This is the official implementation for Equivariant Enengy-guided SDE for Inverse Molecule Design. Our related work is EGSDE: Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation via Energy-Guided Stochastic Differential Equations (NIPS 2022).
In this paper, we propose equivariant energy-guided stochastic differential equations
(EEGSDE), a flexible framework for controllable 3D molecule generation under
the guidance of an energy function in diffusion models. Formally, we show that
EEGSDE naturally exploits the geometric symmetry in 3D molecular conformation, as long as the energy function is invariant to orthogonal transformations. Empirically, under the guidance of designed energy functions, EEGSDE significantly
improves the baseline on QM9, in inverse molecular design targeted to quantum
properties and molecular structures. Furthermore, EEGSDE is able to generate
molecules with multiple target properties by combining the corresponding energy
functions linearly.

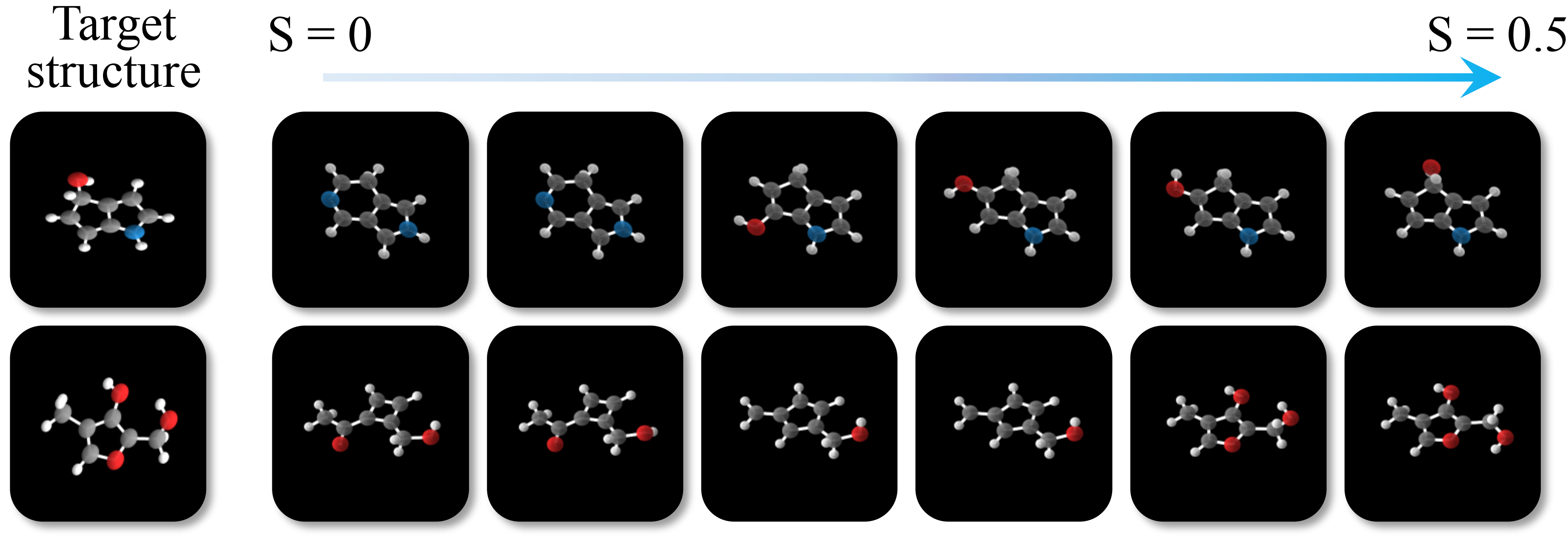
The molecular structures of EEGSDE align better with target structures then conditional EDM.

As the scaling factor grows,
the generated structures align better with the target structure. S = 0 corresponds to the conditional
EDM.
conda create -c rdkit -n EEGSDE rdkit python=3.7
source activate EEGSDE
conda install pytorch==1.11.0 torchvision==0.12.0 torchaudio==0.11.0 cudatoolkit=11.3
pip install msgpack
conda install -c openbabel openbabel
pip install ase==3.19.0
pip install imageio
We provide the pretrained checkpoints and the corresponding args on QM9 dataset here. Please put them in the pretrained_models/dir. For example, when generating molecules with desired mu, please put the args and pretrained checkpoints of diffusion models in pretrained_models/cEDM_mu, put the args and pretrained checkpoints of property prediction model used in energy function in pretrained_models/predict_mu and put the args and pretrained checkpoints of the property prediction model for evaluation in pretrained_models/evaluate_mu.
| Condition | Diffusion Models | Prediction Model in Energy Function | Prediction Model for Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cv | cEDM_Cv | predict_Cv | evaluate_Cv |
| mu | cEDM_mu | predict_mu | evaluate_mu |
| alpha | cEDM_alpha | predict_alpha | evaluate_alpha |
| gap | cEDM_gap | predict_gap | evaluate_gap |
| homo | cEDM_homo | predict_homo | evaluate_homo |
| lumo | cEDM_lumo | predict_lumo | evaluate_lumo |
| mu,Cv | cEDM_mu_Cv | - | - |
| gap,mu | cEDM_gap_mu | - | - |
| alpha,mu | cEDM_alpha_mu | - | - |
| fingerprint | cEDM_fingerprint | predict_fingerprint | - |
python run_train_property_prediction_energy.py --exp_name predict_mu --conditioning mu --model egnn_dynamics --lr 1e-4 --nf 192 --n_layers 7 --weight_decay 1e-16 --save_model True --diffusion_steps 1000 --sin_embedding False --n_epochs 3000 --diffusion_noise_schedule polynomial_2 --diffusion_noise_precision 1e-5 --dequantization deterministic --include_charges False --normalize_factors [1,8,1] --dataset qm9_second_half
The exp_name is the name of experiments. The conditioning is which property to condition and is chosen from alpha/homo/lumo/gap/mu/Cv. Take the above command for example, the results will be saved in pretrained_models/predict_mu/.
Take generating molecules with desired mu as an example:
python run_EEGSDE_single_property.py --exp_name eegsde_mu --l 1.0 --property mu --generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_mu/generative_model_ema_2020.npy --args_generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_mu/args_2020.pickle --energy_path pretrained_models/predict_mu/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path pretrained_models/predict_mu/args_2000.pickle --classifiers_path pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/args.pickle --batch_size 100 --iterations 100 --save True
The exp_name is the name of experiments. The l is the scale factor of the energy function. Take the above command for example, the results will be saved in outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0. The property is which property to condition and is chosen from alpha/homo/lumo/gap/mu/Cv. The generators_path and args_generators_path is the path of model and args with conditional EDM. The energy_path and args_energy_path is the path of model and args with property prediction model used in EEGSDE. The classifiers_path and args_classifiers_path is the path of model and args with the property prediction model for evaluation. The save is whether save the generated molecules. The batch_size is the number of generated molecules each iteration. The iterations is the number of iterations.
Run EEGSDE to generate molecules with desired multiple quantum properties by combining the corresponding energy functions linearly
Generate molecules with desired alpha and mu:
python run_EEGSDE_multi_property.py --exp_name eegsde_alpha_mu --l1 1.5 --l2 1.5 --generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_alpha_mu/generative_model_ema_2080.npy --args_generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_alpha_mu/args_2080.pickle --energy_path1 pretrained_models/predict_alpha/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path1 pretrained_models/predict_alpha/args_2000.pickle --energy_path2 pretrained_models/predict_mu/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path2 pretrained_models/predict_mu/args_2000.pickle --classifiers_path1 pretrained_models/evaluate_alpha/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path1 pretrained_models/evaluate_alpha/args.pickle --classifiers_path2 pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path2 pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/args.pickle --batch_size 50 --iterations 200
The exp_name is the name of experiments. The l1 and l2 is the scale factor of the two energy function respectively. Take the above command for example, the results will be saved in outputs/eegsde_alpha_mu/l1_1.5_l2_1.5. The generators_path and args_generators_path is the path of model and args with conditional EDM. The energy_path1 and args_energy_path1 is the path of model and args with the first property prediction model used in EEGSDE. The energy_path2 and args_energy_path2 is the path of model and args with the second property prediction model used in EEGSDE. The classifiers_path1 and args_classifiers_path1 is the path of model and args with the first property prediction model for evaluation. The classifiers_path1 and args_classifiers_path1 is the path of model and args with the second property prediction model for evaluation. The batch_size is the number of generated molecules each iteration. The iterations is the number of iterations.
Generate molecules with desired gap and mu:
python run_EEGSDE_multi_property.py --exp_name eegsde_gap_mu --l1 1.0 --l2 1.0 --generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_gap_mu/generative_model_ema_1960.npy --args_generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_gap_mu/args_1960.pickle --energy_path1 pretrained_models/predict_gap/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path1 pretrained_models/predict_gap/args_2000.pickle --energy_path2 pretrained_models/predict_mu/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path2 pretrained_models/predict_mu/args_2000.pickle --classifiers_path1 pretrained_models/evaluate_gap/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path1 pretrained_models/evaluate_gap/args.pickle --classifiers_path2 pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path2 pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/args.pickle --batch_size 50 --iterations 200
Generate molecules with desired mu and Cv:
python run_EEGSDE_multi_property.py --exp_name eegsde_mu_Cv --l1 1.0 --l2 10.0 --generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_mu_Cv/generative_model_ema_1820.npy --args_generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_mu_Cv/args_1820.pickle --energy_path1 pretrained_models/predict_mu/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path1 pretrained_models/predict_mu/args_2000.pickle --energy_path2 pretrained_models/predict_Cv/model_ema_2000.npy --args_energy_path2 pretrained_models/predict_Cv/args_2000.pickle --classifiers_path1 pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path1 pretrained_models/evaluate_mu/args.pickle --classifiers_path2 pretrained_models/evaluate_Cv/best_checkpoint.npy --args_classifiers_path2 pretrained_models/evaluate_Cv/args.pickle --batch_size 50 --iterations 200
Train the time-dependent fingerprint prediction model (multi-label classifier) used in energy function
python run_train_fingerprint_prediction_energy.py --exp_name predict_fingerprint --model egnn_dynamics --batch_size 128 --lr 1e-4 --nf 192 --n_layers 7 --weight_decay 1e-16 --save_model True --diffusion_steps 1000 --sin_embedding False --n_epochs 3000 --diffusion_noise_schedule polynomial_2 --diffusion_noise_precision 1e-5 --dequantization deterministic --include_charges False --load_charges True --normalize_factors [1,8,1] --dataset qm9
The exp_name is the name of experiments. Take the above command for example, the results will be saved in pretrained_models/predict_fingerprint/.
python run_EEGSDE_fingerprint.py --exp_name eegsde_qm9_fingerprint --l 0.5 --generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_fingerprint/generative_model_ema_1560.npy --args_generators_path pretrained_models/cEDM_fingerprint/args_1560.pickle --energy_path pretrained_models/predict_fingerprint/model_ema_1750.npy --args_energy_path pretrained_models/predict_fingerprint/args_1750.pickle --batch_size 50 --save True
The exp_name is the name of experiments. The l is the scale factor of the energy function. Take the above command for example, the results will be saved in outputs/eegsde_qm9_fingerprint/l_0.5.
The generators_path and args_generators_path is the path of model and args with conditional EDM.
The energy_path and args_energy_path is the path of model and args with fingerprint prediction model used in EEGSDE. The save is whether save the generated molecules.
python run_visualize.py --data_path outputs/eegsde_qm9_fingerprint/l_0.5/samples --save_path outputs/eegsde_qm9_fingerprint/l_0.5/visualize
The data_path is the path of molecules, which are saved as .txt files. The save_path is the path for saving the visualization results.
Step 1: run run_gaussian_convert_gjf.py to convert the .txt file, which save the generated molecules, to .gjf file for Gaussian software
python run_gaussian_convert_gjf.py --samples_root outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0/samples --gif_root outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0/gjf
The samples_root is the path for the generated molecules, which are saved as .txt files. The gif_root is the path for saving the .gjf files.
Step 2: use the Gaussian software to compute the properties of generated molecules based on the .gjf files in Step 1
For example, if you have installed the Gaussian software on the Linux server, you can use the run_gaussian_bash.py to analyze the properties of generated molecules, which will generate .log files.
python run_gaussian_bash.py --samples_root outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0/gjf --save_root outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0/gjf_property
The samples_root is the path for the .gjf files in Step 1. The save_root is the path for saving the outputs of the Gaussian software, which are .log files.
python run_gaussian_evaluation.py --log_root outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0/gjf_property --property mu --label_path outputs/eegsde_mu/l_1.0/context.pt
The log_root is the path for the .log files in Step 2. The property is chosen from alpha/homo/lumo/gap/mu. The label_path is the path for desired properties.
The code for re-training equivariant diffusion model is available at "Train a Conditional EDM" in EDM.
The code for re-training the property classifier for evaluation is available at "Train a property classifier network" in EDM and we also provide these checkpoints in previous Pretrained Checkpoints section.
If you find this repository helpful, please cite as:
@article{bao2022equivariant,
title={Equivariant Energy-Guided SDE for Inverse Molecular Design},
author={Bao, Fan and Zhao, Min and Hao, Zhongkai and Li, Peiyao and Li, Chongxuan and Zhu, Jun},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.15408},
year={2022}
}