ANTM: An Aligned Neural Topic Model for Exploring Evolving Topics
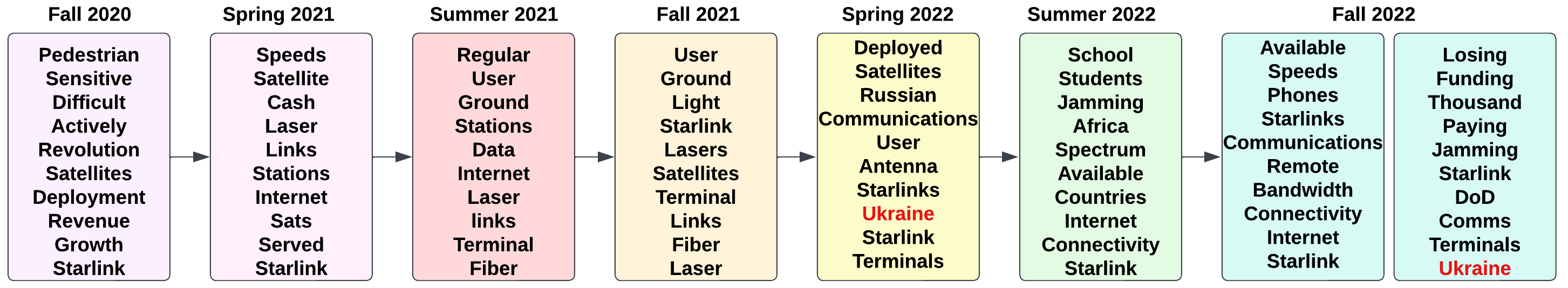
Dynamic topic models are effective methods that primarily focus on studying the evolution of topics present in a collection of documents. These models are widely used for understanding trends, exploring public opinion in social networks, or tracking research progress and discoveries in scientific archives. Since topics are defined as clusters of semantically similar documents, it is necessary to observe the changes in the content or themes of these clusters in order to understand how topics evolve as new knowledge is discovered over time. Here, we introduce a dynamic neural topic model called ANTM, which uses document embeddings (data2vec) to compute clusters of semantically similar documents at different periods, and aligns document clusters to represent their evolution. This alignment procedure preserves the temporal similarity of document clusters over time and captures the semantic change of words characterized by their context within different periods. Experiments on four different datasets show that ANTM outperforms probabilistic dynamic topic models (e.g. DTM, DETM) and significantly improves topic coherence and diversity over other existing dynamic neural topic models (e.g. BERTopic).
Installation can be done using:
pip install antmAs implemented in the notebook, we can quickly start extracting evolving topics from DBLP dataset containing computer science articles.
from antm import ANTM
import pandas as pd
# load data
df=pd.read_parquet("./data/dblpFullSchema_2000_2020_extract_big_data_2K.parquet")
df=df[["abstract","year"]].rename(columns={"abstract":"content","year":"time"})
df=df.dropna().sort_values("time").reset_index(drop=True).reset_index()
# choosing the windows size and overlapping length for time frames
window_size = 6
overlap = 2
#initialize model
model=ANTM(df,overlap,window_size,umap_n_neighbors=10, partioned_clusttering_size=5,mode="data2vec",num_words=10,path="./saved_data")
#learn the model and save it
topics_per_period=model.fit(save=True)
#output is a list of timeframes including all the topics associated with that periodfrom antm import ANTM
import pandas as pd
# load data
df=pd.read_parquet("./data/dblpFullSchema_2000_2020_extract_big_data_2K.parquet")
df=df[["abstract","year"]].rename(columns={"abstract":"content","year":"time"})
df=df.dropna().sort_values("time").reset_index(drop=True).reset_index()
# choosing the windows size and overlapping length for time frames
window_size = 6
overlap = 2
#initialize model
model=ANTM(df,overlap,window_size,mode="data2vec",num_words=10,path="./saved_data")
topics_per_period=model.load()#find all the evolving topics
model.save_evolution_topics_plots(display=False)
#plots a random evolving topic with 2-dimensional document representations
model.random_evolution_topic()
#plots partioned clusters for each time frame
model.plot_clusters_over_time()
#plots all the evolving topics
model.plot_evolving_topics()#returns pairwise jaccard diversity for each period
model.get_periodwise_pairwise_jaccard_diversity()
#returns proportion unique words diversity for each period
model.get_periodwise_puw_diversity()
#returns topic coherence for each period
model.get_periodwise_topic_coherence(model="c_v") You can use the notebooks provided in "./experiments" in order to run ANTM on other sequential datasets.
To cite ANTM, please use the following bibtex reference:
@misc{rahimi2023antm,
title={ANTM: An Aligned Neural Topic Model for Exploring Evolving Topics},
author={Hamed Rahimi and Hubert Naacke and Camelia Constantin and Bernd Amann},
year={2023},
eprint={2302.01501},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.IR}
}