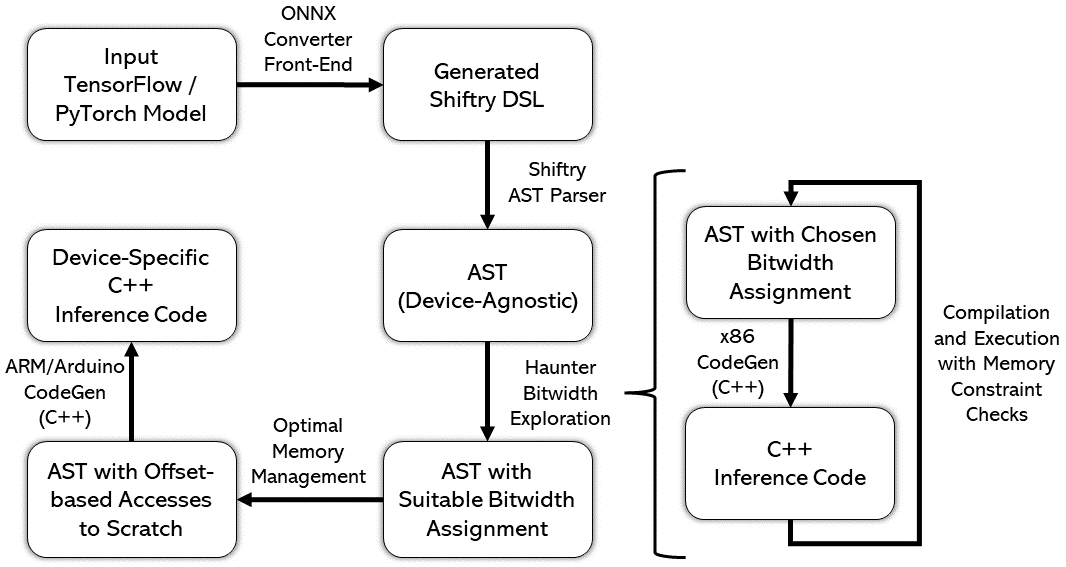
Instructional repository for reproducing the experiments from our paper MinUn: Accurate ML Inference on Microcontrollers.
Parts of this repository are still in active development. If you wish for more information, or wish to point out an error, please consider raising a GitHub issue.
This repository is segregated into different directories based on the different experiment tables presented in the ArXiv version of the paper.
We shall only provide setup instructions, model training and conversion instructions, and workarounds to common system-related issues in this particular README.
For experiment-specific instructions and results, please refer to the READMEs in the individual directories after having followed the instructions presented here.
MinUn is currently only available for Linux. All of our experiments have been tested with Python 3.7.16 running on Ubuntu 22.04. We recommend users to make use of these specific versions for preventing deprecation issues.
Additionally, we recommend that a user create a virtual environment using conda before following the rest of the instructions (one can, alternatively, also use venv).
-
Download Anaconda.
-
Go to the download directory and install
conda:
chmod u+x Anaconda3-*.sh
./Anaconda3-*.sh
- Then, refresh your terminal (you can simply close the current terminal and open a new one) and do:
conda create -n minun python=3.7
- The previous step creates an environment by the name of
minun. You can now installpip3and prerequisite software packages in this environment (you'll have to activateminunenvironment each time you refresh the terminal):
conda activate minun
conda install pip3
- Create the following three directories:
mkdir Train
mkdir Convert
mkdir Compile
- Clone the requisite repositories in each specific directory:
cd Train/
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/EdgeML.git
cd ../Convert/
git clone https://github.com/shubhamugare/EdgeML.git
cd ../Compile/
git clone https://github.com/krantikiran68/EdgeML.git
If you wish to train (from scratch) any of the TinyML models developed by Microsoft Research India, feel free to, alternatively, follow the elaborate instructions provided in the EdgeML README. Else, if you already have a trained TF / PyTorch / ONNX model, you can safely skip this section and move to the conversion setup section.
Please ensure that your conda environment is active, as described previously.
- Change directory to
Train/EdgeML/tf:
cd ../Train/EdgeML/tf/
- Run the following installation commands (alternatively, you can also follow the more elaborate README.md instructions from
Train/EdgeML/tf):
# For CPU-based training.
pip install -r requirements-cpu.txt
pip install -e .
# For GPU-based training.
pip install -r requirements-gpu.txt
pip install -e .
- Change directory to
Train/EdgeML/pytorch:
cd ../Train/EdgeML/pytorch/
- Run the following installation commands (alternatively, you can also follow the more elaborate README.md instructions from
Train/EdgeML/pytorch):
# For CPU-based training.
pip install -r requirements-cpu.txt
pip install -e .
# For GPU-based training.
pip install -r requirements-gpu.txt
pip install -e .
pip install -e edgeml_pytorch/cuda/
Once you have a trained model available in ONNX, you need to use a converter which generates the SeeDot DSL and dumps the model tensors to be used by Shiftry / MinUn.
You don't need to install anything specific for running the ONNX converters. Please move onto the next section.
Once the model has been specified in SeeDot DSL and the weights have been dumped, Shiftry / MinUn compilers will accomplish the remaining heavy-lifting to generate the final C / C++ inference codes for your target devices.
Please ensure that your conda environment is active, as described previously.
The setup instructions for the compilers are as follows:
- Change directory to
Train/EdgeML/tools/SeeDot/:
cd ../tools/SeeDot/
- Run the following installation commands (alternatively, you can also follow the more elaborate README.md instructions from
Train/EdgeML/tools/SeeDot):
sudo apt install gcc g++ build-essential cmake protobuf-compiler libprotobuf-dev
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Note: Bokeh-2.1.1 sometimes raises import errors with Jinja2. If you face such an issue, simply uninstall your current version of Bokeh, change the tools/SeeDot/requirements.txt from bokeh==2.1.1 to bokeh==2.4.1, and re-run the previous command.
Your full setup is now complete!
TODO: Provide a self-contained training example in this README.
https://github.com/onnx/tensorflow-onnx
https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/super_resolution_with_onnxruntime.html
TODO: Provide a full conversion example in this README.
Once a trained ONNX model has been obtained, please follow the instructions from the ONNX Converter README by changing directory to:
cd ../../../../Convert/EdgeML/Tools/SeeDot/seedot/compiler
/ONNX/
TODO: Provide a full compilation example in this README.
Please proceed to the directory pertaining to the table name, whose results you wish to replicate, and follow the README files provided there.
During the compiler execution, a number of system issues can arise, leading to compilation failure. We hope to address these common issues in this section. Our list is not comprehensive by any stretch of imagination and, as such, we would appreciate the user for reporting additional failures experienced by them.
At times, the generated C / C++ code for the x86 platform can segfault during execution, leading to compilation failure. This essentially hinders the Haunter algorithm from exploring the bitwidth space.
We've noticed this failure is common for generated codes which require a large amount of stack during execution (more than the default 2MB provided in Linux). A workaround, as discussed here is to run the following command in the terminal, before running Shiftry / MinUn:
ulimit -s 16384
ulimit -S 16384
If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{10.1145/3589610.3596278,
author = {Jaiswal, Shikhar and Goli, Rahul Kranti Kiran and Kumar, Aayan and Seshadri, Vivek and Sharma, Rahul},
title = {MinUn: Accurate ML Inference on Microcontrollers},
year = {2023},
isbn = {9798400701740},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3589610.3596278},
doi = {10.1145/3589610.3596278},
abstract = {Running machine learning inference on tiny devices, known as TinyML, is an emerging research area. This task requires generating inference code that uses memory frugally, a task that standard ML frameworks are ill-suited for. A deployment framework for TinyML must a) be parametric in the number representation to take advantage of the emerging representations like posits, b) carefully assign high-precision to a few tensors so that most tensors can be kept in low-precision while still maintaining model accuracy, and c) avoid memory fragmentation. We describe MinUn, the first TinyML framework that holistically addresses these issues to generate efficient code for ARM microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino Uno, Due and STM32H747) that outperforms the prior TinyML frameworks.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGPLAN/SIGBED International Conference on Languages, Compilers, and Tools for Embedded Systems},
pages = {26–39},
numpages = {14},
keywords = {Number Representations, Memory Management, TinyML, Embedded Devices, Compilers, Programming Languages},
location = {Orlando, FL, USA},
series = {LCTES 2023}
}
@misc{jaiswal2022minun,
title = {MinUn: Accurate ML Inference on Microcontrollers},
author = {Shikhar Jaiswal and Rahul Kiran Kranti Goli and Aayan Kumar and Vivek Seshadri and Rahul Sharma},
year = {2022},
eprint = {2210.16556},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
primaryClass = {cs.LG}
}