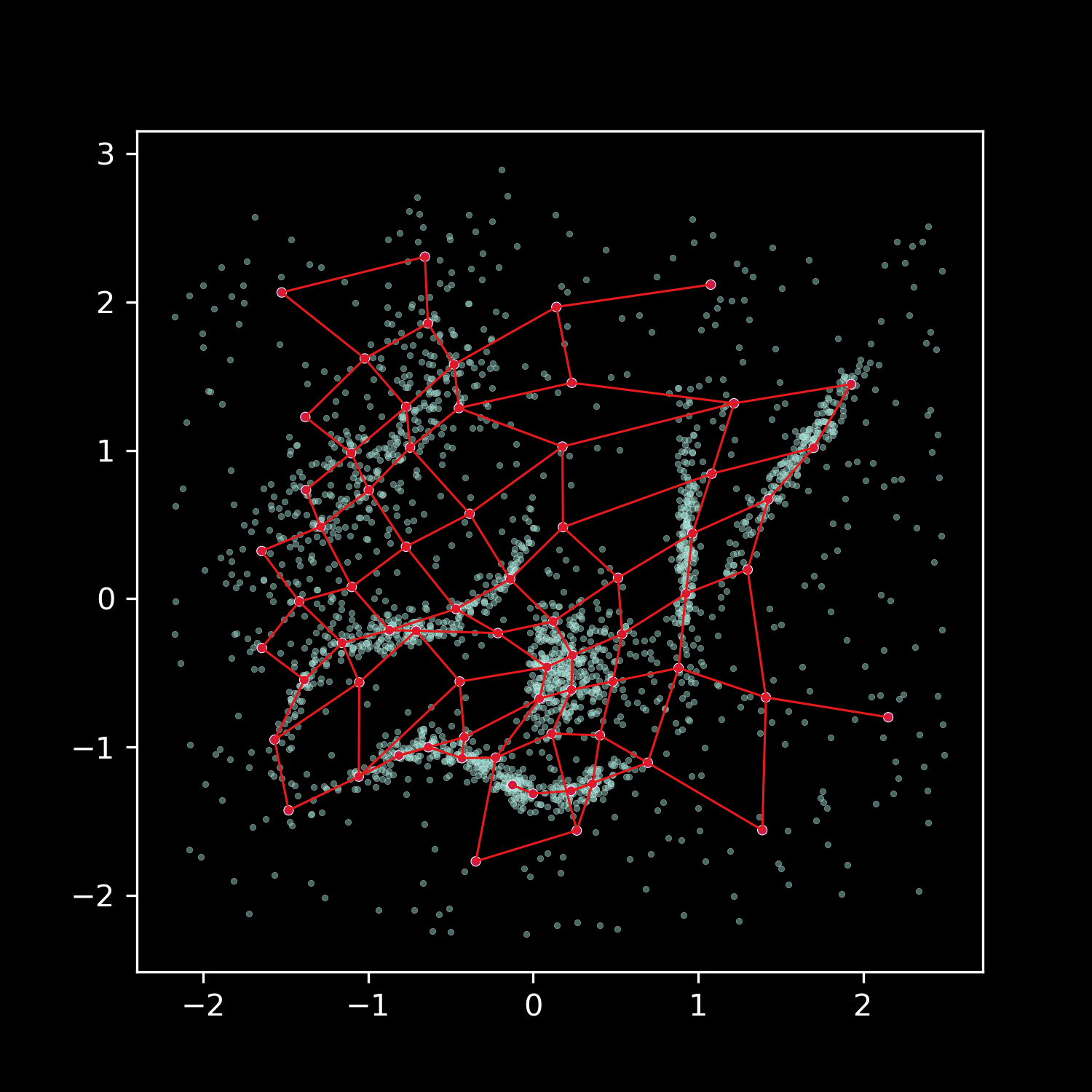
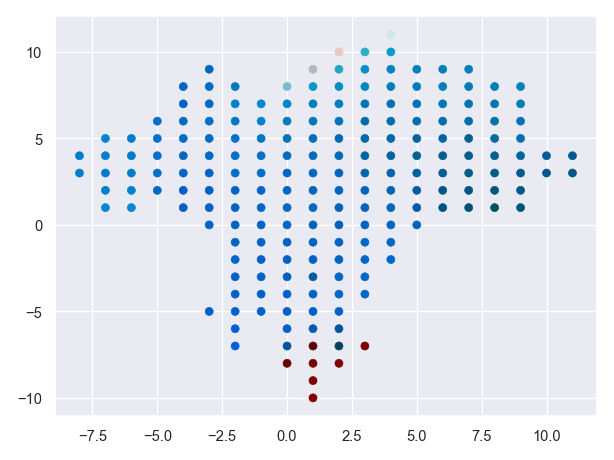
DBGSOM is short for Directed Batch Growing Self-Organizing Map. A SOM is a type of artificial neural network that is used to to produce a low-dimensional representation of a higher dimensional data set while preserving the topological structure of the data. It can be used for supervised and unsupervised vector quantization, classification and many different data visualization tasks.
- Compatible with scikit-learn's API and can be used as a drop-in replacement for other clustering and classification algorithms
- Can handle high-dimensional and non-uniform data distributions
- Good results without parameter tuning
- Better topology preservation and faster training time than classical SOMs
- Interpretability of the results through plotting
The DBGSOM algorithm works by constructing a two-dimensional map of prototypes (neurons) where each neuron is connected to its neighbors. The first neurons on the map are initialized with random weights from the input data. The input data is then presented to the SOM. Each sample gets assigned to it's nearest neuron. The neuron weights are then updated to the samples that were mapped to each neuron. Neighboring neurons affect each others updates, so the low dimensional ordering of the map is preserved. The DBGSOM algorithm uses a growing mechanism to expand the map as needed. New neurons are added to the edge of the map where the quantization error of the boundary neurons is above a given growing threshold.
DBGSOM can be installed from PyPi via pip.
pip install DBGSOMdbgsom implements the scikit-learn API. We have the SomClassifier and SomVQ for classification and clustering/vector quantization.
from dbgsom import SomVQ, SomClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
digits_X, digits_y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
quantizer = SomVQ()
classifier = SomClassifier()
quantizer.fit_predict(X=digits_X)
classifier.fit_predict(X=digits_X, y=digits_y)Here are a few example use cases for DBGSOM.
- Python > 3.7
- Numpy
- NetworkX
- tqdm
- scikit-learn
- seaborn
- pandas
- A directed batch growing approach to enhance the topology preservation of self-organizing map, Mahdi Vasighi and Homa Amini, 2017, https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.02.015
- Reference implementation by the authors in Matlab: https://github.com/mvasighi/DBGSOM
- Statistics-enhanced Direct Batch Growth Self- organizing Mapping for efficient DoS Attack Detection, Xiaofei Qu et al., 2019, 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2922737
- Entropy-Defined Direct Batch Growing Hierarchical Self-Organizing Mapping for Efficient Network Anomaly Detection, Xiaofei Qu et al., 2021 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064200
- Self-Organizing Maps, 3rd Edition, Teuvo Kohonen, 2003
- MATLAB Implementations and Applications of the Self-Organizing Map, Teuvo Kohonen, 2014
- Smoothed self-organizing map for robust clustering, P. D’Urso, L. De Giovanni and R. Massari, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.06.038
dbgsom is licensed under the MIT license.