This repository has a MQTT rtk caster and mqtt rtk client. The caster is to be deployed on a Kubernetes cluster using the deployment yaml in the same repository. The image is created using the dockerfile.
docker built -t geerd/mqtt-rtk-caster:0.1 .
Were 0.1 is the version and geerd the docker repository you want to upload the image. The image can be uploaded using:
docker push geerd/mqtt-rtk-caster:0.1
docker run -e IP_CASTER="194.145.246.68" \
-e RTCM_PORT="2101" \
-e CASTER_USER="kpn" \
-e CASTER_PASS="kpn" \
-e MOUNTPOINT="HELMOND" \
-e MQTT_USER="userid" \
-e MQTT_PASS="passwd" \
-e MQTT_IP="127.0.0.1" \
-e MQTT_PORT="1883" \
geerd/mqtt-rtk-caster:0.9
When starting up the APU, make sure that you choose the Linux 3.18.0+ kernel from the Advanced options for Ubuntu booting menu. The log in is:
Username: XXX
Password: XXX
To make sure that you are indeed in the right kernel, you can run the command:
uname -r
- Establish ssh connection to the APU with the abovementioned username and password
- Do the next commands:
sudo ssh -L 443:10.38.253.129:443 XXXX@XXXXXXX -p 22022 -N
kubectl port-forward service/rabbitmq 1883:1883
- Open another terminal and run the following command in order to create a set of virtual ports (for the GPSD)
socat -d -d pty,raw,echo=0 pty,raw,echo=0
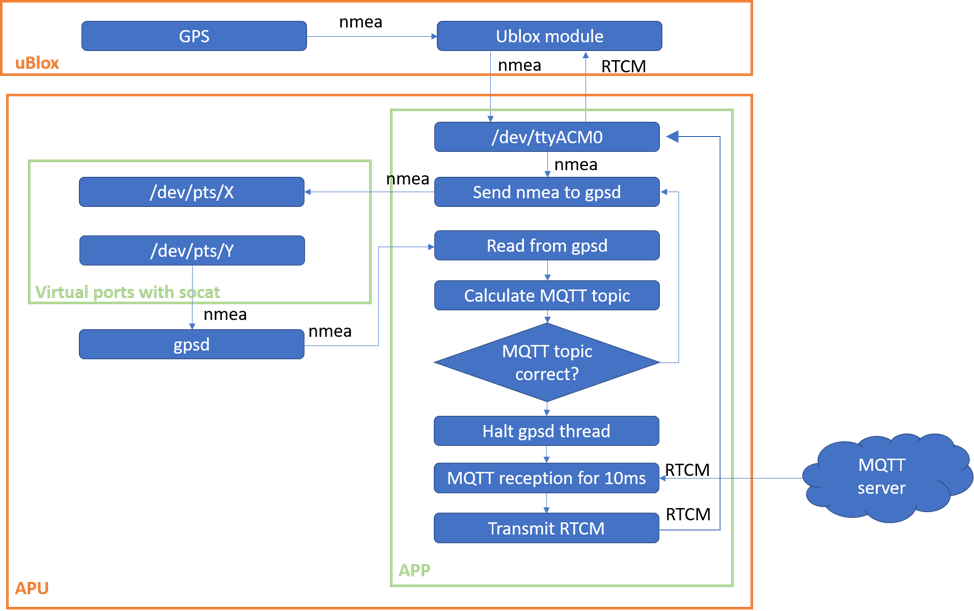
- Run the GPSD with the following command, where Y is the output of the virtual port (see also below the figure at "Description of MQTT Client")
gpsd -N -n -D6 /dev/pts/Y
- Edit in
car.pythe virtual port number based on the output of step 3, double check that USB in attached to /dev/ttyACM0 and run:
sudo python3 ./car.py
Parameters that are subject to change in car.py:
- Port numbers.
- Baud rate of serial ports. NOTE that a change of the baud rate on the USB port, requires a change of the baud rate of the ublox module
- Time duration of reading RTCM messages from MQTT server.
- Python 3.4 or newer
- Python Libraries: gps, serial, paho-mqtt and quadkey
First, a connection with the MQTT server is established and two serial ports are defined; /dev/ttyACM0 (USB) for the communication with the uBlox module and /dev/pts/X for the transmission of the nmea to gpsd. Then, a thread is starting which is constantly reading and writing nmea sentences. Via the USB port, the APP received nmea from uBlox and transmits them to the gpsd via a set of virtual ports. Then, the APP is reading the GPS coordinates through the gpsd. Based on those coordinates, the quadkey is calculated and thus the MQTT topic can be defined. If the MQTT topic is the same as the one used in the previous loop, the APP halts the gpsd thread for 10ms, reads the RTCM message from that topic and transmits it to ublox via the USB port. If the MQTT topic is different (after movement of the ublox), the APP unsubscribes from the old topic, subscribes to the new one and goes back to reading the nmea sentences.