In this project a Neural Network will be used to classify different stages of the Alzheimer's Disease, using MRI Pictures. Someone who wants to clone the project can choose between two datasets, one from Kaggle (https://www.kaggle.com/tourist55/alzheimers-dataset-4-class-of-images), and the well known ADNI Dataset (Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: https://adni.loni.usc.edu/).
A very nice paper on Diagnosis of Alzheimer's is Classification and Visualization of Alzheimer’s Disease using Volumetric Convolutional Neural Network and Transfer Learning (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-54548-6). I will use a similar approach using transfer learning, but skip the step of using a volumetric convolutional neural network because that would need a lot more training data. For now I won't use an Inception network either.
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
import torch
from torch import nn
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision.datasets import ImageFolder
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
from IPython.display import clear_output
import os
from src.model import *
from src.utils import *
from src.train import *
models_path = './models'
dataset_path = "./reduction"
if not os.path.exists(models_path):
os.makedirs(models_path)Perform data augmentation and take a look at the dimensions of the data
#data augmentation and preprocessing
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),transforms.CenterCrop(256),transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.1784,0.1784, 0.1784], std=[0.2025,0.2025, 0.2025]) ])
alz_dataset = ImageFolder(os.path.join(dataset_path, "train"), transform=transform)
train_dataset, val_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(alz_dataset, ( round(len(alz_dataset)*0.9), round(len(alz_dataset)*0.1) ))
second = ImageFolder(os.path.join("Alzheimers-ADNI", "train"), transform=transform)
s_train_dataset, s_val_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(alz_dataset, ( round(len(alz_dataset)*0.9), round(len(alz_dataset)*0.1) ))
#Datasets we are going to be working with
datasets = {'train': train_dataset, 'val': val_dataset}
s_datasets = {'train': s_train_dataset, 'val': s_val_dataset}
test_dataset = ImageFolder(os.path.join(dataset_path, "test"), transform=transform)
#Output some infos about the data and datasets
print("Training data lenght: ", len(datasets["train"]))
print("Test data lenght: ", len(datasets["train"]))
print("Dimensions of an image: ", datasets["train"][0][0].shape)Training data lenght: 576
Test data lenght: 576
Dimensions of an image: torch.Size([3, 256, 256])
plt.imshow(transforms.ToPILImage()(alz_dataset[1][0][0]))<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x17a2be06fd0>
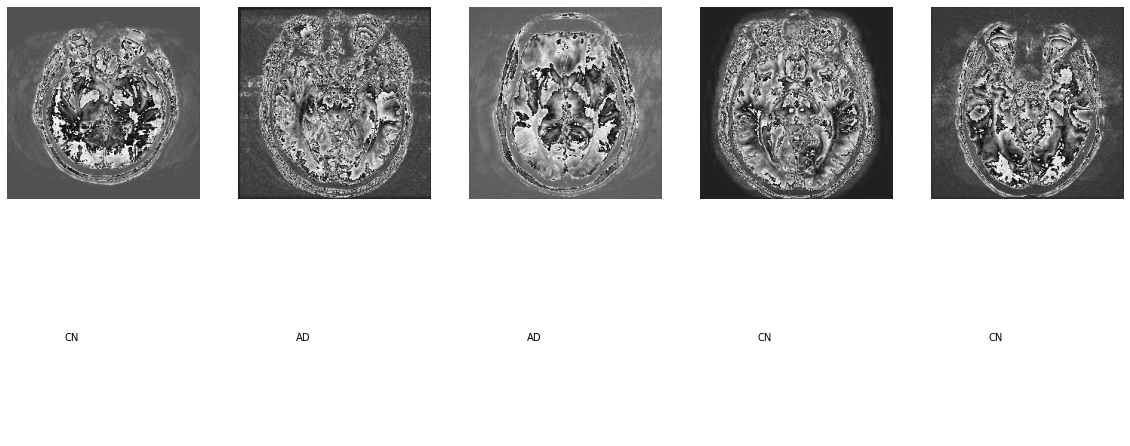
There are 5 classes of patients:
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Early Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Late Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Control Normals
show_examples(datasets["train"])We have to set following things in a configuration file, so at a later point we can use raytune for Hyperparameter search:
config = {"batch_size":4, "lr":1e-3}dataloaders = {x: torch.utils.data.DataLoader(datasets[x], batch_size=config["batch_size"], shuffle=True, num_workers=8, drop_last=True) for x in ['train', 'val']}
s_dataloaders = {x: torch.utils.data.DataLoader(s_datasets[x], batch_size=config["batch_size"], shuffle=True, num_workers=8, drop_last=True) for x in ['train', 'val']}
test_loader =torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, num_workers=8, drop_last=False)The approach is simple: First a Convolutional autoencoder is trained to encode and decode the images, than the encoder part which gained a good performance in extracting the features from MRI's is saved and transferred to be used in combination with 2 linear layers which will do the classification. In the second step only these two last layers will be trained.
autoencoder = ResAE()classifier = AlzheimerClassifier(hparams= {"classes": 2})device = "cpu"
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda:0"
if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
autoencoder = nn.DataParallel(autoencoder)
classifier = nn.DataParallel(classifier)
autoencoder.to(device)
classifier.to(device)
clear_output()At this point only Adam will be used, no fancy stuff
#Autoencoder
optim_a = torch.optim.Adam(autoencoder.parameters(), lr = 1e-3)
#Classifier
optim_b = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr = 1e-3)For the autoencoder the usual MSE Loss will be used, for the classifier (clearly) the Cross Entropy
#Autoencoder
loss_a = nn.MSELoss()
#Classifier
loss_b = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()lambda_a = lambda epoch: 0.9 ** epoch
scheduler_a = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optim_a, lr_lambda=lambda_a)
scheduler_b = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optim_b, lr_lambda=lambda_a)Of course we have to keep track of the whole progress using Tensorboard, and use self-defined callbacks like early stopping and occasional saving if the model performs well.
autoencoder = train_autoencoder(autoencoder, s_dataloaders,loss_a, optim_a, scheduler_a, device, num_epochs=10, early_stop=5)Epoch 9/9
train loss: 0.1493
val loss: 0.1548
100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 10/10 [59:04<00:00, 354.44s/it]
Training complete in 59m 4s
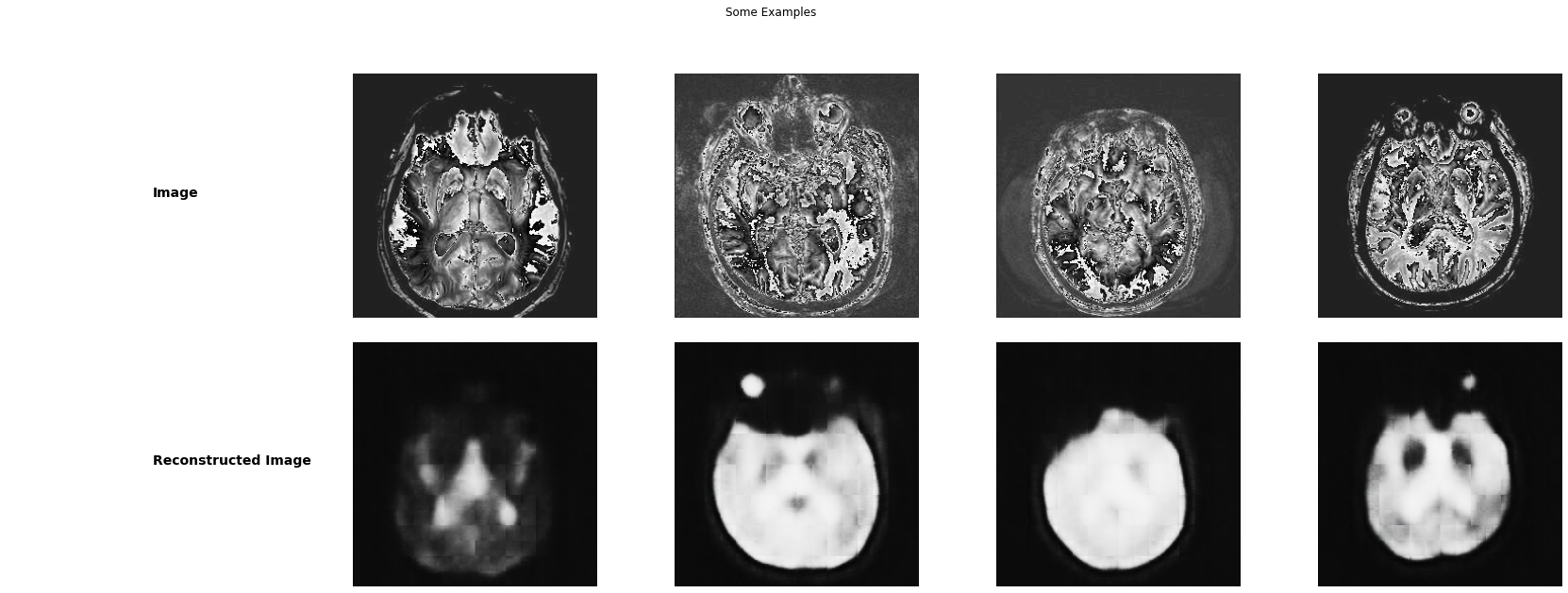
Test the autoencoder
show_ae_results(test_loader, autoencoder)autoencoder.load_state_dict(torch.load(os.path.join(models_path, "autoencoder.pth")))<All keys matched successfully>
torch.save(autoencoder.encoder.state_dict(), os.path.join(models_path, "encoder.pth"))classifier.encoder.load_state_dict(torch.load(os.path.join(models_path, "encoder.pth")))<All keys matched successfully>
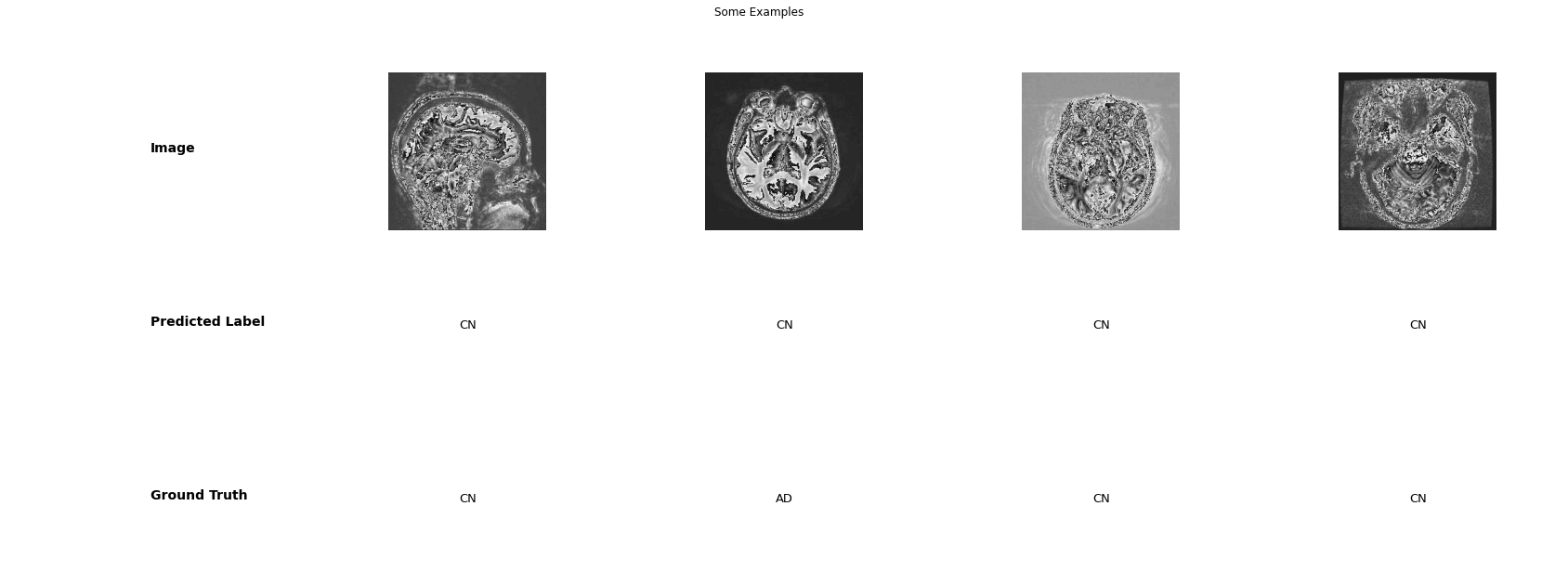
classifier = train_classifier(classifier, dataloaders,loss_b, optim_b, scheduler_b, device, num_epochs=50, early_stop=5)#Testing the model
classifier.to("cpu")
classifier.load_state_dict(torch.load("./models/classifier.pth"))
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True)
test_model(test_loader, classifier)
print("Acurracy: ", test_acurracy(test_loader, classifier)*100, "%")Acurracy: 76.99115044247787 %