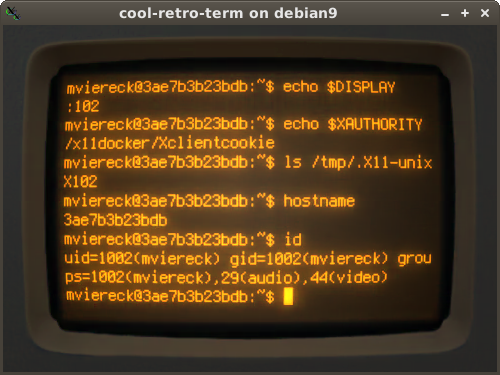
Graphical applications or desktops in docker are similar in usage to a Virtual Machine. They are isolated from host, and it is possible to run applications that would not run on host due to missing dependencies. For example, it is possible to run latest development versions or outdated versions of applications, or multiple versions at the same time.
Practical differences to a VM: docker containers need much less resources. x11docker discardes containers after use. Persistant data and configuration storage is done with shared folders. Persistant container system changes can be done in Dockerfile; system changes in running containers are discarded after use.
- Avoids X security leaks by running additional X servers.
- Improves container security:
- Restricts container capabilities to bare minimum.
- Container user is same as host user to avoid root in container.
- No dependencies inside of docker images.
- No obliging dependencies on host beside X and docker. Recommended:
nxagent,xpraandXephyr. - Wayland support.
- Optional features:
- Persistent data storage with shared host folders and a persistant
HOMEin container. - Sound with pulseaudio or ALSA.
- Hardware acceleration for OpenGL.
- Clipboard sharing.
- Language locale creation.
- Persistent data storage with shared host folders and a persistant
- Network setup with SSH, VNC or HTML5 possible.
- Supports init systems
tini,runit,openrc,SysVinitandsystemdin container. - Developed on debian 9. Tested on fedora 25, CentOS 7, openSUSE 42.3, Ubuntu 16.04, Manjaro 17, Mageia 6 and Arch Linux.
- Easy to use. Examples:
x11docker jess/cathodex11docker --desktop --size 320x240 x11docker/lxde
x11docker-gui is an optional graphical frontend for x11docker.
x11docker-guineeds packagekaptain. If your distribution misses it, look at kaptain repository.- If
kaptainis not installed on your system,x11docker-guitries to use imagex11docker/kaptain.
Just type x11docker IMAGENAME [IMAGECOMMAND]. Get an overview of options with x11docker --help. For desktop environments in image add option --desktop (or short option -d).
General syntax:
To run a docker image with new X server (auto-choosing X server):
x11docker [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND]
x11docker [OPTIONS] -- "[DOCKER_RUN_OPTIONS]" IMAGE [COMMAND [ARG1 ARG2 ...]]
To run a host application on a new X server:
x11docker [OPTIONS] --exe COMMAND
x11docker [OPTIONS] --exe -- COMMAND [ARG1 ARG2 ...]
To run only a new empty X server:
x11docker [OPTIONS]
For a first test, you can run with bash x11docker respective bash x11docker-gui.
For manual installation, make x11docker executable with chmod +x x11docker and move it to /usr/bin.
As root, you can install, update and remove x11docker on your system:
x11docker --install: install x11docker and x11docker-gui from current directory.x11docker --update: download and install latest release from github.x11docker --update-master: download and install latest master version from github.x11docker --remove: remove all files installed by x11docker.
Copies x11docker and x11docker-gui to /usr/bin. Creates an icon in /usr/share/icons. Creates x11docker.desktop in /usr/share/applications. Copies README.md, CHANGELOG.md and LICENSE.txt to /usr/share/doc/x11docker.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mviereck/x11docker/master/x11docker -O /tmp/x11docker
sudo bash /tmp/x11docker --update
rm /tmp/x11docker
Description of some commonly used options. Get an overview of all options with x11docker --help.
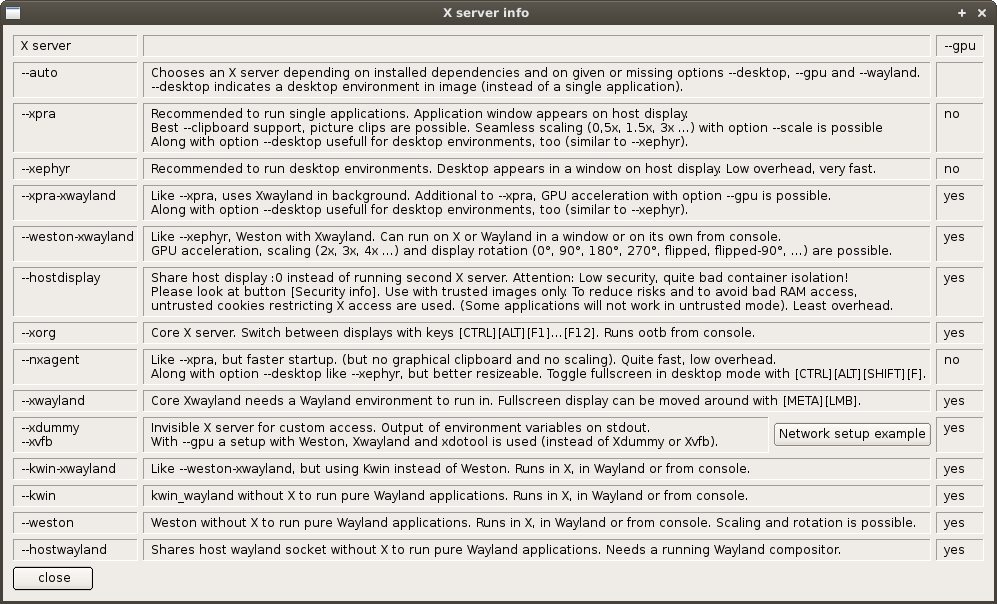
x11docker assumes that you want to run a single application in seamless mode, i.e. a single window on your regular desktop. If you want to run a desktop environment in image, add option --desktop. If you don't specify a desired X server, x11docker chooses the best matching one depending on chosen options and installed dependencies.
- Seamless mode is supported with options
--xpraand--nxagent. As a fallback insecure option--hostdisplayis possible.- If neither
xpranornxagentare installed, but x11docker finds a desktop capable X server likeXephyr, it avoids insecure option--hostdisplayand runs Xephyr with a host window manager. - You can specify a host window manager with option
--wm WINDOWMANAGER, for example--wm openbox.
- If neither
- Desktop mode is supported with all X server options except
--hostdisplay. If available, x11docker prefersXephyrandnxagent
Changes in a running docker image are lost, the created docker container will be discarded. For persistent data storage you can share host directories:
- Option
--homecreates a host directory in~/x11docker/IMAGENAMEthat is shared with the container and mounted as home directory. Files in container home and configuration changes will persist. - Option
--sharedir DIRmounts a host directory at the same location in container without settingHOME. - Option
--homedir DIRis similar to--homebut allows you to specify a custom host directory for data storage. - Special cases for
$HOME:--homedir $HOMEwill use your host home as container home. Discouraged, use with care.--sharedir $HOMEwill mount your host home as a subfolder of container home.
For persistant changes of image system, adjust Dockerfile and rebuild. To add custom applications to x11docker example images, you can create a new Dockerfile based on them. Example:
# xfce desktop with Midori internet browser
FROM x11docker/xfce
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y midori
Hardware acceleration for OpenGL is possible with option --gpu. This will work out of the box in most cases with open source drivers on host. Otherwise have a look at Dependencies.
Clipboard sharing is possible with option --clipboard. Image clips are possible with --xpra and --hostdisplay. Some X server options need package xclip on host.
Sound is possible with options --pulseaudio and --alsa.
- For pulseaudio sound with
--pulseaudioyou needpulseaudioon host and in image. - For ALSA sound with
--alsayou can specify the desired sound card with e.g.--env ALSA_CARD=Generic. Get a list of available sound cards withaplay -l.
You have two possibilities to set language locale in docker image.
- For support of chinese, japanese and korean characters install a font like
fonts-arphic-umingin image.
x11docker provides option --lang $LANG for flexible language locale settings.
- x11docker will check on container startup if the desired locale is already present in image and enable it.
- If x11docker does not find the locale, it creates it on container startup.
- Debian images need package
locales. - x11docker will only look for or create
UTF-8/utf8locales.
- Debian images need package
- Examples:
--lang defor German,--lang zh_CNfor Chinese,--lang rufor Russian,--lang $LANGfor your host locale.
You can choose between already installed language locales in image setting environment variable LANG, e.g. in image with ENV LANG=en_US.utf8 or with x11docker option --env LANG=en_US.utf8.
- Already installed locales in image can be checked with
docker run IMAGENAME locale -a. - Example to create a language locale in image:
RUN apt-get install -y locales
ENV LANG en_US.utf8
RUN localedef --verbose --force -i en_US -f UTF-8 en_US.utf8 || echo "localedef exit code: $?"
For troubleshooting, run x11docker or x11docker-gui in a terminal.
- x11docker shows warnings if something is insecure, missing or going wrong.
- Use option
--verboseto see logfile output, too.- Option
--debugcan provide additional informations. - Use options
--stdout --stderr --silentto get application output only. - You can find the latest dispatched logfile at
~/.cache/x11docker/x11docker.log.
- Option
- Make sure your x11docker version is up to date with
x11docker --update(latest release) orx11docker --update-master(latest beta). - Some applications need more privileges or capabilities than x11docker provides as default.
- Reduce container isolation with options
--hostipc --hostnet --cap-default --sys-adminand try again. If the application runs, reduce this insecure options to encircle the issue. - You can run container application as root with
--user=root.
- Reduce container isolation with options
- Get help in the issue tracker.
- Most times it makes sense to store the
--verboseoutput (orx11docker.log) at pastebin.
- Most times it makes sense to store the
x11docker can run with standard system utilities without additional dependencies on host or in image. As a core it only needs an X server and, of course, docker to run docker images on X.
x11docker checks dependencies for chosen options on startup and shows terminal messages if some are missing.
Basics:
- If no additional X server is installed, only less isolated option
--hostdisplaywill work out of the box within X, and option--xorgfrom console. (To use--xorgwithin X, look at setup for option --xorg). - As a well working base for convenience and security, it is recommended to install
xpra(seamless applications) andXephyr(desktop mode).- It is recommended to use latest stable xpra version from https://xpra.org.
- Alternativly, you can install
nxagentfor both seamless and desktop mode.
- Already installed on most systems with an X server:
xrandr,xauthandxdpyinfo.
Advanced usage:
- Clipboard sharing with option
--clipboardneedsxclip. (Not needed for--xpra,--nxagentand--hostdisplay). Image clipboard sharing is possible with--xpraand--hostdisplay. - Sound:
- Option
--alsahas no dependencies.- You can install ALSA libraries in image to support virtual devices (debian images:
libasound2).
- You can install ALSA libraries in image to support virtual devices (debian images:
- Option
--pulseaudioneedspulseaudioon host and in image.
- Option
- Hardware acceleration with option
--gpu- Works best with open source drivers on host and OpenGL/Mesa in image. In most cases everything will work out of the box with just setting
--gpu. - To provide good X isolation: Beside
xpra, also installXwayland,westonandxdotoolon host. Without these, you still can use--gpuwith--hostdisplayand--xorg. - Packages for OpenGL/Mesa in image:
- debian and Ubuntu images:
mesa-utils mesa-utils-extra. - CentOS and fedora images:
glx-utils mesa-dri-drivers - Alpine and NixOS images:
mesa-demos mesa-dri-ati mesa-dri-intel mesa-dri-nouveau mesa-dri-swrast - Arch Linux images:
mesa-demos
- debian and Ubuntu images:
- Proprietary closed source drivers from NVIDIA corporation need some manual setup and have some restrictions. Consider to use free
nouveaudriver instead.- x11docker can automatically install closed source nvidia drivers in container at every container startup. It gives some setup instructions in terminal output.
- The image should contain
modprobe(packagekmod) andxz. x11docker installs them if they are missing, but that slows down container startup. - You need the very same driver version as on host. It must not be a
deborrpmpackage but anNVIDIA_[...].runfile. Store it at one of the following locations:~/.local/share/x11docker(current user only)/usr/local/share/x11docker(system wide)
- Look at NVIDIA driver download page or try the direct download link provided in x11docker terminal output.
- Closed source driver installation fails on image systems that are not based on
glibc. This affects especially Alpine based images. NVIDIA corporation does not provide the source code that would allow you to use your hardware with different systems. - Alternativly, you can install a driver version matching your host setup in image yourself. Note that this image will not be portable anymore.
- Works best with open source drivers on host and OpenGL/Mesa in image. In most cases everything will work out of the box with just setting
Rarer needed dependencies for special options:
--nxagentprovides a fast and lightweight alternative toxpraandXephyr. Needsnxagentto be installed.--kwinand--kwin-xwaylandneedkwin_wayland, included in modernkwinpackages.--xdummyneeds dummy video driverxserver-xorg-video-dummy(debian) orxorg-x11-drv-dummy(fedora).--xvfbneedsXvfb--xfishtankneedsxfishtankto show a fish tank.--dbusis needed only for QT5 application in Wayland. It needsdbusordbus-launchin image.--starterneedsxdg-user-dirto locate yourDesktopfolder for starter icons.--install,--updateand--removeneedwget,unzipandxdg-icon-resource.
List of all host packages for all possible x11docker options (debian package names):
xpra xserver-xephyr xvfb weston xwayland nxagent kwin xserver-xorg-video-dummy xfishtank xclip xdg-utils xauth xdotool xrandr unzip wget, further (deeper surgery in system):pulseaudio xserver-xorg-legacy.
root permissions are needed only to run docker. X servers run as unprivileged user.
Running x11docker as unprivileged user:
- x11docker checks whether docker needs a password to run and whether
suorsudoare needed to get root privileges. A password prompt appears if needed. - If that check fails and does not match your setup, use option
--pw FRONTEND.FRONTENDcan be one ofsu sudo gksu gksudo lxsu lxsudo kdesu kdesudo beesu pkexecornone.
Running x11docker as root:
- Commands other than
dockerare executed as unprivileged user determined withlogname. (You can specify another host user with--hostuser USER). - Unfortunately, some systems do not provide
DISPLAYandXAUTHORITYfor root, but needed for nested X servers like Xephyr.- Tools like
gksuorgksudocan help. - Some
sudoimplementations provide-Eto keep the user environment:sudo -E x11docker [...].
- Tools like
Scope of x11docker is to run dockered GUI applications while preserving and improving container isolation. Core concept is:
- Run a second X server to avoid X security leaks.
- This in opposite to widespread solutions that share host X socket of display :0, thus breaking container isolation, allowing keylogging and remote host control. (x11docker provides this with option
--hostdisplay). - Authentication is done with MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE, stored separate from file
~/.Xauthority.
- This in opposite to widespread solutions that share host X socket of display :0, thus breaking container isolation, allowing keylogging and remote host control. (x11docker provides this with option
- Create container user similar to host user to avoid root in container.
- You can also specify another user with
--user=USERNAMEor a non-existing one with--user=UID:GID. - If you want root permissions in container, use option
--sudouserthat allowssuandsudowith passwordx11docker. Alternatively, you can run with--user=root.
- You can also specify another user with
- Disables possible root password and deletes entries in
/etc/sudoers. - Reduce container capabilities to bare minimum.
- Uses docker run options
--cap-drop=ALL --security-opt=no-new-privileges. - This restriction can be disabled with x11docker option
--cap-defaultor reduced with--sudouser.
- Uses docker run options
Weaknesses / ToDo:
- If docker daemon runs with
--selinux-enabled, SELinux restrictions are degraded for x11docker containers with docker run option--security-opt label=type:container_runtime_tto allow access to new X unix socket. A more restrictive solution is desirable. Compare: SELinux and docker: allow access to X unix socket in /tmp/.X11-unix - User namespace remapping is disabled to allow options
--homeand--homedirwithout file ownership issues. (Though, this is less a problem as x11docker already avoids root in container).
x11docker shows warning messages in terminal if chosen options degrade container isolation.
Most important:
--hostdisplayshares host X socket of display :0 instead of running a second X server.- Danger of abuse is reduced providing so-called untrusted cookies, but do not rely on this.
- If additionally using
--gpuor--clipboard, option--hostipcand trusted cookies are enabled and no protection against X security leaks is left. - If you don't care about container isolation,
x11docker --hostdisplay --gpuis an insecure, but quite fast setup without any overhead.
--gpuallows access to GPU hardware. This can be abused to get window content from host (palinopsia bug) and makes GPU rootkits possible.--pulseaudioand--alsaallow catching audio output and microphone input from host.
Rather special options reducing security, but not needed for regular use:
--sudouserallows sudo with passwordx11dockerfor container user. If an application breaks out of container, it can do anything. Allows some container capabilties that x11docker would drop otherwise.--cap-defaultdisables x11docker's container hardening and falls back to default docker container privileges.--dbus-system,--systemd,--sysvinit,--openrcand--runitallow some container capabilities that x11docker would drop otherwise.--systemdalso shares access to/sys/fs/cgroup.--hostipcsets docker run option--ipc=host. (Allows MIT-SHM / shared memory. Disables IPC namespacing.)--hostnetsets docker run option--net=host. (Allows dbus connection to host. Shares host network stack.)
If no X server option is specified, x11docker automatically chooses one depending on installed dependencies and on given or missing options --desktop, --gpu and --wayland.
- For single applications, x11docker prefers
--xpra. Alternativly, it tries--nxagent. - With option
--desktop, x11docker assumes a desktop environment in image and prefers--xephyr. - With option
--gpufor hardware acceleration, x11docker prefers--xpra-xwaylandfor single applications, or--weston-xwaylandfor desktop environments. - If none of above can be started due to missing dependencies, x11docker uses
--hostdisplayor--xorg. - With option
--wayland, x11docker creates a Wayland environment without X. See also chapter Wayland.
To run an X server entirely in docker, look at x11docker/xwayland.
Beside the X servers to choose from there are options --wayland, --weston, --kwin and --hostwayland to run pure Wayland applications without X.
- Option
--waylandautomatically set up a Wayland environment with some special environment variables and a dbus system daemon in container to support both QT5 and GTK3 applications. - Options
--kwinand--westonrun Wayland compositorskwin_waylandorweston.- For QT5 applications without option
--waylandyou need to manually add options--dbusand--env QT_QPA_PLATFORM=wayland.
- For QT5 applications without option
- Option
--hostwaylandcan run single applications on host Wayland desktops like Gnome 3, KDE 5 and Sway.
Examples:
- xfce4-terminal (GTK3) in Wayland:
x11docker --wayland x11docker/xfce xfce4-terminal
- KDE plasma shell (QT5) in a pure Wayland environment with hardware acceleration. Option
--kwinis used askwin_waylandon host supports plasma panel placing while default--westondoes not:
x11docker --kwin --wayland --gpu -- x11docker/plasma plasmashell
You can also run Wayland applications from host with option --exe.
- gnome-calculator (GTK3) and neverball (SDL) from host in Weston without X:
x11docker --weston --exe gnome-calculator
x11docker --weston --exe neverball
- Option
--xorgruns from console without additional setup. - To run a second core Xorg server from within an already running X session, you have to edit or create file
/etc/X11/Xwrapper.configand replace line:
allowed_users=console
with lines:
allowed_users=anybody
needs_root_rights=yes
On debian 9 and Ubuntu 16.04 you need to install package xserver-xorg-legacy.
(Depending on your hardware and system setup, you may not need line needs_root_rights=yes).
Running x11docker without an image name (or explicitly with option --xonly) creates an empty X server. In that case, or enforced with option --showenv, x11docker writes some environment variables on stdout. You can use this for custom access to new X server. Example:
read Xenv < <(x11docker --xephyr --showenv)
# run xterm from host on new X server
env $Xenv xterm
# run docker image on new X server
export $Xenv
docker run --env DISPLAY --env XAUTHORITY -v $XAUTHORITY:$XAUTHORITY -v $XSOCKET:$XSOCKET x11docker/xfce
If you like to, you can run two docker images sharing the same X server. Example:
read Xenv < <(x11docker --xephyr --showenv x11docker/lxde) # LXDE desktop in Xephyr
env $Xenv x11docker --hostdisplay x11docker/xfce thunar # Thunar from another image appears on LXDE desktop
x11docker supports init systems as PID 1 in container. Init in container solves the zombie reaping issue.
As default, x11docker uses docker built-in tini with docker run option --init.
- You can disable init in container with option
--no-init. - On some distributions docker's init
/usr/bin/docker-initis missing in docker package. Compare #23. To provide a replacement, downloadtini-staticfrom https://github.com/krallin/tini and store it at one of following locations:~/local/share/x11docker/usr/local/share/x11docker
Example installation code:
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/x11docker
cd ~/.local/share/x11docker
wget https://github.com/krallin/tini/releases/download/v0.18.0/tini-static
chmod +x tini-static
x11docker sets up the init system to run desired command. No special setup is needed beside installing the init system in image. Installing dbus in image is recommended.
--systemd: systemd in container.- To get a faster startup, it helps to look for services that fail to start in container and to mask them in image with
systemctl mask servicename. - Tested with fedora, debian and Arch Linux images. Debian 10 images run well; debian 9 images additionally need insecure option
--sys-admin. - Image example based on debian buster: x11docker/cinnamon
- To get a faster startup, it helps to look for services that fail to start in container and to mask them in image with
--runit: runit in container.- For a bit faster startup, failing services can be disabled by deleting their softlinks in
/etc/runit/runsvdir/default. - Image examples based on Void Linux: x11docker/enlightenment and x11docker/lumina.
- For a bit faster startup, failing services can be disabled by deleting their softlinks in
--openrc: OpenRC in container.- cgroup usage possible with option
--sharecgroup. - Image example based on Alpine Linux: x11docker/fvwm
- cgroup usage possible with option
--sysvinit: SysVinit in container.- Tested with devuan images from gitlab/paddy-hack.
x11docker automatically supports elogind in container with init system options --sysvinit, --runit and --openrc.
- You must set option
--sharecgroupto allowelogindin container. - If your host does not run with
elogind(but e.g. withsystemd), x11docker needs an elogind cgroup mountpoint at/sys/fs/cgroup/elogind. Run x11docker with root privileges to automatically create it. - Same goes for
elogindon host andsystemdin container; a cgroup mountpoint forsystemdmust be created. x11docker does this automatically if it runs as root. - Example to manually create elogind cgroup mountpoint on a systemd host:
mount -o remount,rw cgroup /sys/fs/cgroup # remove write protection
mkdir -p /sys/fs/cgroup/elogind
mount -t cgroup cgroup /sys/fs/cgroup/elogind -o none,name=elogind
mount -o remount,ro cgroup /sys/fs/cgroup # restore write protection
- Example to manually create a systemd cgroup mountpoint on an elogind host:
mkdir -p /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd
mount -t cgroup cgroup /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd -o none,name=systemd
Some desktop environments and applications need a running dbus daemon and/or dbus user session.
- use
--dbus-systemto run dbus system daemon. This includes option--dbus. Some desktops like cinnamon or deepin depend more on dbus system daemon than on a full blown init system. - use
--dbusto run image command withdbus-launch(fallback:dbus-run-session) for a dbus user session.
Collection of rarer needed but sometimes useful options. Most of interest:
--showid: Show container ID on stdout.--showenv: Show X environment variables on stdout.--env VAR=VALUE: Set environment variable in container.--cap-default: Allow default docker container capabilities.--user USER: Specify a container user different from current host user.--display N: Specify X display number for new X server.--runfromhost CMD: Run command from host on new X server.--runasroot CMD: Run command as root on container startup.
You can run x11docker on remote servers with ssh -X like a regular X application.
Example for an SSH setup with xpra:
read Xenv < <(x11docker --xdummy --display=30 x11docker/lxde pcmanfm)
echo $Xenv && export $Xenv
# replace "start" with "start-desktop" to forward a desktop environment
xpra start :30 --use-display --start-via-proxy=no
On another system in your network, attach with xpra over SSH:
xpra attach ssh:HOSTNAME:30 # replace HOSTNAME with IP or host name of ssh server
You can detach the SSH connection and reattach later again without terminating the application:
xpra detach ssh:HOSTNAME:30
You can stop xpra server without terminating x11docker:
xpra stop ssh:HOSTNAME:30
Warning: don't try this on localhost due to an xpra memory bug. On localhost, use xpra attach :30 instead.
To provide dockered applications as HTML5 web applications, you need xpra and websockify. Example:
read Xenv < <(x11docker --xdummy x11docker/lxde pcmanfm)
echo $Xenv && export $Xenv
# replace "start" with "start-desktop" to forward a desktop environment
xpra start $DISPLAY --use-display --html=on --bind-tcp=localhost:14501 --start-via-proxy=no
Now you can access your application at https://localhost:14501. Option settings are possible at https://localhost:14501/connect.html. Further infos at xpra wiki: HTML5 clients.
Broadway is a GTK3 specific feature to allow HTML5 web applications. The image needs libgtk-3-bin (debian) or gtk3 (Arch Linux) to be installed. A possible setup with x11docker:
x11docker --nothing --env BROADWAY_DISPLAY=:5 --env GDK_BACKEND=broadway \
-- --publish=8085:8085 x11docker/xfce "broadwayd :5 & sleep 2 && xfce4-terminal"
Now you can access the dockered web application at https://localhost:8085. A sample setup without x11docker is moondev/gtk3-docker.
Sample setup for VNC access:
read Xenv < <(x11docker --xdummy --showenv x11docker/lxde)
env $Xenv x11vnc -noshm -forever -localhost -rfbport 5910
In another terminal, start VNC viewer with vncviewer localhost:5910.
See man x11vnc for many details and further infos.
Option -noshm disables shared memory (MIT-SHM). To allow shared memory, remove -noshm and use isolation breaking x11docker option --hostipc.
There are short and simple but insecure alternatives for x11docker.
This is similar to x11docker option --hostdisplay:
- Share access to host X server with environment variable
DISPLAYand X unix socket in/tmp/.X11-unix. - Allow access with
xhostfor current local user and create a similar container user. - Allow shared memory with
--ipc=hostto avoid RAM access failures and rendering glitches due to extensionMIT-SHM.
xhost +SI:localuser:$(id -un)
docker run --rm -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
-v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:rw \
--user $(id -u):$(id -g) \
--ipc=host \
IMAGENAME IMAGECOMMAND
This nice short solution has the disadvantage of breaking container isolation. X security leaks like keylogging and remote host control can be abused by container applications.
This is similar to x11docker option --xephyr:
- Run Xephyr with disabled shared memory (extension
MIT-SHM) and disabled extensionXTEST. - Set
DISPLAYand share access to new unix socket/tmp/.X11-unix/X1. - Create unprivileged container user to avoid root in container.
Xephyr :1 -extension MIT-SHM -extension XTEST &
docker run --rm -e DISPLAY=:1 \
-v /tmp/.X11-unix/X1:/tmp/.X11-unix/X1:rw \
--user $(id -u):$(id -g) \
IMAGENAME IMAGECOMMAND
This solution is more secure than the above one as it does not give access to display :0 with host applications and does not need --ipc=host. To use this with single applications you can run a host window manager on Xephyr display, too, for example with env DISPLAY=:1 x-window-manager.
Some example images can be found on docker hub: https://hub.docker.com/u/x11docker/
-
Single GUI application in container:
- Terminal:
x11docker x11docker/xfce xfce4-terminal - Telegram messenger with persistant
HOMEfor configuration storage:x11docker --home xorilog/telegram - Fractal generator XaoS:
x11docker patricknw/xaos - Glxgears with hardware acceleration:
x11docker --gpu x11docker/xfce glxgears - Firefox with shared Download folder:
x11docker --hostipc --sharedir $HOME/Downloads jess/firefox - Chromium browser:
x11docker -- jess/chromium --no-sandbox - Tor browser:
x11docker jess/tor-browser - Atom editor with your host home as container home:
x11docker --homedir=$HOME jess/atom - VLC media player with shared Video folder and pulseaudio sound:
x11docker --pulseaudio --sharedir=$HOME/Videos jess/vlc
- Terminal:
-
Desktop in container:
-
Minimal images:
- FVWM:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/fvwm(based on alpine, 22.5 MB) - fluxbox:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/fluxbox(based on debian, 87 MB)
- FVWM:
-
Lightweight, small image:
- Lumina:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/lumina(based on Void Linux) - LXDE:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/lxde - LXQt:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/lxqt - Xfce:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/xfce - CDE Common Desktop Environment:
x11docker --desktop --hostnet x11docker/cde
- Lumina:
-
Medium:
- Mate:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/mate - Enlightenment:
x11docker --desktop --gpu --runit x11docker/enlightenment(Based on Void Linux) - Trinity (successor of KDE 3):
x11docker --desktop x11docker/trinity
- Mate:
-
Heavy, option
--gpurecommended:- Cinnamon:
x11docker --desktop --dbus-system x11docker/cinnamon - deepin:
x11docker --desktop --dbus-system x11docker/deepin - KDE Plasma:
x11docker --desktop x11docker/plasma - KDE Plasma as nested Wayland compositor:
x11docker --hostdisplay --gpu x11docker/plasma startplasmacompositor
- LiriOS:
x11docker --desktop lirios/unstable
- Cinnamon:
-
LXDE desktop with wine and a persistent home folder to preserve installed Windows applications, with pulseaudio sound and hardware acceleration:
x11docker --desktop --home --pulseaudio --gpu x11docker/lxde-wine
-
Sample screenshots can be found in screenshot branch
x11docker --desktop x11docker/lxde-wine

x11docker --desktop x11docker/mate