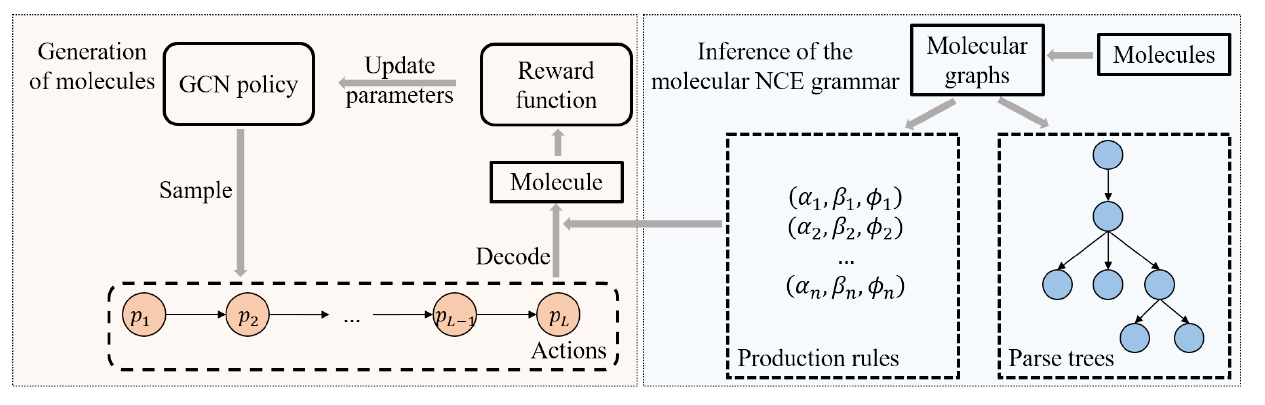
A major challenge in the pharmaceutical industry is to design novel molecules with specific desired properties, especially when the property evaluation is costly. Here, we propose MNCE-RL, a graph convolutional policy network for molecular optimization with molecular neighborhood-controlled embedding grammars through reinforcement learning. We extend the original neighborhood-controlled embedding grammars to make them applicable to molecular graph generation and design an efficient algorithm to infer grammatical production rules from given molecules. The use of grammars guarantees the validity of the generated molecular structures. By transforming molecular graphs to parse trees with the inferred grammars, the molecular structure generation task is modeled as a Markov decision process where a policy gradient strategy is utilized.
Anaconda is recommended to run the project.
conda create -n MNCERL python=3.6
source activate MNCERL
Install rdkit and Cython:
conda install -c conda-forge rdkit
conda install Cython
Install related packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
cd MyLib
python setup.py install
Prepare data:
cd Data
ls *.tar.gz|while read line
do
tar -xzvf ${line}
done
You can run training and evaluations by:
python main.py -c PATH_TO_CONFIG
For example:
python main.py -c tasks.Optimize_logp_limited.config_seed1
Please refer to config_example.py for the format of the config file. In the "tasks" directory, we have provided the pretrained model, and the config.py and results for all the tasks presented in our paper.
To train and evaluations with custom data, the molecules in SMILES format can be parsed by:
python mkdata.py -c PATH_TO_CONFIG
For example:
python mkdata.py -c tasks.Makedata_zinc.config
Please refer to tasks/Makedata_zinc/config.py for the format of the config file. Then the parsed custom data can be used to train models by specifying the "data_path" in the training config file.
Xu, C., Liu, Q., Huang, M., & Jiang, T. (2020). Reinforced Molecular Optimization with Neighborhood-Controlled Grammars. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33.