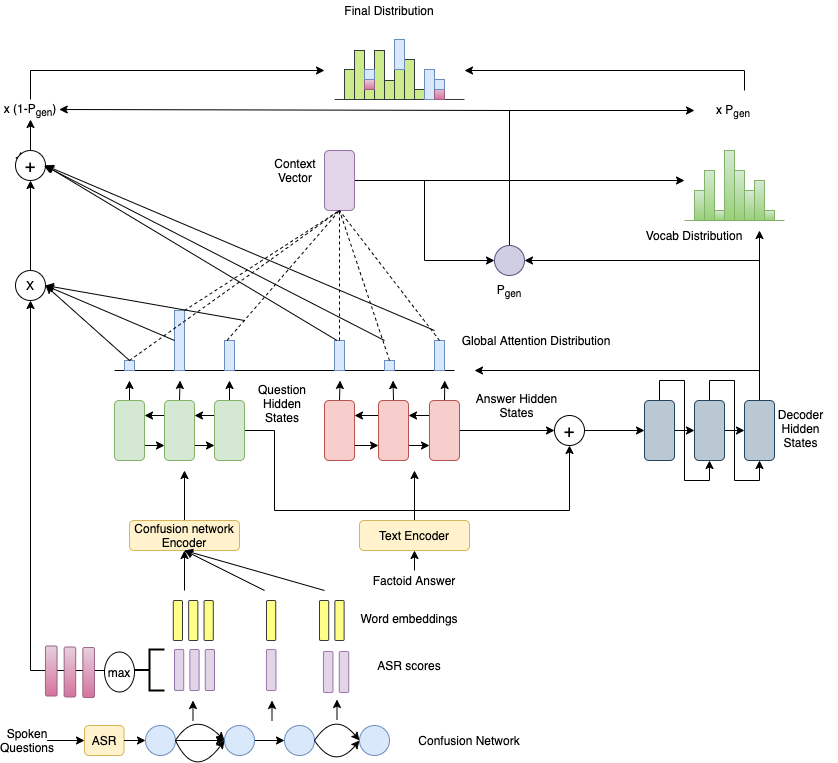
Code base for paper ConfNet2Seq: Full Length Answer Generation from Spoken Questions. The dataset is contained in data directory. train.ques, train.ans, train.tgt contains data triplet (question, factoid answer, target full length answer) in each line respectively.
The codebase is built over OpenNMT
All dependencies can be installed via:
pip install -r requirements.txtThe data files are present in data directory. The confusion network and audio files can be downloaded from https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1nFtsOrSdE5v6Bjsw-B90MBYWvVtFBsYr?usp=sharing
Pad the answer text file.
python add_padding.py --input <answer-filename> --output <padded-answer-filename> --padding <num of pad>
python preprocess.py -train_confnet data/ques-train.txt -train_src data/ans-train.txt -train_tgt data/tgt-train.txt -valid_confnet data/ques-val.txt -valid_src data/ans-val.txt -valid_tgt data/tgt-val.txt -save_data data/demo --dynamic_dict --share_vocabThe data consists of parallel source (src) and target (tgt) data containing one sentence per line with tokens separated by a space:
ques-train.txt: text file containing path to a question confusion network in each lineans-train.txt: text file containing the padded factoid answer in each linetgt-train.txt: text file containing the target full length answerques-val.txt: text file containing the path to a validation question confusion network in each lineans-val.txt: validation text file containing the path to the padded factoid answer in each linetgt-val.txt: validation text file containing the target full length answer
Validation files are required and used to evaluate the convergence of the training. It usually contains no more than 5000 sentences.
After running the preprocessing, the following files are generated:
demo.train.pt: serialized PyTorch file containing training datademo.valid.pt: serialized PyTorch file containing validation datademo.vocab.pt: serialized PyTorch file containing vocabulary data
Internally the system never touches the words themselves, but uses these indices.
python train.py -data data/demo -save_model demo-model -word_vec_size 300 -model_type lattice -encoder_type brnn -layers 2 -rnn_size 512 \
-data data/demo -batch_size 32 -valid_batch_size 32 -valid_steps 2500 -dropout 0.5 -start_decay_steps 10000 -coverage_attn -copy_attn \
--share_embeddingspython translate.py -model <model_path> --data_type lattice -src data/ans-test.txt -confnet data/ques-test.txt -tgt data/tgt-test.txt -share_vocab -beam_size 10 -replace_unk -output pred.txt --batch_size 10python preprocess.py --help
python train.py --help
python translate.py --helpOpenNMT-py is run as a collaborative open-source project. The original OpenNMT-py code was written by Adam Lerer (NYC) to reproduce OpenNMT-Lua using Pytorch.
@inproceedings{pal2020confnet2seq,
title={ConfNet2Seq: Full Length Answer Generation from Spoken Questions},
author={Vaishali Pal and Manish Shrivastava and Laurent Besacier},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Text, Speech and Dialogue (TSD 2020)},
year={2020},
publisher = {Springer}
}