An experimental implementation of some common Maze generation algorithms modified to support N dimensions. All topics loosely inspired by the Mazes for Programmers book and Think Labyrinth.
The Node and Point classes are the foundation of the dimensionally agnostic mazes, they are not very performant but that is not the purpose of this project. If you try and run anything higher than a 4th-dimensional maze you really have to reduce the length of the dimensions down otherwise the runtime increases exponentially.
Perfect maze generation algorithms don't actually have any concept of the "start" or "end" of a maze and they simply carve out connections between different nodes. This is not ideal as you cannot see any weaving or texture within the maze without inspecting it in some way.
The following approach of forcing a "start" and "end" node into a maze helps highlight the defining characteristics of the different algorithms as each algorithm has its own footprint.
- Generate a maze.
- Collect a list of all "Dead end" nodes that touch the edge of the maze.
- Compute the "all pairs all paths" problem between all of these dead ends.
- Find the pairs with the longest distance and mark them as the "start" and "end".
There are some cool performance modifications to the breadth first search described in step 3, if you are interested the entrypoints are src/graph/solver.h and src/graph/dijkstra.h.
| OpenGL | CLI output | |
|---|---|---|
| 2D | ✅ | ✅ |
| 3D | ✅ | ✅ |
| ND | ❌ | ✅ |
All mazes render with a text CLI output highlighting the start node, the end node, and the path required to navigate between them.
2D and 3D mazes can have their graphs rendered using OpenGL. 3D mazes render like a stacked 2D maze, however it's difficult to see the solution happening "inside" the maze so only the 3D solution is included in this document.
There was a brief attempt to render a 4-dimensional maze by cycling through slices of it in 3 dimensions, however what appeared onscreen didn't make much sense. This is expected unless you slip LSD in your tea.
⬆️ Back to top
See src/graph/maze/mazebinary.h
and click here to read more about this algorithm.
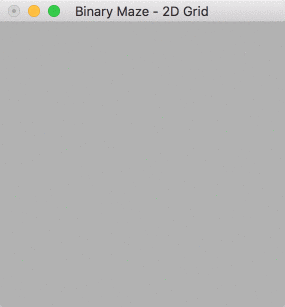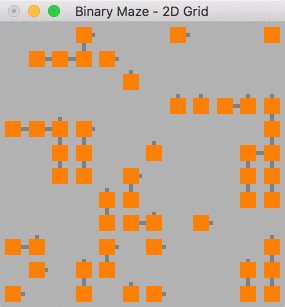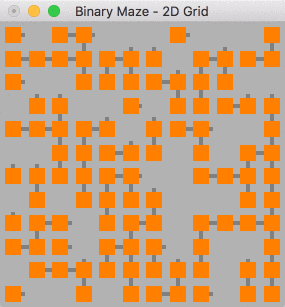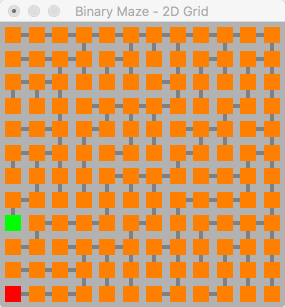
The binary algorithm can be summed up briefly as "For every node, go up or go right". As such this was quite a simple one to translate into higher dimensions, simply stack the extra dimensions in the decision making part of the algorithm.
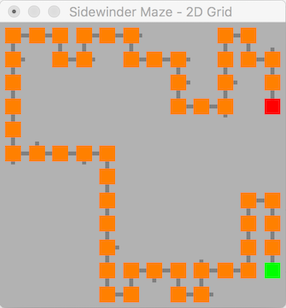
This algorithm produces a maze with long spanning edges over one side of each axis, this is a side effect of the algorithm as described above as when you are at the top most edge, the only choice you can make is "go right". In the 2D graph shown below these spanning edges can be seen along the top and right-hand sides of the maze.
This algorithm forms a solution with very distinctive V shape snaking from one edge of the maze to another passing through these edge paths, this effect is still visible in 3D.
| Read full 2D solution log | Read full 3D solution log |
|---|
Generating a Binary maze of 12 by 12 | Generating a Binary maze of 8 by 8 by 8
Solution took 0.0354854 seconds | Solution took 1.0908 seconds
Solution has a distance of 42 | Solution has a distance of 41
(x:-6)(y:-3) to (x:-6)(y:-6) | (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:-4) to (x:-2)(y:-4)(z:-4)
start at (x:-6)(y:-3) | start at (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:-4)
positive 1 on y (x:-6)(y:-2) | positive 1 on z (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:-3)
positive 1 on x (x:-5)(y:-2) | positive 1 on z (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:-2)
positive 1 on y (x:-5)(y:-1) | positive 1 on x (x:-3)(y:-4)(z:-2)
positive 1 on y (x:-5)(y:0) | positive 1 on z (x:-3)(y:-4)(z:-1)
positive 1 on x (x:-4)(y:0) | positive 1 on y (x:-3)(y:-3)(z:-1)
positive 1 on y (x:-4)(y:1) | positive 1 on x (x:-2)(y:-3)(z:-1)
positive 1 on y (x:-4)(y:2) | positive 1 on x (x:-1)(y:-3)(z:-1)
...Read full log for more... | ...Read full log for more...
A 4D binary solution is shown below.
It is interesting to note that the solution distance is similar for both a 2D, 3D, and a 4D maze.
$ ./binary_nd -d 4
Using seed: 1491155959567
Generating a Binary maze of 6 by 6 by 6 by 6
Ensuring solution
Solution took 15.0695 seconds and has a distance of 40
start at (A:0)(B:0)(C:0)(D:0)
positive 1 on D (A:0)(B:0)(C:0)(D:1)
positive 1 on A (A:1)(B:0)(C:0)(D:1)
positive 1 on A (A:2)(B:0)(C:0)(D:1)
positive 1 on C (A:2)(B:0)(C:1)(D:1)
positive 1 on A (A:3)(B:0)(C:1)(D:1)
positive 1 on C (A:3)(B:0)(C:2)(D:1)
positive 1 on A (A:4)(B:0)(C:2)(D:1)
positive 1 on C (A:4)(B:0)(C:3)(D:1)
positive 1 on D (A:4)(B:0)(C:3)(D:2)
positive 1 on C (A:4)(B:0)(C:4)(D:2)
positive 1 on A (A:5)(B:0)(C:4)(D:2)
...Read full log for more...
⬆️ Back to top
See src/graph/maze/mazesidewinder.h
and click here to read more about this algorithm.
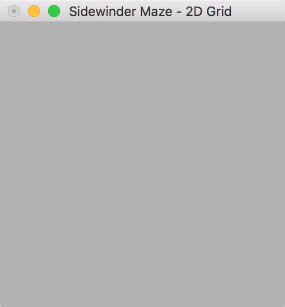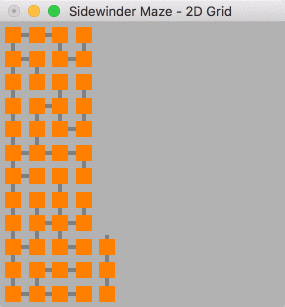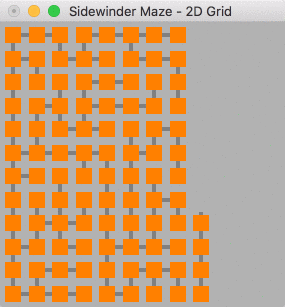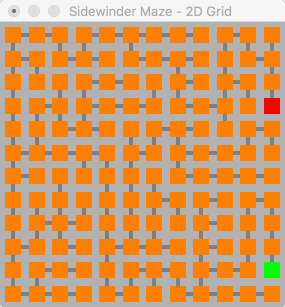
The sidewinder algorithm is similar to the binary algorithm, however it results in only one spanning path along a single axis of the maze. This is referred to as the "backbone" within the source code, it can be seen on the left-hand side of the 2D graph below. The backbone and associated generation logic was very difficult to abstract for higher dimensions, and the solution shown here is very buggy. The code fails far more frequently than it runs, and in order to get any usable output the size of the maze had to be reduced significantly.
Despite the failings of this algorithm when it runs you can still see a similar pattern in the small 3D maze as in the 2D maze, both solutions pass through the backbone on one axis. In the 3D maze the solution intersects with 5 "backbone" nodes, these nodes are the the ones furthest away from the end node.
| Read full 2D solution log | Read full 3D solution log |
|---|
Generating a Sidewinder maze of 12 by 12 | Generating a Sidewinder maze of 5 by 5 by 5
Solution took 0.0258571 seconds | Solution took 0.00741086 seconds
Solution has a distance of 54 | Solution has a distance of 15
(x:5)(y:-5) to (x:5)(y:2) | (x:0)(y:-2)(z:-1) to (x:1)(y:-2)(z:0)
start at (x:5)(y:-5) | start at (x:0)(y:-2)(z:-1)
positive 1 on y (x:5)(y:-4) | positive 1 on y (x:0)(y:-1)(z:-1)
positive 1 on y (x:5)(y:-3) | negative 1 on x (x:-1)(y:-1)(z:-1)
positive 1 on y (x:5)(y:-2) | negative 1 on x (x:-2)(y:-1)(z:-1)
negative 1 on x (x:4)(y:-2) | positive 1 on z (x:-2)(y:-1)(z:0)
negative 1 on y (x:4)(y:-3) | positive 1 on y (x:-2)(y:0)(z:0)
negative 1 on y (x:4)(y:-4) | positive 1 on z (x:-2)(y:0)(z:1)
negative 1 on y (x:4)(y:-5) | positive 1 on y (x:-2)(y:1)(z:1)
...Read full log for more... | ...Read full log for more...
Similar to the comments above, as the extra dimensions accrue the more likely you are to end up with multiple unlinked graphs rather than a spanning tree. The more dimensions, the less likely this is to run. The length of each dimension has been reduced to demonstrate a working maze.
$ ./bin/sidewinder_nd -l 3
Generating a Sidewinder maze of 3 by 3 by 3 by 3
Ensuring solution
Solution took 0.0367572 seconds and has a distance of 16
start at (A:1)(B:0)(C:0)(D:2)
positive 1 on B (A:1)(B:1)(C:0)(D:2)
positive 1 on A (A:2)(B:1)(C:0)(D:2)
positive 1 on B (A:2)(B:2)(C:0)(D:2)
negative 1 on A (A:1)(B:2)(C:0)(D:2)
positive 1 on C (A:1)(B:2)(C:1)(D:2)
negative 1 on A (A:0)(B:2)(C:1)(D:2)
negative 1 on C (A:0)(B:2)(C:0)(D:2)
negative 1 on B (A:0)(B:1)(C:0)(D:2)
negative 1 on B (A:0)(B:0)(C:0)(D:2)
negative 1 on D (A:0)(B:0)(C:0)(D:1)
negative 1 on D (A:0)(B:0)(C:0)(D:0)
positive 1 on C (A:0)(B:0)(C:1)(D:0)
positive 1 on B (A:0)(B:1)(C:1)(D:0)
positive 1 on A (A:1)(B:1)(C:1)(D:0)
finish at (A:1)(B:0)(C:1)(D:0)
⬆️ Back to top
See src/graph/maze/mazealdousbroder.h
and click here to read more about this algorithm.
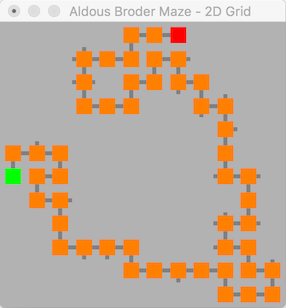
A very simple algorithm invented as a way to demonstrate the generation of uniform spanning trees, it was very trivial to implement and the algorithm required no refactoring or manipulation to scale the number of dimensions. It can be summarised as
Choose a random node, then choose a random neighbour node, if not visited carve a passage
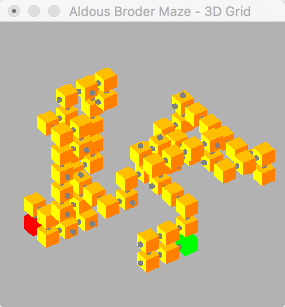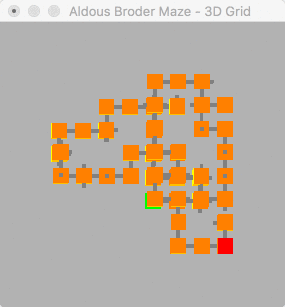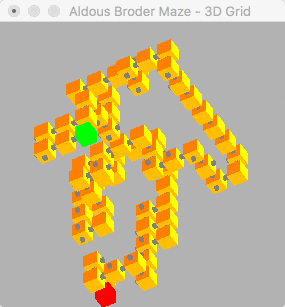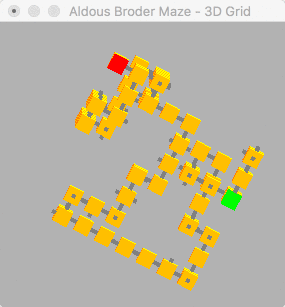
This algorithm generates longer winding passage than the binary algorithm, due to this feature the solution distance increases as extra dimensions are added. This generates a very visible snake like path in both 2D and 3D.
| Read full 2D solution log | Read full 3D solution log |
|---|
Generating a Aldous Broder maze of 12 by 12 | Generating a Aldous Broder maze of 8 by 8 by 8
Solution took 0.0530468 seconds | Solution took 1.91582 seconds
Solution has a distance of 50 | Solution has a distance of 71
(x:-6)(y:-1) to (x:1)(y:5) | (x:0)(y:1)(z:-4) to (x:3)(y:3)(z:3)
start at (x:-6)(y:-1) | start at (x:0)(y:1)(z:-4)
positive 1 on y (x:-6)(y:0) | positive 1 on x (x:1)(y:1)(z:-4)
positive 1 on x (x:-5)(y:0) | positive 1 on x (x:2)(y:1)(z:-4)
positive 1 on x (x:-4)(y:0) | negative 1 on y (x:2)(y:0)(z:-4)
negative 1 on y (x:-4)(y:-1) | negative 1 on x (x:1)(y:0)(z:-4)
negative 1 on x (x:-5)(y:-1) | negative 1 on x (x:0)(y:0)(z:-4)
negative 1 on y (x:-5)(y:-2) | negative 1 on y (x:0)(y:-1)(z:-4)
positive 1 on x (x:-4)(y:-2) | positive 1 on z (x:0)(y:-1)(z:-3)
...Read full log for more... | ...Read full log for more...
The paths generated by this algorithm are deeper than the Binary algorithm, on average an Aldous Broder of 6^4 produces a maze with a solution depth of 141.
$ ./aldous_broder_nd -d 4
Using seed: 1502657336674
Generating a Aldous Broder maze of 6 by 6 by 6 by 6
Ensuring solution
Solution took 44.5247 seconds and has a distance of 126
start at (A:4)(B:0)(C:0)(D:0)
positive 1 on A (A:5)(B:0)(C:0)(D:0)
positive 1 on D (A:5)(B:0)(C:0)(D:1)
positive 1 on D (A:5)(B:0)(C:0)(D:2)
positive 1 on C (A:5)(B:0)(C:1)(D:2)
positive 1 on B (A:5)(B:1)(C:1)(D:2)
positive 1 on D (A:5)(B:1)(C:1)(D:3)
negative 1 on A (A:4)(B:1)(C:1)(D:3)
positive 1 on D (A:4)(B:1)(C:1)(D:4)
positive 1 on B (A:4)(B:2)(C:1)(D:4)
positive 1 on B (A:4)(B:3)(C:1)(D:4)
negative 1 on C (A:4)(B:3)(C:0)(D:4)
...Read full log for more...
⬆️ Back to top
See src/graph/maze/mazewilsons.h
and click here to read more about this algorithm.
Like the Aldous-Broder algorithm Wilsons algorithm also generates uniform spanning trees, it uses Loop erased random walks to achieve this uniform spanning tree in a much more efficient manner.
This algorithm was very complex and messy to implement in a dimensionally agnostic manner, it was particularly difficult to keep track of the random walk. The resulting maze is very similar to ones generated using Aldous-Broder.
| Read full 2D solution log | Read full 3D solution log |
|---|
Generating a Wilsons maze of 12 by 12 | Generating a Wilsons maze of 8 by 8 by 8
Solution took 0.0299658 seconds | Solution took 2.43029 seconds
Solution has a distance of 51 | Solution has a distance of 97
(x:-5)(y:5) to (x:-2)(y:-6) | (x:-4)(y:-2)(z:-2) to (x:-3)(y:2)(z:3)
start at (x:-5)(y:5) | start at (x:-4)(y:-2)(z:-2)
negative 1 on x (x:-6)(y:5) | negative 1 on y (x:-4)(y:-3)(z:-2)
negative 1 on y (x:-6)(y:4) | negative 1 on y (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:-2)
negative 1 on y (x:-6)(y:3) | positive 1 on z (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:-1)
positive 1 on x (x:-5)(y:3) | positive 1 on z (x:-4)(y:-4)(z:0)
negative 1 on y (x:-5)(y:2) | positive 1 on y (x:-4)(y:-3)(z:0)
positive 1 on x (x:-4)(y:2) | positive 1 on y (x:-4)(y:-2)(z:0)
positive 1 on y (x:-4)(y:3) | positive 1 on z (x:-4)(y:-2)(z:1)
...Read full log for more... | ...Read full log for more...
The paths generated by this algorithm are very similar to Aldous Broder, on average a Wilsons of 6^4 produces a maze with a solution depth of 143.
$ ./wilsons_nd -d 4
Using seed: 1502657601278
Generating a Wilsons maze of 6 by 6 by 6 by 6
Ensuring solution
Solution took 36.0249 seconds and has a distance of 116
start at (A:5)(B:3)(C:3)(D:3)
positive 1 on D (A:5)(B:3)(C:3)(D:4)
positive 1 on D (A:5)(B:3)(C:3)(D:5)
negative 1 on C (A:5)(B:3)(C:2)(D:5)
positive 1 on B (A:5)(B:4)(C:2)(D:5)
positive 1 on C (A:5)(B:4)(C:3)(D:5)
positive 1 on B (A:5)(B:5)(C:3)(D:5)
negative 1 on C (A:5)(B:5)(C:2)(D:5)
negative 1 on C (A:5)(B:5)(C:1)(D:5)
negative 1 on C (A:5)(B:5)(C:0)(D:5)
negative 1 on A (A:4)(B:5)(C:0)(D:5)
negative 1 on A (A:3)(B:5)(C:0)(D:5)
...Read full log for more...
⬆️ Back to top
See src/graph/maze/mazerecursivebacktracker.h
and click here to read more about this algorithm.
This is a simple algorithm that required no special modification to work in higher dimensions, it generates very deep mazes with a long solution distance.
The deep solutions generated by this algorithm span most of the available maze, this is visible in both 2D and 3D. As the number of dimensions increases the solution depth increases relative to the number of nodes.
| Read full 2D solution log | Read full 3D solution log |
|---|
Generating a Recursive Backtracker maze of 12x12 | Generating a Recursive Backtracker maze of 8x8x8
Solution took 0.0244822 seconds | Solution took 0.817039 seconds
Solution has a distance of 94 | Solution has a distance of 228
(x:5)(y:-4) to (x:5)(y:5) | (x:0)(y:2)(z:-4) to (x:1)(y:-4)(z:-2)
start at (x:5)(y:-4) | start at (x:0)(y:2)(z:-4)
negative 1 on y (x:5)(y:-5) | negative 1 on y (x:0)(y:1)(z:-4)
negative 1 on y (x:5)(y:-6) | negative 1 on y (x:0)(y:0)(z:-4)
negative 1 on x (x:4)(y:-6) | negative 1 on x (x:-1)(y:0)(z:-4)
negative 1 on x (x:3)(y:-6) | positive 1 on z (x:-1)(y:0)(z:-3)
negative 1 on x (x:2)(y:-6) | positive 1 on x (x:0)(y:0)(z:-3)
positive 1 on y (x:2)(y:-5) | positive 1 on x (x:1)(y:0)(z:-3)
positive 1 on x (x:3)(y:-5) | negative 1 on y (x:1)(y:-1)(z:-3)
...Read full log for more... | ...Read full log for more...
The paths generated by this algorithm are massively deep, on average a recursive backtracker maze of 6^4 will have a solution of 1027.
$ ./recursive_backtracker_nd -d 4
Using seed: 1502658426288
Generating a Recursive Backtracker maze of 6 by 6 by 6 by 6
Ensuring solution
Solution took 30.173 seconds and has a distance of 804
start at (A:4)(B:0)(C:3)(D:4)
positive 1 on D (A:4)(B:0)(C:3)(D:5)
positive 1 on B (A:4)(B:1)(C:3)(D:5)
negative 1 on A (A:3)(B:1)(C:3)(D:5)
negative 1 on D (A:3)(B:1)(C:3)(D:4)
negative 1 on B (A:3)(B:0)(C:3)(D:4)
negative 1 on A (A:2)(B:0)(C:3)(D:4)
positive 1 on D (A:2)(B:0)(C:3)(D:5)
positive 1 on A (A:3)(B:0)(C:3)(D:5)
positive 1 on C (A:3)(B:0)(C:4)(D:5)
positive 1 on B (A:3)(B:1)(C:4)(D:5)
negative 1 on D (A:3)(B:1)(C:4)(D:4)
...Read full log for more...
Thanks for reading.
To anyone who wants to fix the Sidewinder implementation; Crack on and open a PR. If you get a working implementation I'll buy you a beer.
-
OpenGL
sudo apt-get install freeglut3 sudo apt-get install freeglut3-dev