Link to presentation can be found Here
Slected Topic: Presence of Mental Health Disorders in Tech Workforce
Reason for Choosing this Topic:
Careers in tech/IT are becoming more prominent and with many of us moving towards a career in tech or changing jobs, it’s of interest to look at the presence of mental health disorders in the tech/IT workplace. It's also interesting to consider how a company responds to their employees mental health and services that they may offer.
Questions we Hope to Answer:
- Based on how participants answered survey questions, are we able to predict whether or not an individual has a diagnosed mental health disorder?
- Does the presence of mental health services offered by a company have an effect on an individual’s mental health?
- Do mental health disorders in the tech workplace vary by age, gender, or country they live and work in?
Null Hypothesis: There is no correlation between how participants answer questions to a mental health in tech survey, and their diagnosis of a mental health disorder.
Alternative Hypothesis: Based off how one responds to questions on a survey, you are able to predict if one has a diagnosed mental health disorder.
Label: Have you been diagnosed with a mental health condition by a medical professional?
Square: Hillary
Circle: Rudy
Triangle: Jason
Data Source: OSMI Mental Health in Tech Survey 2016
CSV and JSON file from kaggle. It is a survey dataset from 2016 that has 1433 observations (individuals that participated in survey) with 63 features (questions that were asked).
Software: Jupyter Notebook, Python 3.7.6, Flask, JavaScript, Heroku, SQLite, HTML, Tableau
Libraries: Pandas, Numpy, Scipy, Scikit-learn, SQLAlchemy, Pickle, sqlite3, Bootstrap4
The initial step is to clean the data by removing null values.
- Our data was downloaded from Kaggle.com as a csv file.
- Pandas was used to loop through the data set and functions were printed to look at each column and its response percentage. Any columns with less than a 70% response were dropped from data set, leaving us with 48 features.
- Columns with more than 10 unique responses were added to a list. From that list we dropped any columns with a long response, such as "Why or why not" questions.
- The gender column had a large amount of unique values due to some responses meaning the same thing, however python was not able to recognize that. So we cleaned the data by making certain values equal to one another; for example "Male" = "male" = "M". This allowed us to then bin gender into 3 values: "Male", "Female", and "Other".
- Columns such as Countries where people live and work could be binned. We first looked at the number of unique values for each response and found that most participants in the survey were either from and/or worked in the United States or United Kingdom. We chose to bin these columns into "United States", "United Kingdom", and "Other", leaving us with 45 columns.
- Chi-square tests were ran on each column to determine which columns were significant and should be kept. A p-value of 0.05 was used to determine significance, leaving us with 32 columns.
We used pandas and SQLAlchemy to load the csv files that we started with, and merged tables that we created into a SQLite database. Our database is then able to interact with our machnie learning model, which allows us to make predictions and analyze our results. We chose to use SQLite because it has several characteristics that we were looking for which are listed below:
- Reading and writing operations are fast for SQLite databases.
- SQLite is very easy to learn, additionally there is no added installation and configuration.
- It is availible through a wide variety of tools.
- The main limitation is that the Database size is limited to 2 GB, which was not an issue for us.
Random forest models are classifier algorithms that evolve from many individual decision trees. Each tree learns from a random sample taken from the original dataset; this is done many times, creating a forest of simple tree classifiers that have been trained on a slightly different set of observations. Each of these trees, when on their own are “weak” learners, but when combined create a “strong” learner because the final predictions of random forest are made by averaging the predictions of each individual tree and choosing the most voted prediction.
The random forest model generally has a high accuracy compared to other models and was chosen for the many additional features that it offers. It is robust against overfitting as all the weak learners are trained on different pieces of the data. They are also robust to outliers because each decision tree isolates atypical observations into small leaves and averages them, meaning that extreme values do not affect the entire model. Additionally, random forests run efficiently on large datasets and can handle thousands of input variables without variable deletion. Considering that our original dataset consisted of 63 survey questions (columns) from 1433 participants (rows), it was important to use a model that could make an accurate prediction with so many variables at play. Another benefit of using random forest is that it can be used to rank the importance of input variables in a natural way, allowing us a better understanding of what survey questions are most important when predicting if an individual has a mental health disorder.
- Random forest models are more difficult to interpret when compared to individual decsion trees.
- Training a large number of deep trees can have high computational costs and use alot of memory.
- You reach apoint of diminishing returns once a certain number of samples is used.
OneHotEncoder
- Since data set is categorical, we will be using "OneHotEncoder" from Sklearn library. This will allow us to take categorical data from each column and subsequently split it into multiple response columns for each response. The categorical data is replaced by 1s and 0s, depending on which column has what value. For example, most of questions in survey have either a "yes", "no" or "I don't know" response", meaning that we will get three new columns for each question asked.
Fit and Transform
- Scikit-learn's encoder fit_transform() method was used to first train the label, then to convert all categorical text data into numerical data. Since all of our data was now binary (either 1's or 0's), we did not need to scale.
Get_Feature_Names
- In order to run our model solely on binary data, we used get_feature_names() method so that the new encoded dataframe could be more easily interpreted and then merged the OneHotEncoded features.
Define target and features
We choose the survey question that most clearly addressed our central question, which was do people in working in Tech have diagnosed mental health disorders?
- Target: Have you been diagnosed with a mental health disorder - Yes
- Features: Have you been diagnosed with a mental health disorder - No; Have you been diagnosed with a mental health disorder - Yes
Split into training and testing sets
- To train and validate the model, we split the features and target sets into training and testing sets. This helps determine the relationships between each feature in the features training set and the target training set.
Create a random forest model
- Using the RandomForestClassifier, we used the parameters random_state and n_estimators, which allow us to set the number of trees that will be created by the algorithm. The higher the number of trees create stronger and more stable predictions, but can slow down the model. Making predictions and evaluating the model
- After we ran code to make predictions, we analyzed how well our model worked by using the confusion_matrix
Our model’s accuracy score is 86.11, meaning that it accurately predicts if an individual has a mental health disorder 86.11% of the time, based off how they answer survey questions (assuming they answer honestly). Since this model is not making a prediction that has high consequences, it is merely for the interest of an individual working in tech and wanting to know their likelihood of having (or developing) a mental health disorder, or for the interest of a tech company and wanting to know if offering certain mental health services would be of benefit to their employees, an accuracy of 86.11% is sufficient.
Although for this question, it is also important to look at the precision, which is the measure of how reliable a positive classification is. The precision for classifying a true positive and true negative is 90% and 83%, respectively. This means that if a survey participant is predicted to have a mental health disorder based off their answers to questions (true positive), it is 90% likely that it is true. Likewise, if a participant is predicted to not have a mental health disorder (true negative), it is 83% likely that it is true.
Bootstrapping is a test that relies on random sampling with replacement and in random forests is used on the individual trees where some samples are used multiple times. The idea being that if each tree is trained on different samples, the entire forest will have a lower variance without increasing the bias.
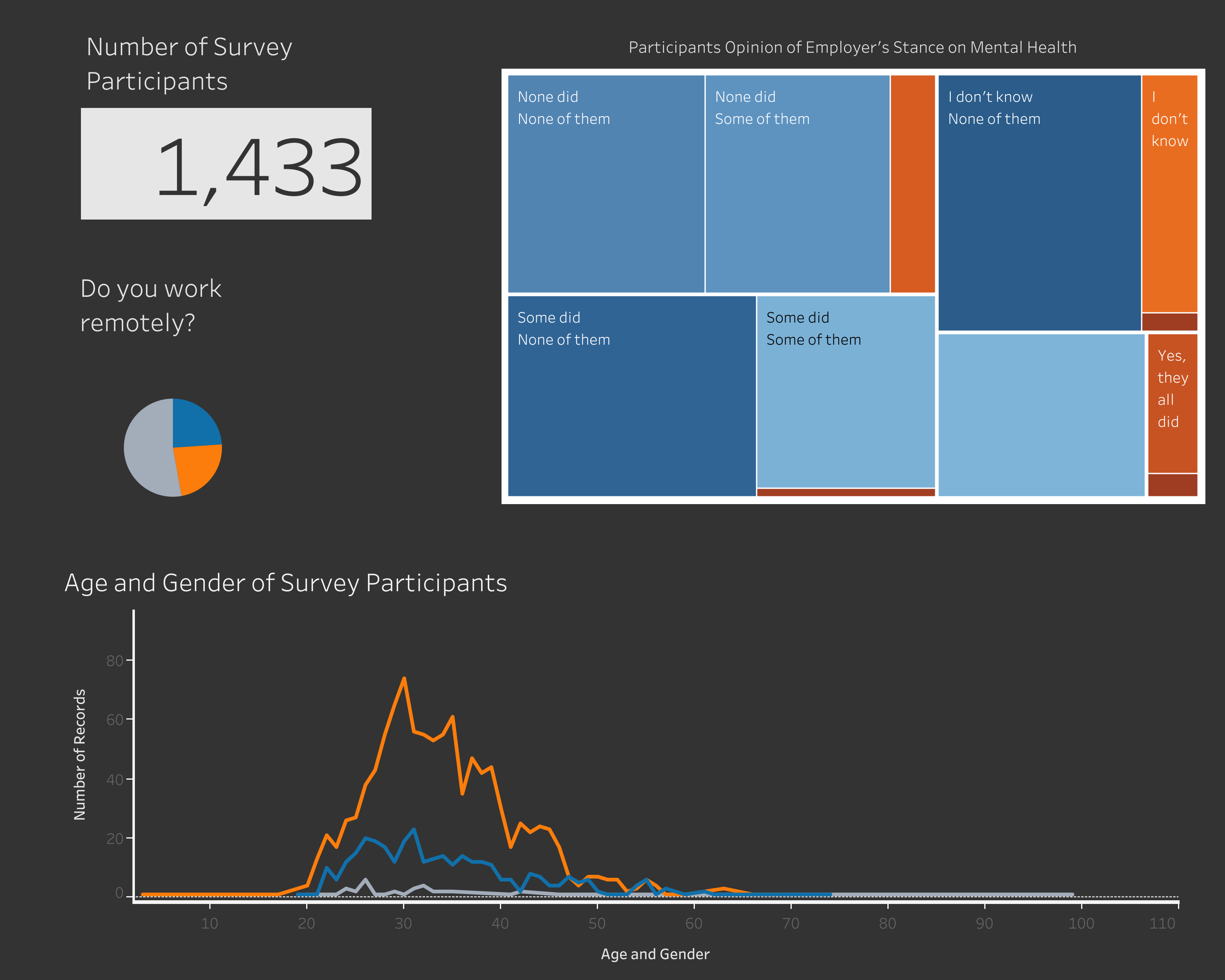 Our Dashboard can be found here.
Our Dashboard can be found here.
We are using Heroku, a cloud service to build and run the web page that is displaying our dashboard.
-
Built a Flask app
-
Connected our Flask app to Heroku
-
Created the framework for our webpage using HTML with Bootstrap4 and Javascript
-
Tableau and Interactive Elements
- Use of different types of graphs (bar, pie, line) to best depict our initial analysis.
- Created Tableau Dashboard for our landing page.
- Map with added layers and filters.
- Embeded all Tableau figures into our webpage using Tableau API.
-
Confusion Matrix from the Random Forest Model


