Control codes based on artificial vector fields
This repository performs the control of a differential robot by using artificial vector fields. To use it, just clone it to your catkin_ws/src folder:
$ git clone https://github.com/adrianomcr/vector_field_control.gitThe node vec_field_alpha.py is used to control the robot to follow a path represented as the zero level set of a function alpha. It requires the global pose of the robot. The current alpha function implemented is:
pose_topic_name(message type:tf2_msgs/TFMessage): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;pose_topic_name(message type:geometry_msgs/Pose): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;pose_topic_name(message type:nav_msgs/Odometry): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;pose_topic_name(message type:turtlesim_msgs/Pose): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;cmd_vel_topic_name(message type:geometry_msgs/Twist): Publish at this topic a velocity command (forward velocity and an angular velocity)
Note: The type of topic whose name is in the parameter pose_topic_name should be selected with the parameter pose_topic_type. This enables the code to get the pose from different message types.
The list of parameters is on the file inside the config folder in the file control_params.yaml. They are:
d_feedback(float): Distance the control point is moved forward from the robot's center;K_F(float): Convergence gain of the vector field;vd(float): Reference forward speed for the espeleorobo;a(float): Stretching of the curve on x axisb(float): Stretching of the curve on y axiscx(float): Center of the curve on x axiscy(float): Center of the curve on y axisgamma(int): Parameter of the curve's shape. Should be an even integerinvert_direction(bool): Flag to invert the sense of the curve's circulationinvert_motion_flag(bool): Flag to invert the motion of the espeleorobo (move backwards);pose_topic_name(string): Name of the topic in which the pose will be obtained;pose_topic_type(string): Type of the topic in which the pose will be obtained (options: TFMessage, Pose, Odometry);cmd_vel_topic_name(string): Name of the topic in which the forward and angular velocities will be published.
To use this node just add the following lines in your launch file:
<!-- Run the node that controls the robot with vector fields -->
<node pkg = "vector_field_control" name = "vector_field" type = "vec_field_alpha.py" args="" output="screen">
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find vector_field_control)/config/control_params.yaml" />
</node>You can simply use the file vector_field.launch:
$ roslaunch vector_field_control vector_field.launchThis node was developed to control the EspeleoRobô, a platform developed by Vale S.A., the biggest mining company in the world. The models necessary to simulate the EspeleoRobô are not yet available for the general public. Thus, the config parameters are set to run an example with the turtlesim simulator.
Similar to the previous case, the node vec_field_radial.py is used to control the robot to follow a path represented as the zero level set of a function alpha. It requires the global pose of the robot. The main difference is that the alpha function is now numerically estimated given a sequence of points.
Note: this implementation considers an open path. When the robot reaches the end of the path it will stop.
pose_topic_name(message type:tf2_msgs/TFMessage): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;pose_topic_name(message type:geometry_msgs/Pose): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;pose_topic_name(message type:nav_msgs/Odometry): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;pose_topic_name(message type:turtlesim_msgs/Pose): Subscribe to this topic to get the pose of the robot. To be selected with parameterpose_topic_type;cmd_vel_topic_name(message type:geometry_msgs/Twist): Publish at this topic a velocity command (forward velocity and an angular velocity)path_topic_name(message type:geometry_msgs/Polygon): Subscribe to this topic to get a sequence of points representing a path to be followed. To be selected with parameterpath_topic_name;
Note: The type of topic whose name is in the parameter pose_topic_name should be selected with the parameter pose_topic_type. This enables the code to get the pose from different message types.
The list of parameters is on the file inside the config folder in the file control_params.yaml. They are:
d_feedback(float): Distance the control point is moved forward from the robot's center;K_F(float): Convergence gain of the vector field;D_alpha(float): Parameter for the construction of the alpha function. An heuristics for this value is the inverse of the maximum path's curvature, no more than that.vd(float): Reference forward speed for the espeleorobo;invert_direction(bool): Flag to invert the sense of the curve's circulationinvert_motion_flag(bool): Flag to invert the motion of the espeleorobo (move backwards);pose_topic_name(string): Name of the topic in which the pose will be obtained;pose_topic_type(string): Type of the topic in which the pose will be obtained (options: TFMessage, Pose, Odometry);cmd_vel_topic_name(string): Name of the topic in which the forward and angular velocities will be published.path_topic_name(string): Name of the topic in which the sequence of points representing a path will be obtained.
To use this node just add the following lines in your launch file:
<!-- Run the node that controls the robot with vector fields -->
<node pkg = "vector_field_control" name = "vector_field" type = "vec_field_radial.py" args="" output="screen">
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find vector_field_control)/config/control_params.yaml" />
</node>You can simply use the file vector_field.launch:
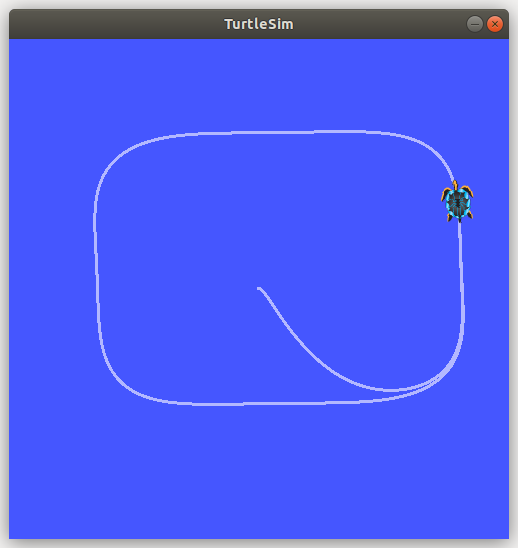
$ roslaunch vector_field_control vector_field.launchExample of the vector field based on alphas (vec_field_alpha.py):
$ roscore
$ rosrun turtlesim turtlesim_node
$ roslaunch vector_field_control vector_field.launchIf everything is ok you should see the following result: