Barebones admin system built on Kohana 2.3.1 with Bootstrap CSS framework, built to work on large desktops and tablets.
jQuery - v1.10.2
jQuery UI - v1.10.3
Bootstrap - v3.1.1 customised
Bootbox - v4.0.0
Bootstrap Datetimepicker - v2.1.11
Moment - v2.2.1
jQuery-File-Upload - v5.32.3
html5shiv - v3.6.2
selectivizr - v1.0.2
respond - v1.3.0
tmpl - v2.4.1
Two test logins are provided 'test' and 'test2' with both passwords set to '123456'.
The default Routing of URLs -> Controllers has been slightly modified to make it easier to identify admin and frontend Controllers. Here's how it works:
- All /admin/* URLs will first try and load a Controller file named 'be_%SECTION_NAME%', if a Controller of that name cannot be found then it will fall back to normal routing.
- All other URLs will first try and load a Controller file named 'fe_%SECTION_NAME%', if a Controller of that name cannot be found then it will fall back to normal routing.
This was done for a few reasons. Normally you would either have an admin directory in the Controllers folder with the same name or a Controller file prefixed with admin, the admin prefix would be fine and work - albeit a bit messy IMO.The admin directory method would cause a class name clash if they were both named the same thing, which is annoying.
There is a single custom Admin route in place that basically removes the admin part from the requested URL when being parsed by the Router code.
All admin section Controllers/Models should extend the base Admin Controller/Model, this stops there being repeated code in every single Controller/Model as there are generic methods in the base Controller which handle things such as add, edit, list pages and template variables for example. As a minimum for an admin section 'module' you must have the following files:
- Controller - Set some class properties and have a basic __construct() method.
- i18n - Language file.
- Model - Set some class constants and properties and also define the database fields.
You can easily extend/amend functionality by overriding the default methods contained in the admin base Controller/Model, you can acheive this either by having the same named method or by overriding, running the parent method and then performing your own logic. I.e. parent::method($args);. This just follows normal OO practices.
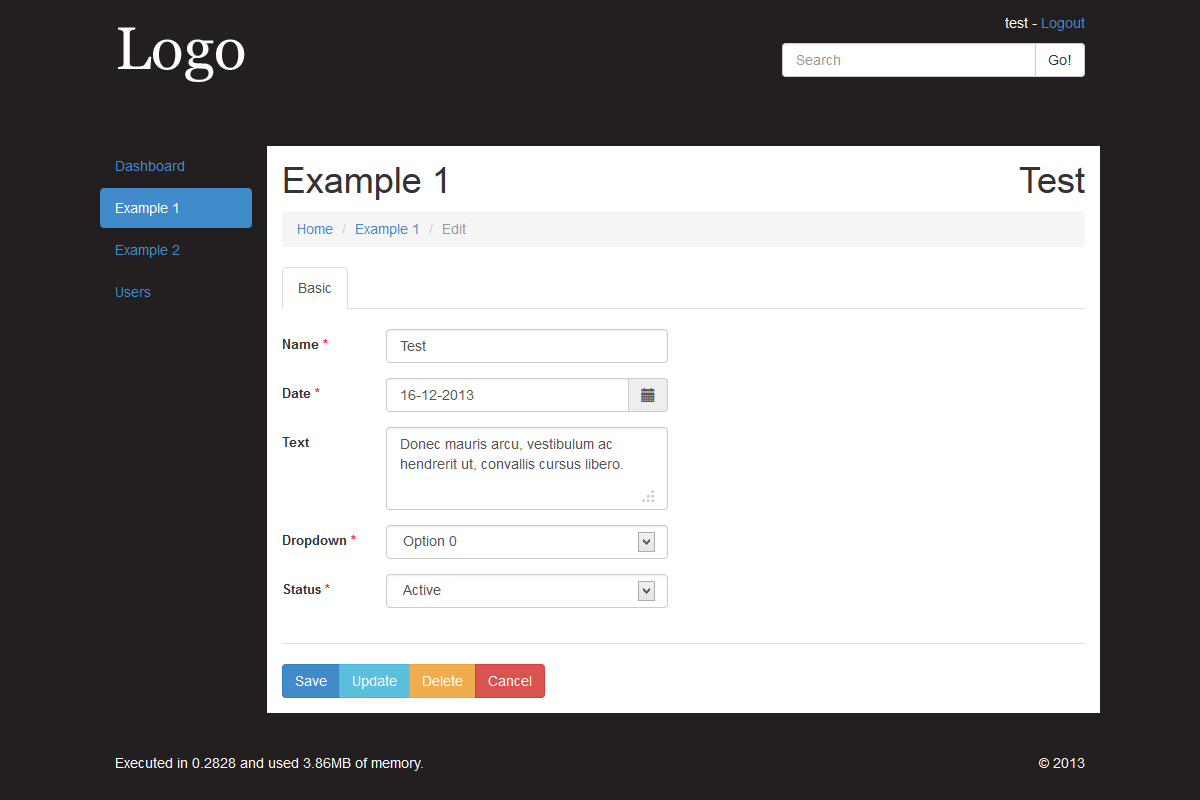
Example 1 shows how minimal a section can be, no overriding of methods and simply relying on the functionality inherited from the base Controllers.
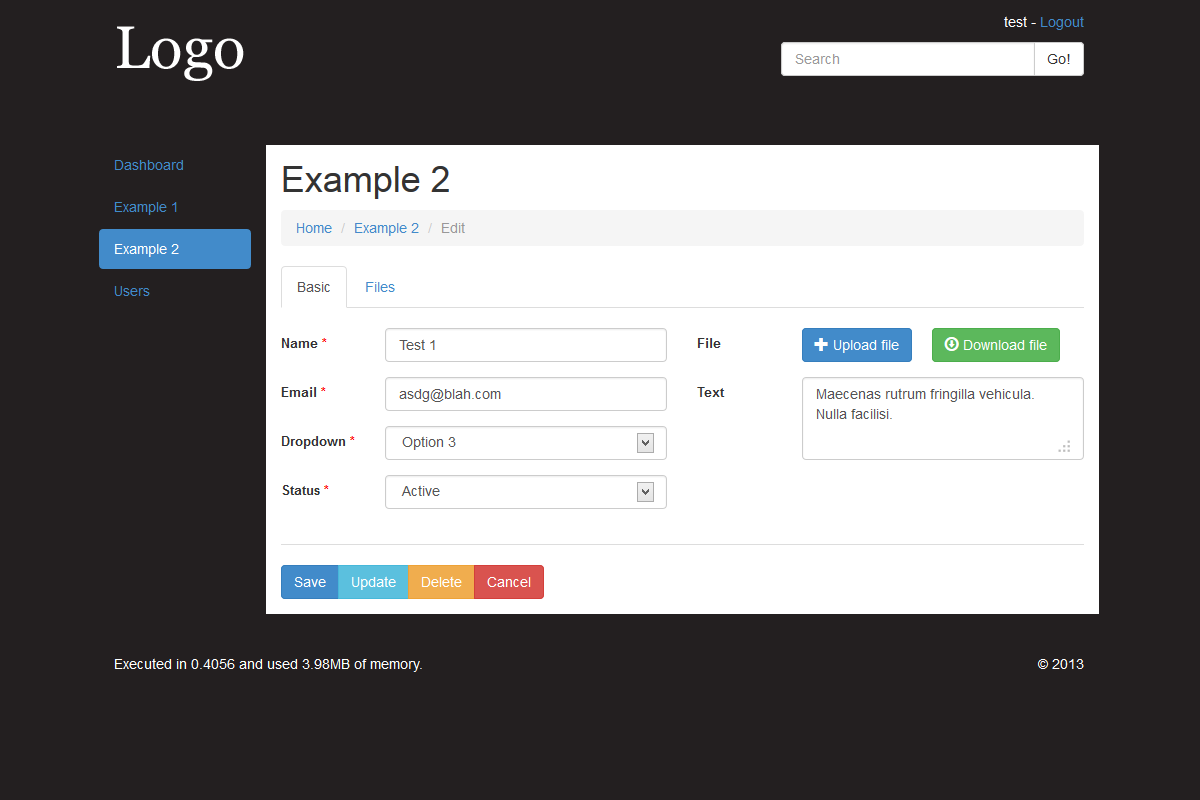
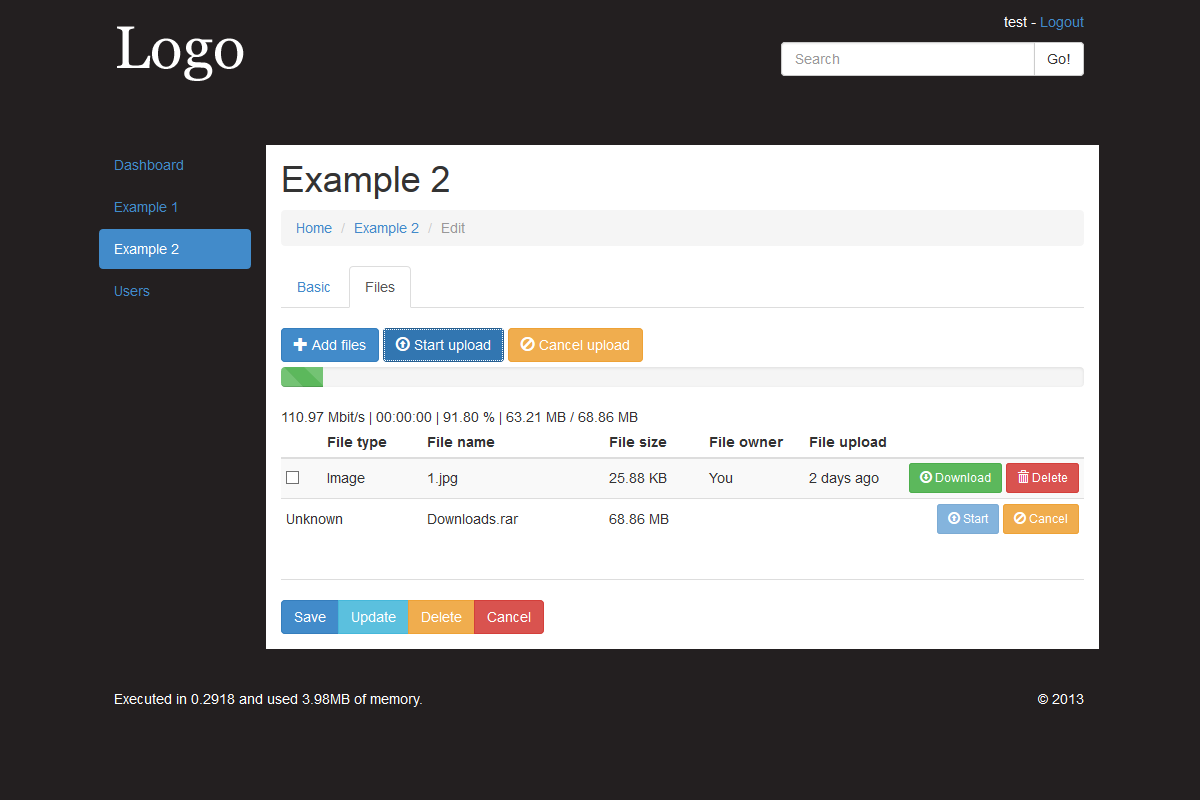
Example 2 shows how you can change/extend certain functionality to suit your needs. Two single upload fields, Multiple uploads via the Files tab, custom validation rules (Model), custom field layout (tab-0.php) and custom template variables set (Controller function section_details()).
Example 3 shows how you can modify the list pages by extending both Controller and Model methods which handle listing the data. In this example a 'type' field is used to add tabs to the list page so that you can quickly sort and filter the data.
There are 9 currently supported field types: Checkbox, File, Input, Input Date, Input Number, Input Password, Radio, Select and Textarea. For each field in the Model a type is set, this is then used to load corresponding view which contains the markup and logic for that type, based on these fields there is also some post processing performed in the model after POST.
File Uploads Files uploaded via the multi-uploader and single uploader are both stored in the files table. File uploads are securely handled both on upload and when stored on the file system, tokens are used when downloading files so that stored path is not revealed. Both methods use the jQuery-File-Upload plugin.
For consistency all database tables and columns should use the following convention..
- Table name should be plural of the object that it is representing.. I.e. for page the table name would be pages, etc.
- Column names should be prefixed the singular name of that object.. I.e. for pages table the column would be page_.
- Tables should always have the following fields: _status(int), _created_date(datetime), _updated_date(datetime), _deleted(int), _deleted_date(datetime) and _last_editor(int).
Obviously normally you wouldn't use Kohana 2 as it's a bit dated now, however it's the framework I personally have most experience with. Saying that, it does the job - better than Procedural non OOP code. If I were to use a modern framework I'd use either laravel, kohana 3 or a self-rolled framework utilising Composer for the components needed.
- JavaScript - Use a JavaScript framework to better architect the logic, making it easily readable and extendable
- Searching - Need to figure out how the top search bar would work searching all items
- Multi-File-Upload - You can't remove items from Multi File Uploader after they've been added
- Date time fields - Need to add datetime and time only field type