The aim of this project is to perform a comparison rather than fine-tuning. To facilitate the comparison, we will utilize the RandomForestClassifier as the base model for all our experiments, using its default parameter values.
Our main focus is to compare the following two strategies:
-
MultiOutput Classifier: This strategy involves training a separate classifier for each target variable.
-
Classifier Chain: This approach combines multiple binary classifiers into a single multi-label model, leveraging the correlations between the target variables.
The dataset used in this project can be accessed through the Kaggle link Link text . It consists of Amazon product reviews and focuses on two labels: positive and negative sentiment.
In this step, we utilized the Hugging Face model SamLowe/roberta-base-go_emotions for emotion extraction. This model is based on the Roberta architecture and has been trained on the go_emotions dataset.
Before applying the emotion extraction model, the data went through a cleaning process to ensure its quality.
The preprocessing step involved tokenization, stemming, and lemmatization to prepare the text data for further analysis.
The data was prepared for the models through vectorization, standardization, and label encoding.
To optimize the clustering process, we employed various techniques. First, we visualized the dendrogram, which helped us determine the best number of clusters. Additionally, we calculated the silhouette score, which further aided in identifying the optimal number of clusters. Finally, we utilized the k-means clustering algorithm to perform the clustering based on the determined number of clusters.
The following plotting shows the emotions after doing K-means Clustering

In this project, we employed a multi-label multi-output classification approach. Our predicted labels are:
- Label (Y): Indicates whether the review is positive or negative.
- Emotion (Y1): Represents the emotions extracted from the review, such as admiration, disappointment, etc.
The evaluation metric used in this experiment is the weighted F1 score, which is ideal for computing the net F1 score for class-imbalanced data distributions.
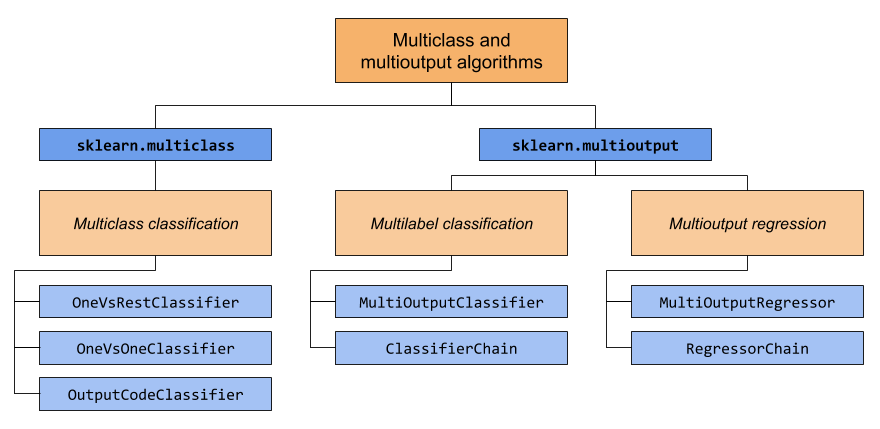
The diagram above illustrates the concept of multi-output classification, where multiple dependent variables are predicted simultaneously.
The first model employed in this project is the MultiOutputClassifier, which is capable of handling multi-label multi-output classification tasks. A multi-output classifier is a type of classifier that can predict multiple target variables simultaneously. We use a RandomForestClassifier as the base estimator for the MultiOutputClassifier. We combine the target arrays into a single 2D array using np.column_stack and fit the multi_output_clf classifier with the combined target array and scaled training features. The MultiOutputClassifier internally trains separate models for each target variable and can parallelize the training process if supported.
In the Classifier Chain strategy applied in this project, the base classifier used is the RandomForestClassifier with a random_state of 42. The Classifier Chain combines multiple binary classifiers into a single model, considering the dependencies between the target variables. The sentiment labels and extracted emotions were combined, and the RandomForestClassifier was utilized as the base model. The chain classifier was trained on the combined data and used for predictions and evaluation. This approach allows for leveraging the correlations between sentiment and emotions in sentiment analysis tasks.
The results obtained from emotions extracted using the Hugging Face model and the emotions obtained from clustering were compared to evaluate their effectiveness in extracting emotions from text.
Modeling Comparison Without Class Reduction (Y2 = 13 Classes)
| Models | Y1 | Y2 | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest Base Model | 82.5% | 54.3% | 68.4% |
| MultiOutputClassifier | 83.9% | 57.1% | 70.5% |
| ChainClassifier | 82.6% | 56.3% | 69.4% |
Modeling Comparison With Class Reduction (Y2 = 6 Classes)
| Models | Y1 | Y2 | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest Base Model | 82.5% | 63.7% | 73.1% |
| MultiOutputClassifier | 82.9% | 66.5% | 74.7% |
| ChainClassifier | 82.6% | 66.3% | 74.4% |