📝 Task: Make a high-quality matching & ranking of applicants' resumes to the specific vacancies.
✅ Result: Up to 94% time savings for HR specialists.
- Roman Prasad, FA
- Solomon Chakaev, HSE
- Nikita Chuikin, HSE
- Vladislav Taskaev, MADI
We were given two JSON-files (you can find them in our repo):
- First containing pairs Resume-[N candidates] with the label
"failed_resumes"/"confirmed_resumes" - Second containing pairs Resume-[N candidates] without labels.
- JSON -> CSV Parsing
- Data cleaning (RegExp & N/A processing)
- Removing non-valuable features by checking their distributions according to the acceptance in train.
Columns, which correlate the most with the target, contain text data:
In vacancies:
'Vacancy Name', 'Keywords', 'Description', 'Comment'
In resumes:
'About', 'Key Skills', 'Position', 'Experience Description', 'Organization', 'Faculty', 'Specialty'.
It should be noted, that the candidate's age and gender are not encountered ethically (there are no visible correlations in age, still, but there is a small inbalance between gender acceptance rates). Hence, we are mostly sticking to NLP practices as we have a task in this sphere. Text preprocessing methods, such as lemmatization, were used but are not implemented in our final approach.
Data preprocessing is fully automated in our Streamlit App (JSON-only files are supported).
Known vacancies can be clustered and a separate classifier can be made for the center of each cluster, whether the vacancy is suitable. At the entrance, this classifier provides similarity between job descriptions and resumes, job titles and resume descriptions, etc. Since there are only 29 vacancies in our data, it makes sense to train a classifier for each of them without additional clustering: you will need it when displaying the solution in production.
When a new vacancy arrives, its similarities with the vacancies we know are considered, and suitable classifiers are found. For each resume, we use trained classifiers of the k nearest neighbors of the new vacancy. The answers are averaged inversely proportional to the distance to these objects. We consider a resume suitable if its score > a given threshold.
At the same time, candidates can be ranked by score in order to give out the most relevant ones first.
...
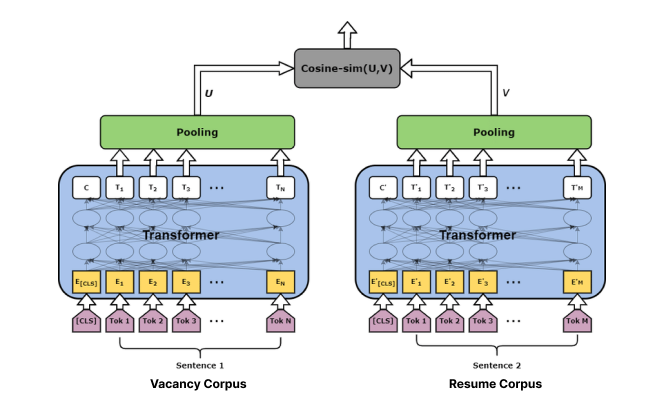
Basic Sentence Transformers illustration for our task.
The mechanism is simple:
Two texts are passed in transformers, being pooled in the end -> Getting vectors of the same shape -> Calculating cosine (or other) similarity between them -> Prediction with threshold -> Ranking.
cointegrated/rubert-tiny2 (Russian BERT) and paraphrase-multilingual-mpnet-base-v2 (Multilingual XLM-roBERTa) were chosen as competitors after a comparison between other available
pre-trained models feasible for our matching.
We can combine all the valuable features, forming the united corpus of text. However, it turned out that splitting text wisely can give us more accuracy in results. It is connected to the finity of small BERT-like transformers attention. Two corpuses for each candidate can be formed:
- One including
'Key Skills', 'Position' - Second containing whole text.
There were no full satisfaction with quality, so we decided to do fine-tuning by generating embeddings for vacancies and resumes using OpenAI's text-to-embedding model as a teacher for our Sentence Transformers.
- Datasets used: HH.ru Vacancies, HH.ru Resumes
- IT-connected jobs & vacancies were extracted from datasets
- Data cleaning (as in Step 1)
- Corpuses were passed to text-to-embedding model by using OpenAI API
- The dataset with vectors was formed by performing Cross-Join to achieve N^2 size (more information for our student model)
- Cosine similarity was calculated
- Fine-tuning process was implemented in PyTorch using Contrastive Loss.
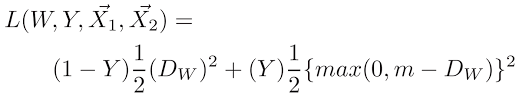
Contrastive Loss Formula.
Metrics comparison here...
You can find each of two model weights in our repo by according name.
Best model...

