An implementation of a quantum computer simulator in Python to simulate the running of Grover's Algorithm.
To get started with the repository, you need to do the following:
Clone the repository to your system:
$ git clone https://github.com/Tiernan8r/quantum_computing_projectMove into the cloned repository:
$ cd quantum_computing_projectSetup a python virtual environment:
$ python -m virtualenv venvActivate the new virtualenvironment
$ source venv/bin/activateDownload the PyPi program requirements:
$ pip install -r requirements.txtVerify that all the tests are working, by running:
$ pip install -r test-requirements.txt$ toxThere are three test actions configured for the repository, tests/pep8/
mypy.
The individual actions can be run using
$ tox -e [action]where [action] is one of tests/pep8/mypy
Once you have the repository set up on your system, you can run the code using one of the following:
The Help message for the CLI gives an overview of the program usage
$ ./qcp/main.py -h
USAGE:
./qcp/main.py [FLAGS] nqbits
FLAGS:
-a/--algorithm The quantum algorithm to simulate, can be one of:
g = Grover's Algorithm
pe = Phase Estimation
s = Toy Sudoku solver
Defaults to 'g' if unset
-h/--help Display this prompt
-g/--gui Display the GUI.
The CLI options vary by choice of algorithm:
GROVERS:
USAGE:
./qcp/main.py --algorithm g [FLAGS] nqbits
ARGS:
nqbits The number of qbit states to simulate, must be >= 2.
FLAGS:
-t/--target The target state, defaults to 0
PHASE ESTIMATION:
USAGE:
./qcp/main.py --algorithm pe [FLAGS] nqbits
ARGS:
nqbits The number of qbit states to simulate, must be >= 2.
FLAGS:
-p/--phase The phase to use for the Phase Shift Gate (if using).
defaults to 0.25.
-u/--unitary The choice of unitary gate to simulate with, can be
one of the following:
* H = Hadamard Gate
* P = Phase Shift Gate (requires the -p flag)
Defaults to 'H' if unset
SUDOKU:
USAGE:
./qcp/main.py --algorithm s
ARGS:
None
FLAGS:
NoneAs you can see, the program is capable of simulating three different quantum algorithms and use cases.
nqbits: is a required parameter, and controls the number of qbibts to simulate in the simulator
Note: The quantum simulator simulates matrices of size
2^nqbits, so be aware that The simulation takes exponentially longer for each extra qbit simulated.
-t/--target: is the target state to search for, must be bounded within 1 < t < 2^nqbits
nqbits: is a required parameter, and controls the number of qbibts to simulate in the simulator
Note: The quantum simulator simulates matrices of size
2^nqbits, so be aware that The simulation takes exponentially longer for each extra qbit simulated.
-u/--unitary is the unitary matrix to use in the phase estimation algorithm, currently there are two choices:
* H = Hadamard Gate
* P = Phase Shift Gate
Note: When the Phase Shift Gate is chosen, the phase to shift by can be overwritten using the
-p/--phaseflag.
A sample application of Grover's Algorithm, where we solve the toy problem of a 2x2 sudoku. Takes no input
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) is provided with the program to make interaction with it easier.
The GUI can be initialised with the following command:
$ ./qcp/main.py -gThis will bring up the GUI, defaulting to Grover's Algorithm.
At the top of the GUI is a drop down list, with the options for the algorithms to simulate, choosing each algorithm in sequence will update the GUI to reflect the input parameters of that algorithm
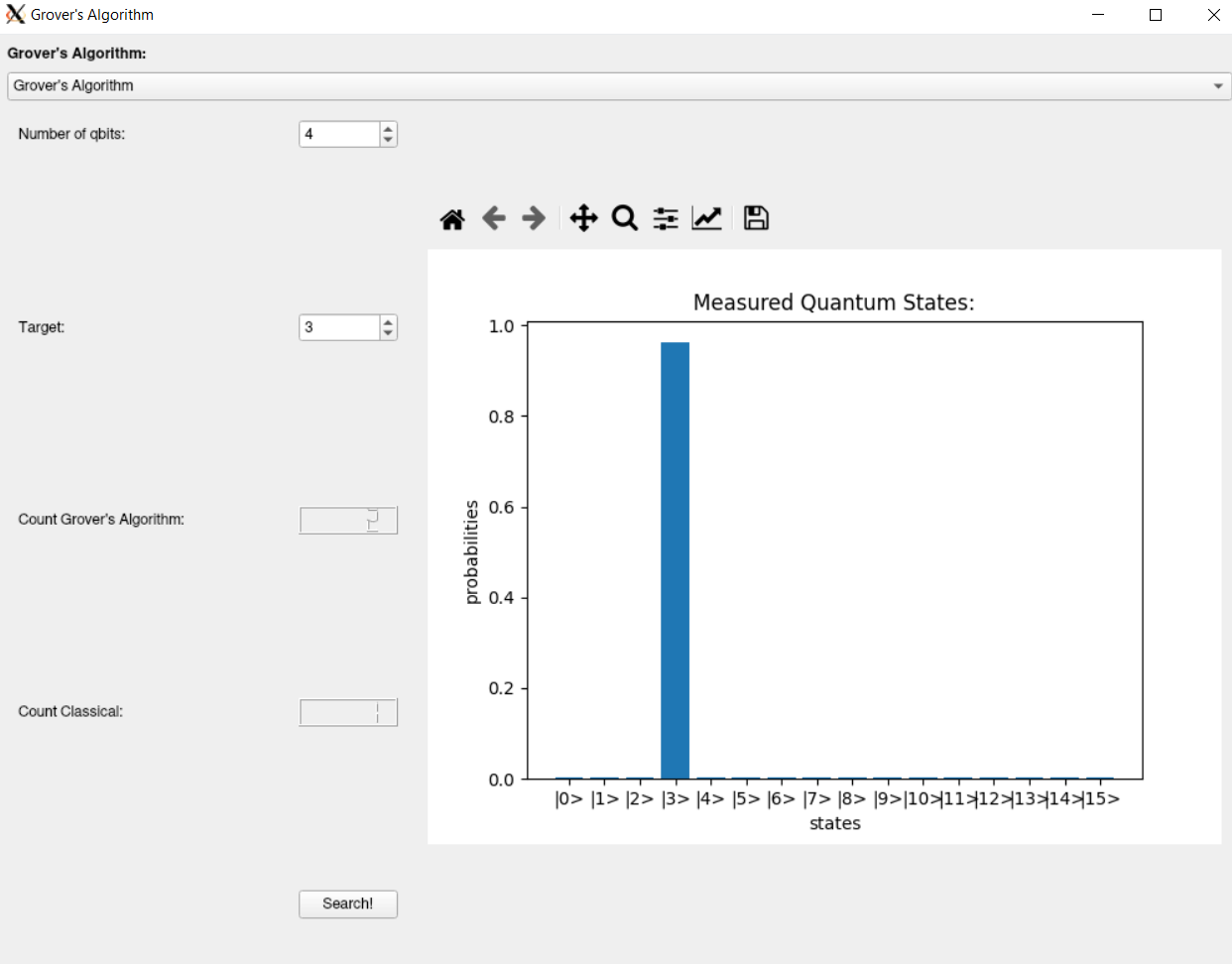
Grover's Algorithm has two input fields.
The first field sets the number of qbits to simulate.
The second is the target state, and is bounded within 0 < t < 2**nqbits
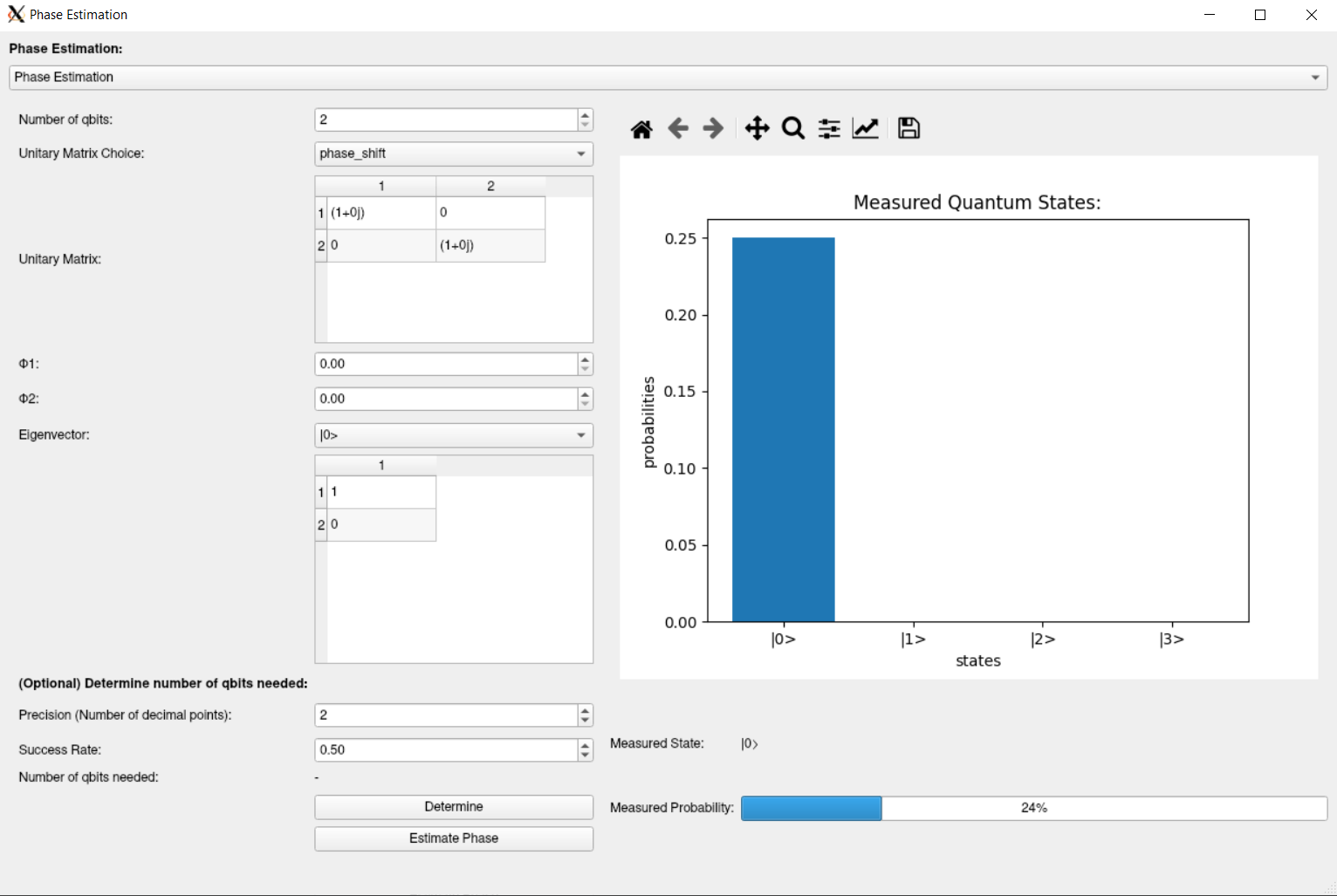
The phase estimation is the most complicated GUI element.
As with Grover's Algorithm, the first input is the number of qbits to simulate.
The phase estimation then requires input of two matrices, a unitary matrix, and an eigenvector.
To help with this input, the GUI has helper elements to select some defaults.
For the Unitary Matrix, a dropdown element is present that allows the user to select two pre-defined
matrices, the HADAMARD gate, or the PHASE_SHIFT gate.
When the drop down list is changed, the table showing the matrix is updated with it's values.
For the PHASE SHIFT gate, two new GUI elements also appear, that allows the user to set the
phases in the two diagonal elements:
Once the user has selected a unitary matrix, they can then follow similar steps to select an eigenvector:
The dropdown list for the eigenvectors changes per choice of unitary matrix:
For the HADAMARD gate, the two choices are the bases |+> & |->.
For the PHASE SHIFT gate, the two choices are the bases |0> & |1>.
Of course, the user can always input custom matrices manually, and the GUI will perform checks on the validity of the matrices before beginning the simulation,
Any integer/float/complex is an acceptable parameter.
If there are any issues with the inputs of the two matrices once the simulation is set to start, the simulation will quit and a useful error message will appear beside the matrix at fault with a message pin-pointing the entry at fault.
At the bottom of the UI element, there are two extra fields: Precision & Success Rate, these determine the number of decimal points we want to estimate the phase to (the "precision"), and the acceptable rate that the results could be inaccurate ("success rate")
If the user wishes to get a more acceptable answer, they can input their parameters, and click the determine button, in which case the UI will calculate the number of qbits to use to get this accuracy, and auto-set the number of qbits field.
The sudoku has no explicit input, which segues nicely to:
Once ready to begin running the quantum algorithm simulation, click the button at the bottom of the GUI labeled "search" or "start".
This will begin the simulation of the chosen algorithm in the background.
While the simulation is running, a visual indicator will appear to show that the simulation is still in progress
Once the search is completed, a plot of the probability of the quantum state being in the target state will be shown on the right.
Grover's Algorithm
As shown in the figure above, the simulation results for Grover's Algorithm also outputs the number of iterations that the quantum simulator took to find the result, and compares it to the equivalent for a classical algorithm.
Phase Estimation
When the phase estimation result is computed, the probabilities are shown in the graph on the right for each state.
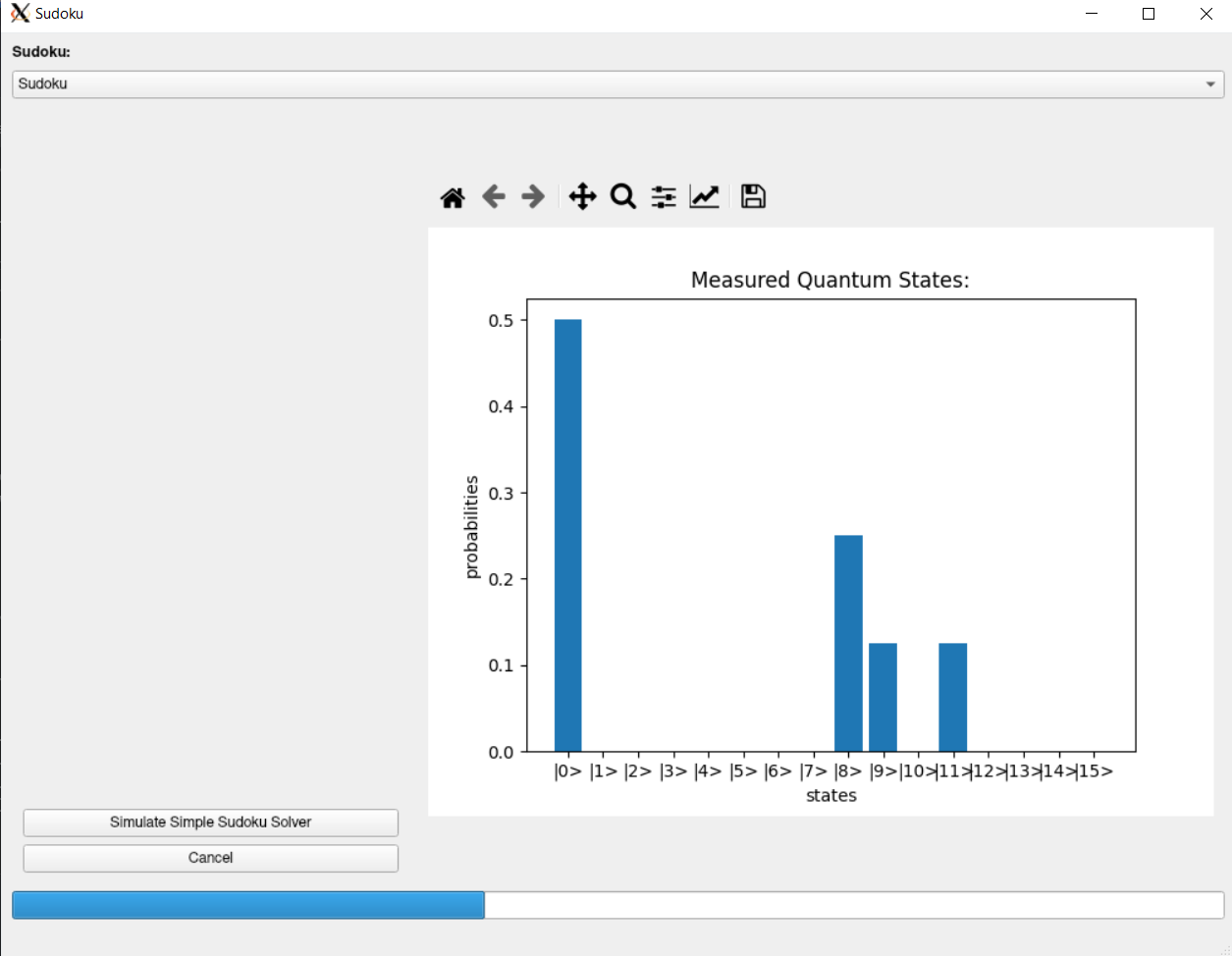
Sudoku
Sudoku also outputs a probability distribution in the graph on the right.
For the simple 2x2 sudoku problem, a sample layout is also shown in a table, with the probability calculated by the algorithm for that state to be the accepted result.