Bank Vaults is a thick, tricky, shifty right with a fast and intense tube for experienced surfers only, located on Mentawai. Think heavy steel doors, secret unlocking combinations and burly guards with smack-down attitude. Watch out for clean-up sets.
Bank Vaults is a wrapper for the official Vault client with automatic token renewal, built in Kubernetes support, dynamic database credential management, multiple unseal options, automatic re/configuration and more.
Bank Vaults is a core building block of the Pipeline PaaS. Some of the usage patterns are highlighted through these blog posts:
Securing Kubernetes deployments with Vault:
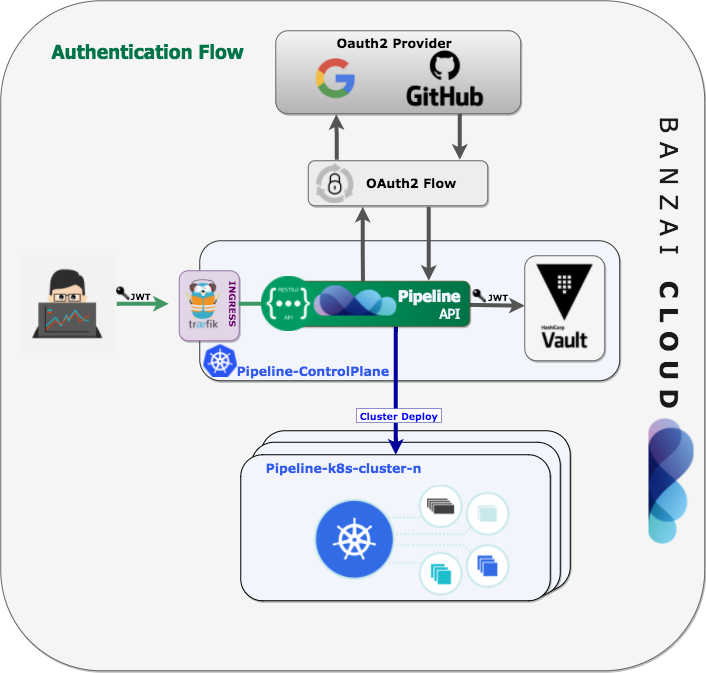
- Authentication and authorization of Pipeline users with OAuth2 and Vault
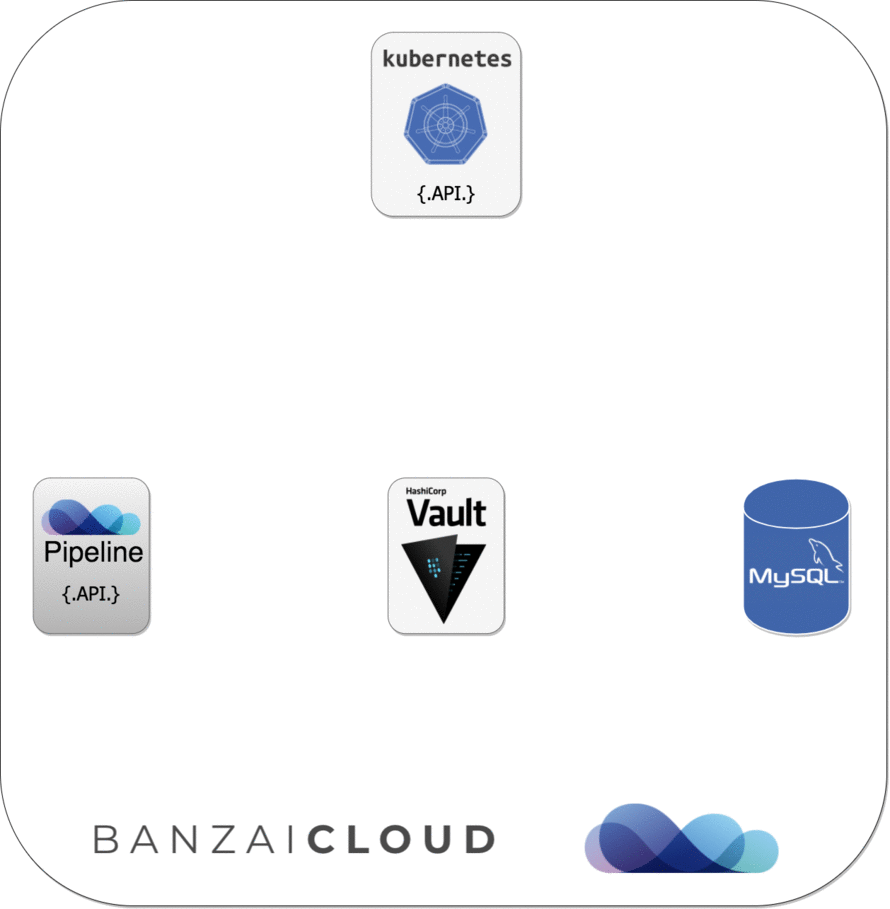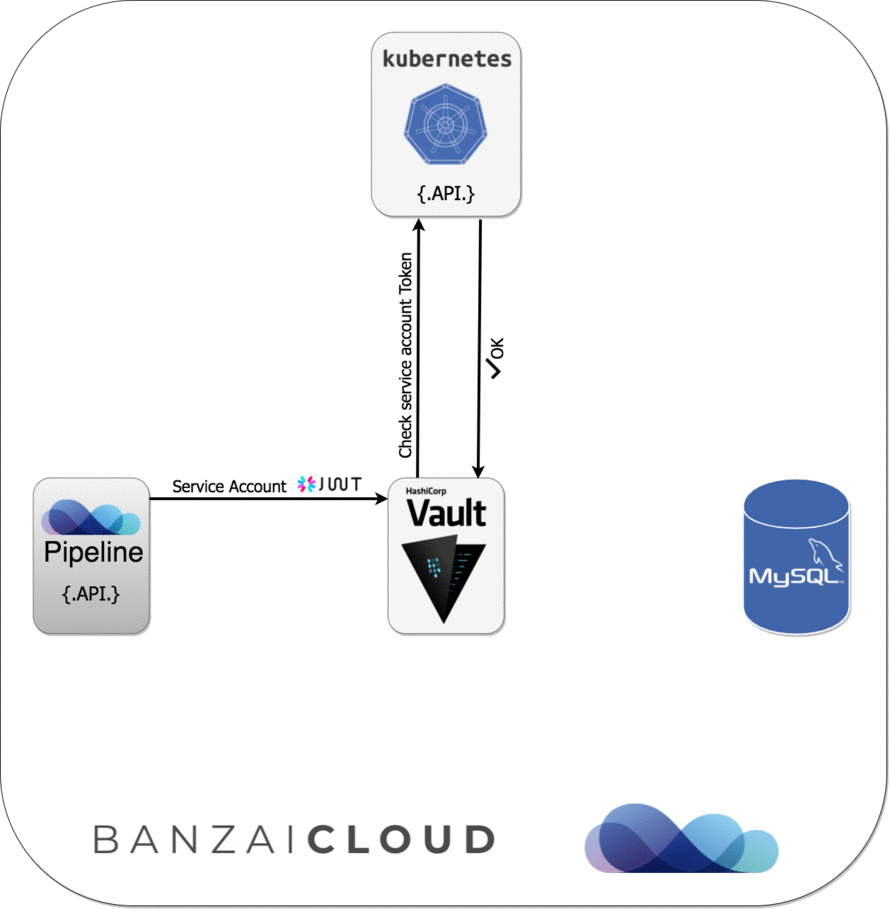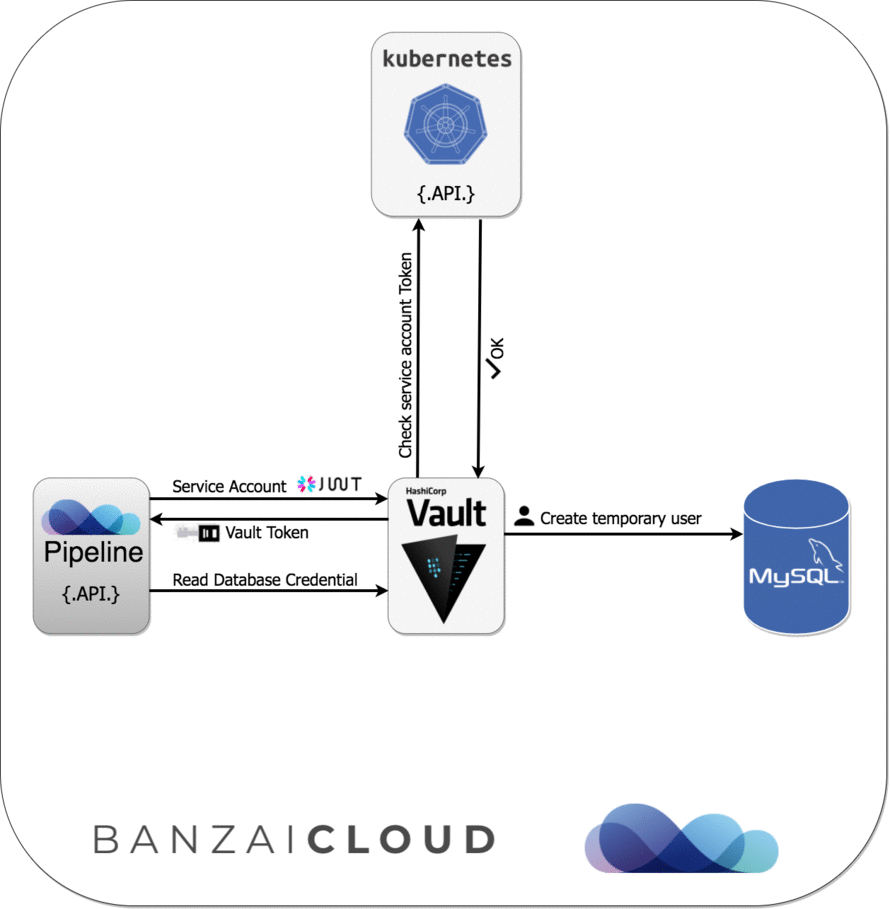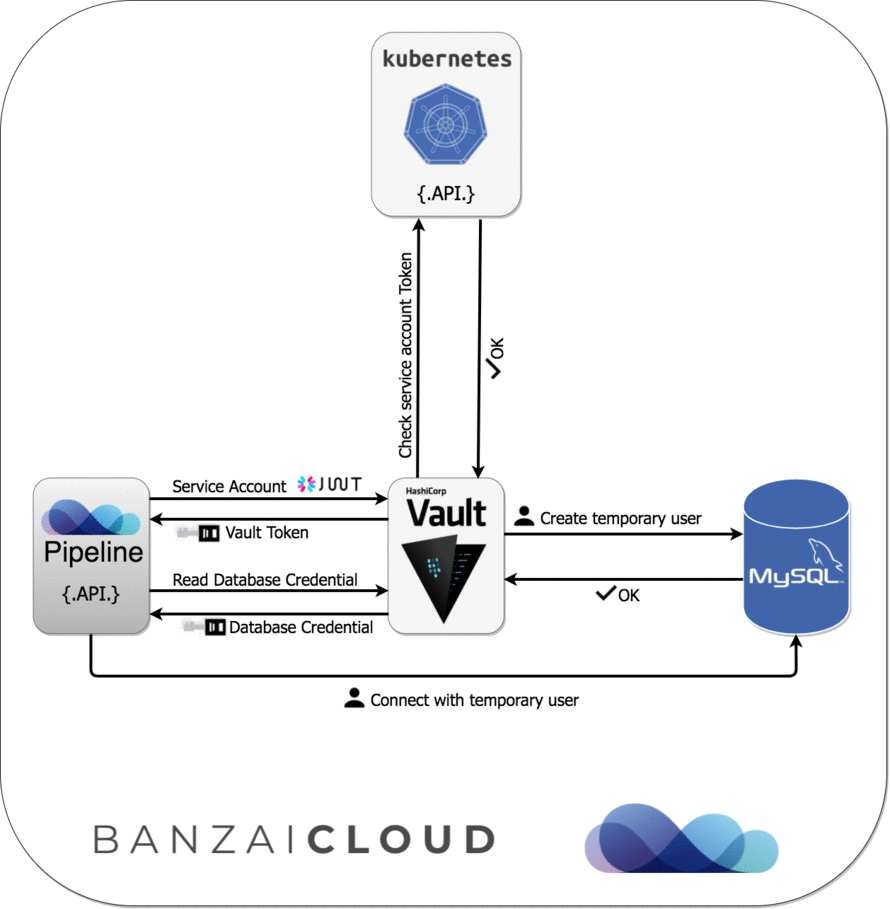
- Dynamic credentials with Vault using Kubernetes Service Accounts
- Dynamic SSH with Vault and Pipeline
- Secure Kubernetes Deployments with Vault and Pipeline
- Vault Operator
- Vault unseal flow with KMS
We use Vault across our large Kubernetes deployments and all the projects were reinventing the wheel. We have externalized all the codebase into this project and removed all the Pipeline and Hollowtrees dependencies thus this project can be used independently as a CLI tool to manage Vault, a Golang library to build upon (OAuth2 tokens, K8s auth, Vault operator, dynamic secrets, cloud credential storage, etc), Helm chart for a HA cluster, operator and a collection of scripts to support some advanced features (dynamic SSH, etc).
We take bank-vaults' security and our users' trust very seriously. If you believe you have found a security issue in bank-vaults, please contact us at [email protected].
- The CLI tool
- The Go library
- Helm Chart
- Operator
- Examples
- Getting and Installing
- Contributing
- Credits
The bank-vaults CLI tool is to help automate the setup and management of HashiCorp Vault.
Features:
- Initializes Vault and stores the root token and unseal keys in one of the followings:
- AWS KMS keyring (backed by S3)
- Azure Key Vault
- Google Cloud KMS keyring (backed by GCS)
- Alibaba Cloud KMS (backed by OSS)
- Kubernetes Secrets (should be used only for development purposes)
- Dev Mode (useful for
vault server -devdev mode Vault servers)
- Automatically unseals Vault with these keys
- Continuously configures Vault with a YAML/JSON based external configuration (besides the standard Vault configuration)
- If the configuration is updated Vault will be reconfigured
- It supports configuring Vault secret engines, auth methods, and policies
# Allows creating policies in Vault which can be used later on in roles
# for the Kubernetes based authentication.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/concepts/policies.html for more information.
policies:
- name: allow_secrets
rules: path "secret/*" {
capabilities = ["create", "read", "update", "delete", "list"]
}
# Allows configuring Auth Methods in Vault (Kubernetes and GitHub is supported now).
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/auth/index.html for more information.
auth:
# Allows creating roles in Vault which can be used later on for the Kubernetes based
# authentication.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/auth/kubernetes.html#creating-a-role for
# more information.
- type: kubernetes
roles:
# Allow every pod in the default namespace to use the secret kv store
- name: default
bound_service_account_names: default
bound_service_account_namespaces: default
policies: allow_secrets
ttl: 1h
# Allows creating team mappings in Vault which can be used later on for the GitHub
# based authentication.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/auth/github.html#configuration for
# more information.
- type: github
config:
organization: banzaicloud
map:
# Map the banzaicloud dev team on GitHub to the dev policy in Vault
teams:
dev: dev
# Map myself to the root policy in Vault
users:
bonifaido: allow_secrets
# Allows creating roles in Vault which can be used later on for AWS
# IAM based authentication.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/auth/aws.html for
# more information.
- type: aws
config:
access_key: VKIAJBRHKH6EVTTNXDHA
secret_key: vCtSM8ZUEQ3mOFVlYPBQkf2sO6F/W7a5TVzrl3Oj
iam_server_id_header_value: vault-dev.example.com # consider setting this to the Vault server's DNS name
roles:
# Add roles for AWS instances or principals
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/api/auth/aws/index.html#create-role
- name: dev-role-iam
bound_iam_principal_arn: arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/dev-vault
policies: allow_secrets
period: 1h
# Allows creating group mappings in Vault which can be used later on for the LDAP
# based authentication.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/auth/ldap.html#configuration for
# more information.
# Start an LDAP testing server: docker run -it --rm -p 389:389 -e LDAP_TLS=false --name ldap osixia/openldap
# Start an LDAP admin server: docker run -it --rm -p 6443:443 --link ldap:ldap -e PHPLDAPADMIN_LDAP_HOSTS=ldap -e PHPLDAPADMIN_LDAP_CLIENT_TLS=false osixia/phpldapadmin
- type: ldap
description: LDAP directory auth.
config:
url: ldap:https://localhost
binddn: "cn=admin,dc=example,dc=org"
bindpass: "admin"
userattr: uid
userdn: "ou=users,dc=example,dc=org"
groupdn: "ou=groups,dc=example,dc=org"
groups:
# Map the banzaicloud dev team on GitHub to the dev policy in Vault
developers:
policies: allow_secrets
# Map myself to the allow_secrets policy in Vault
users:
bonifaido:
groups: developers
policies: allow_secrets
# Allows configuring Secrets Engines in Vault (KV, Database and SSH is tested,
# but the config is free form so probably more is supported).
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/secrets/index.html for more information.
secrets:
# This plugin stores database credentials dynamically based on configured roles for
# the MySQL database.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/secrets/databases/mysql-maria.html for
# more information.
- path: secret
type: kv
description: General secrets.
options:
version: 1
# This plugin stores arbitrary secrets within the configured physical storage for Vault.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/secrets/kv/index.html for
# more information.
- type: database
description: MySQL Database secret engine.
configuration:
config:
- name: my-mysql
plugin_name: "mysql-database-plugin"
connection_url: "{{username}}:{{password}}@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/"
allowed_roles: [pipeline]
username: "${env "ROOT_USERNAME"}" # Example how to read environment variables
password: "${env "ROOT_PASSWORD"}"
roles:
- name: pipeline
db_name: my-mysql
creation_statements: "GRANT ALL ON *.* TO '{{name}}'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '{{password}}';"
default_ttl: "10m"
max_ttl: "24h"
# Create a named Vault role for signing SSH client keys.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/secrets/ssh/signed-ssh-certificates.html#client-key-signing for
# more information.
- type: ssh
path: ssh-client-signer
description: SSH Client Key Signing.
configuration:
config:
- name: ca
generate_signing_key: "true"
roles:
- name: my-role
allow_user_certificates: "true"
allowed_users: "*"
key_type: "ca"
default_user: "ubuntu"
ttl: "24h"
# The RabbitMQ secrets engine generates user credentials dynamically based on configured permissions and virtual hosts.
# See https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/secrets/rabbitmq/index.html
- type: rabbitmq
description: local-rabbit
configuration:
config:
- name: connection
connection_uri: "https://localhost:15672"
username: guest
password: guest
roles:
- name: prod_role
vhosts: '{"/web":{"write": "production_.*", "read": "production_.*"}}'This repository contains several Go packages for interacting with Vault:
-
authA GitHub OAuth2 based authentication system as a Gin Middleware, stores JWT bearer tokens in Vault.
-
vaultA wrapper for the official Vault client with automatic token renewal, and Kubernetes support.
-
databaseA helper for creating database source strings (MySQL/PostgreSQL) with database credentials dynamically based on configured Vault roles (instead of
username:password). -
pkg/tlsA simple package to generate self-signed TLS certificates. Useful for bootstrapping situations, when you can't use Vault's PKI secret engine.
We have a fully fledged, production ready Helm chart for Vault using bank-vaults. With the help of this chart you can run a HA Vault instance with automatic initialization, unsealing and external configuration which used to be a tedious manual operation. This chart can be used easily for development purposes as well.
We have a Vault operator built on bank-vaults features as:
- external, API based configuration (secret engines, auth methods, policies) to automatically re/configure a Vault cluster
- automatic unsealing (AWS, GCE, Azure, Alibaba, Kubernetes Secrets (for dev purposes), Oracle)
- TLS support
The operator flow is the following:
The source code can be found inside the operator directory.
kubectl apply -f operator/deploy/rbac.yaml
kubectl apply -f operator/deploy/operator.yamlThis will create a Kubernetes CustomResourceDefinition called Vault.
A documented example of this CRD can be found in operator/deploy/cr.yaml.
Some examples are in cmd/examples/main.go
- Vault client example
- Dynamic secrets for MySQL example with Gorm
- JWTAuth tokens example with a Gin middleware
go get github.com/banzaicloud/bank-vaults/cmd/bank-vaultsThe bank-vaults CLI command needs certain cloud permissions to function properly (init, unseal, configuration).
The Service Account in which the Pod is running has to have the following IAM Roles:
- Cloud KMS Admin
- Cloud KMS CryptoKey Encrypter/Decrypter
- Storage Admin
A CLI example how to run bank-vaults based Vault configuration on Google Cloud:
bank-vaults configure --google-cloud-kms-key-ring vault --google-cloud-kms-crypto-key bank-vaults --google-cloud-kms-location global --google-cloud-storage-bucket vault-ha --google-cloud-kms-project continual-flow-276578The Access Policy in which the Pod is running has to have the following IAM Roles:
- Key Vault All Key permissions
- Key Vault All Secret permissions
The Instance profile in which the Pod is running has to have the following IAM Policies:
- KMS:
kms:Encrypt, kms:Decrypt - S3:
s3:GetObject, s3:PutObject
An example command how to init & unseal Vault on AWS:
bank-vaults unseal --init --mode aws-kms-s3 --aws-kms-key-id 9f054126-2a98-470c-9f10-9b3b0cad94a1 --aws-s3-region eu-west-1 --aws-kms-region eu-west-1 --aws-s3-bucket bank-vaultsA CLI example how to run bank-vaults based Vault unsealing on Alibaba Cloud:
bank-vaults unseal --mode alibaba-kms-oss --alibaba-access-key-id ${ALIBABA_ACCESS_KEY_ID} --alibaba-access-key-secret ${ALIBABA_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET} --alibaba-kms-region eu-central-1 --alibaba-kms-key-id ${ALIBABA_KMS_KEY_UUID} --alibaba-oss-endpoint oss-eu-central-1.aliyuncs.com --alibaba-oss-bucket bank-vaultsThe Service Account in which the Pod is running has to have the following Roles rules:
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "update"]If you find this project useful here's how you can help:
- Send a pull request with your new features and bug fixes
- Help new users with issues they may encounter
- Support the development of this project and star this repo!
Kudos to HashiCorp for open sourcing Vault and making secret management easier and more secure.