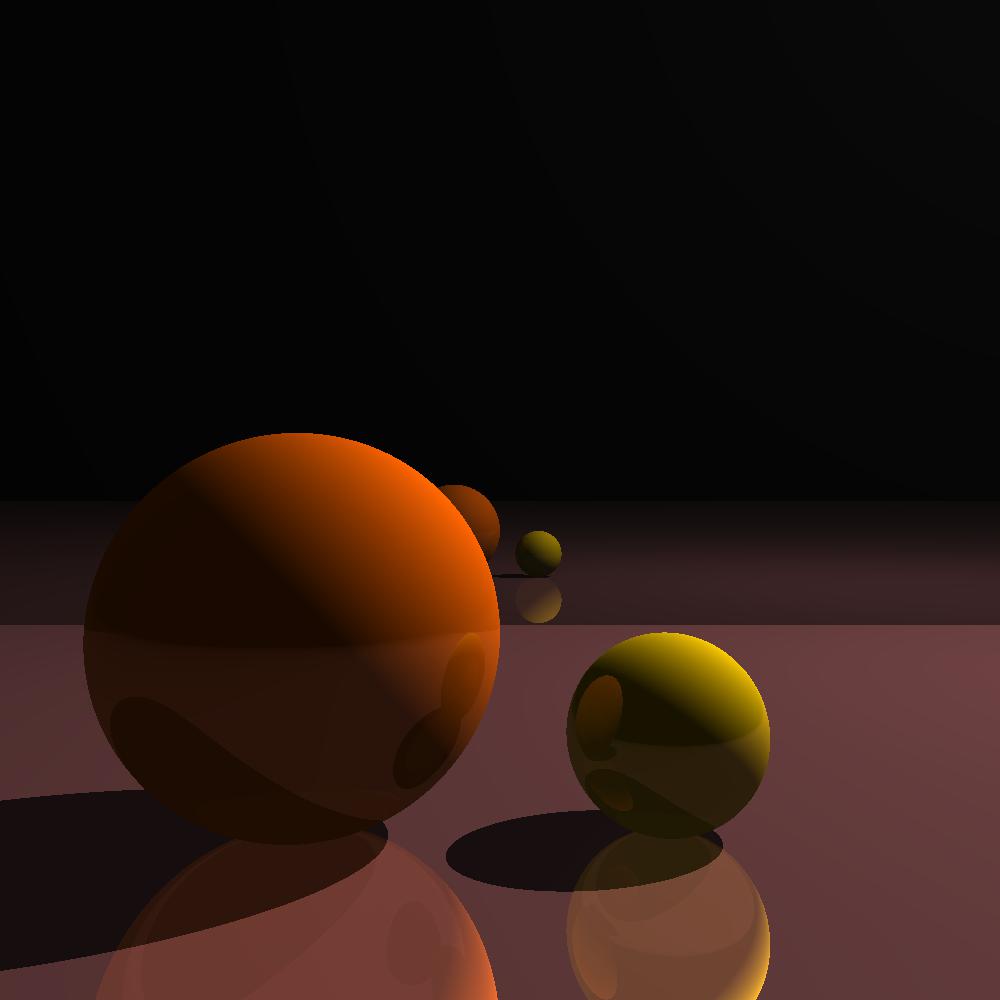
In this work, ray tracing is implemented to render the scenes with sphere and plane objects. The space consists of the spheres and planes that user gave as input. Each object has their own color and diffuse and reflection coefficient that help us mimic the material that it is made of. The eye point is at the origin and the screen extends from (-50, -50, 100) to (50, 50, 100). There is a point light source at (500, 500, 500) and the resolution is 1000x1000 pixels. In this project diffuse shading is made and reflections and shadows are added.
You can change the light and eye position in the Scene class by replacing with your own values.
Run your program like:
>>> python3 ray_racing.py input.txt
Input of the program is read from a text file which is given as an argument to the program. The format of the input file is:
Ambient Color (Light color)
Ambient Coefficient (Can be think of as light color intensity)
N: Number of spheres
Next N x 5 rows:
color of sphere i
position of sphere i
radius of sphere i
diffuse coefficient of sphere i
reflection coefficient of sphere i
N: Number of planes
Next N x 5 rows:
color of plane i
point on plane i
normal of plane i
diffuse coefficient of plane i
reflection coefficient of plane i
The output is a jpg file named “scene.jpg” saved in the same directory with the program. If user would like to display the image using Matplotlib, set “show=True” when calling render method.
More examples can be seen in the examples folder.
I will briefly explain the ray tracing method that is implemented. My program is implemented with Python in an object oriented manner. There is the Scene class where all the tracing algorithm is implemented.
Ray tracing is implemented in the following way: Each pixel in the screen is iterated. A ray is shot in the middle of a pixel. The (x,y,z) coordinates of the middle point is calculated with
x = (i / 10) - 50 + 0.05 y = ((999-j) / 10) - 50 + 0.05 z = 100
i,j are the row and column number respectively. The screen width and height is 100 so i and j values are divided by 10. Each pixel is 0.1x0.1. Thus, in order to find the middle point, 0.05 is added.
Then, a ray is generated where its start point is the eye and the direction is the (x,y,z) coordinates that we found - eye. Then, each object in the scene is iterated and checked if it intersects with the ray. The sphere-ray intersection is calculated using simple geometry. The calculations are made as if the sphere is at the origin for the ease of calculation. Therefore, the starting point of the ray is shifted accordingly. The ray formula,p+t.d, is inserted in the sphere formula, x2+y2+z2+r2= 0, and solved for t.
The resulting equation is d.d t2 + 2 p.d t + p.p -r2=0. The discriminant is calculated from this equation. If it less than 0, that means ray and sphere don’t intersect; otherwise they intersect at point with parameters t0 and t1. If those t values are greater than 1, the objects are visible on the screen. Otherwise, they are behind screen so that we cannot see them.
The plane-ray intersection is simpler than sphere-ray intersection. The dot product of ray and the plane normal is taken. If it is absolute value is greater than epsilon this means that the ray and the plane intersects. Then the t parameter is calculated as follows: t =(pplane- p ).n / d.n where nis plane normal and pplane is a point on the plane. A ray can intersect with multiple objects but only the foremost one must be visible on the screen. Thus, the object with minimum t value is stored.
The illumination at the intersection point is calculated in a recursive manner. For shadows, a ray whose starting point is the intersection point and the direction is (light - starting point) is created. Then, all the objects iterated again and checked if any of them intersects with the ray. In this case, only the objects with 1 > t > 0.0001 can block the light because it means that ray and object intersects at a point between the sphere and the light. Instead of 0, the threshold is set to 0.0001 to avoid from the errors occuring because of the objects’ intersection with themselves. If anything blocks that point the diffuse color is not put, thus multiplied by 0. Then ambient light is calculated by multiplying the ambient color with ambient coefficient and color of surface and then dividing it to 256. It is added to the total color anyway because the shadows are never pure black. Then, the diffuse shading is calculated. For this purpose, first the dot product of light ray and surface normal at that point is calculated. This term defines how dark/light that point will appear. if this is less than 0 that means that point on the surface is not illuminated by light. So we take the maximum of this value with 0 and multiply it with the surface’s diffuse coefficient and color. To calculate reflection, first it is check if the max reflection depth is reach. If it isn’t, the reflected rays direction is calculated by taking the dot product of surface normal and initial ray direction. The start point of this reflected ray is the intersection point but it is shifted a little to prevent errors. Then we check if this ray intersects with any object. If it does, the same function is called again with new parameters which are the intersected surface, reflected ray and depth + 1. Then, all these values (ambient color, diffuse color and reflection color) are summed up to get the final color of the pixel and it is returned.
The generated image is saved as a jpg file using Python’s PIL library.