See hangman.ipynb
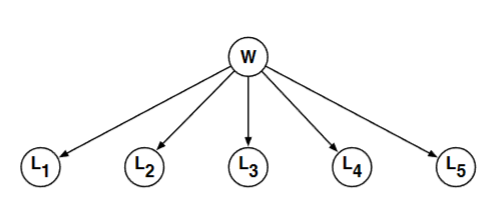
Consider the belief network shown below, where the random variable
where
Now imagine a game in which you are asked to guess the word
Let's work an example. Suppose that after three guesses - the letters D, I, M - you've learned that the letter I does not appear and that the letters D and M appear as follows:
Now consider your next guess: call it
In other words, pick the letter
where in the third line we have exploited the conditional independence (CI) of the letters
And the first term we obtain from Bayes rule:
In the numerator of Bayes rule are two terms; the left term is equal to zero or one (depending on whether the evidence is compatible with the word
where again all the right terms inside the sum are equal to zero or one. Note that the denominator merely sums the empirical frequencies of words that are compatible with the observed evidence.
Now let's consider the general problem. Let
The second key computation is the predictive probability, based on the evidence, that the letter