Reasoning in Conversation: Solving Subjective Tasks through Dialogue Simulation for Large Language Models
❗❗REPO UNDER CONSTRUCTION❗❗
This repo contains the code for paper Reasoning in Conversation: Solving Subjective Tasks through Dialogue Simulation for Large Language Models.
Compared to objective tasks, subjective tasks focus more on interpretation or emotional response rather than a universally accepted reasoning pathway. Based on the characteristics of the tasks and the strong dialogue-generation capabilities of LLMs, we propose RiC (Reasoning in Conversation), a method that focuses on solving subjective tasks through dialogue simulation.
The motivation of RiC is to mine useful contextual information by simulating dialogues instead of supplying CoT style rationales, thereby offering potential useful knowledge behind dialogues for giving the final answers. We evaluate both API-based and open-source LLMs including GPT-4, ChatGPT, and OpenChat across twelve tasks. Experimental results show that RiC can yield significant improvement compared with various baselines.
Main results in zero-shot setup.
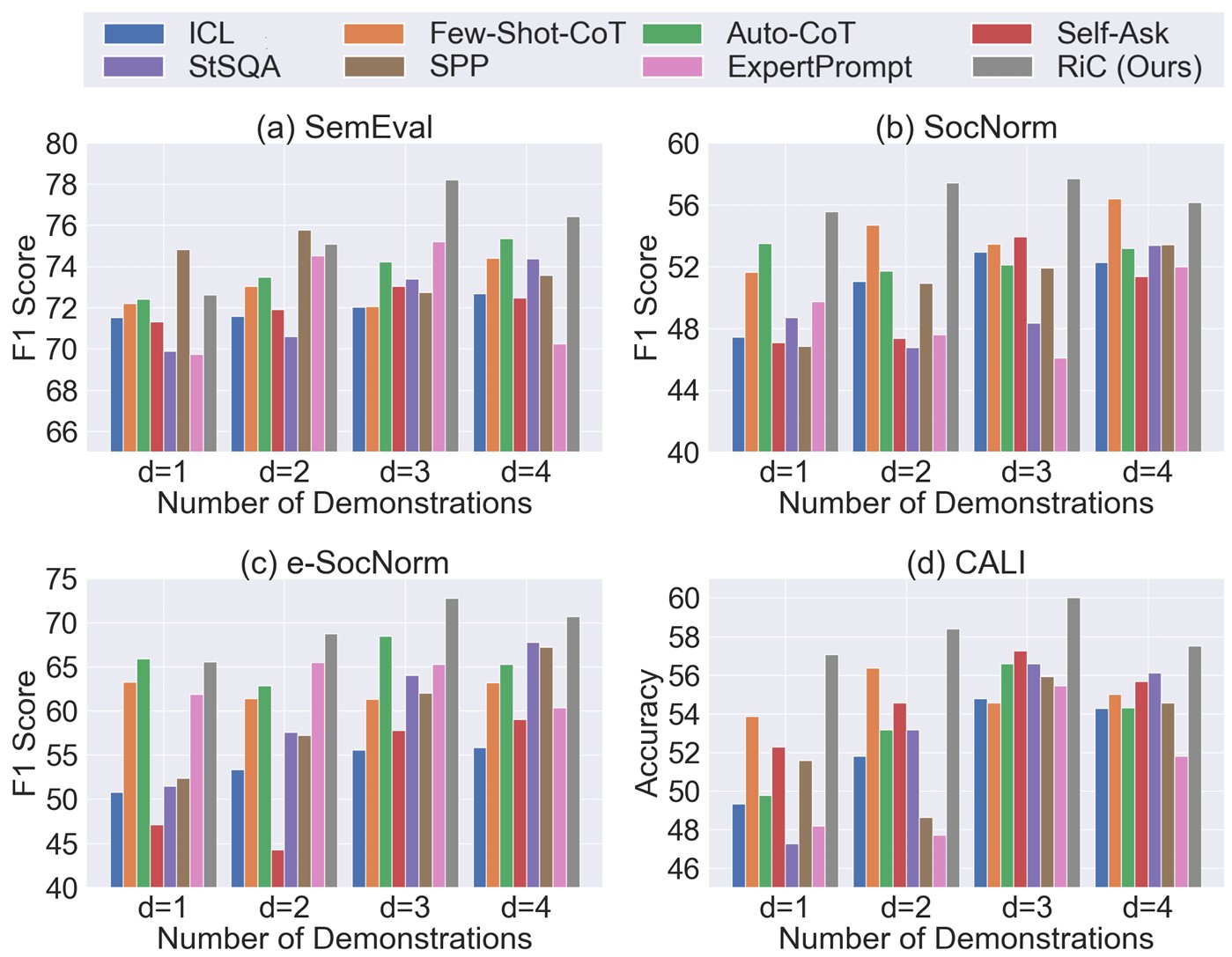
Performance of baselines and our RiC method by using different numbers of demonstrations.
Comming Soon!
Comming Soon!
@inproceedings{wang-etal-2024-reasoning,
title = "Reasoning in Conversation: Solving Subjective Tasks through Dialogue Simulation for Large Language Models",
author = "Wang, Xiaolong and
Wang, Yile and
Zhang, Yuanchi and
Luo, Fuwen and
Li, Peng and
Sun, Maosong and
Liu, Yang",
editor = "Ku, Lun-Wei and
Martins, Andre and
Srikumar, Vivek",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2024",
address = "Bangkok, Thailand",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.acl-long.844",
pages = "15880--15893",
}