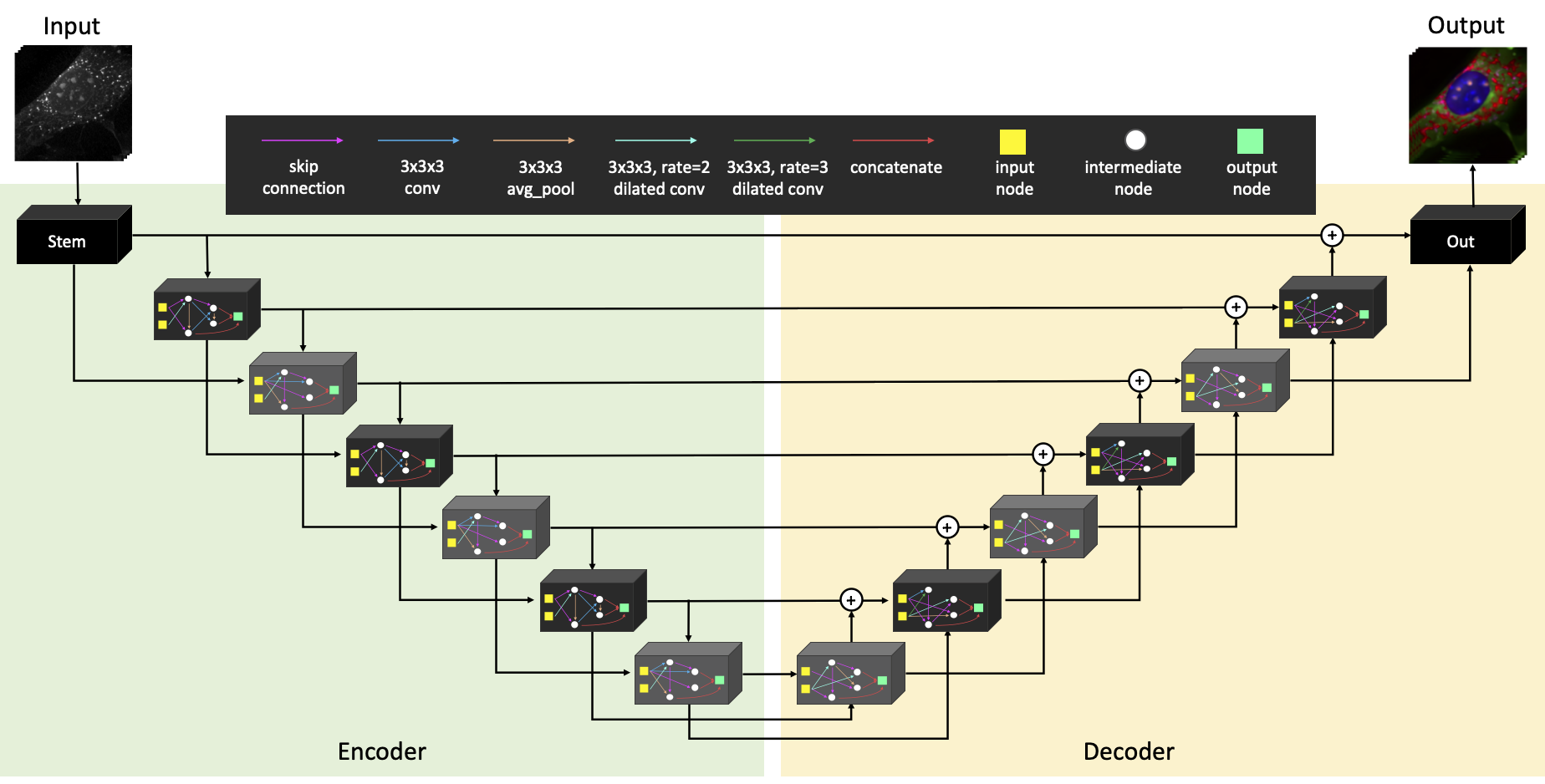
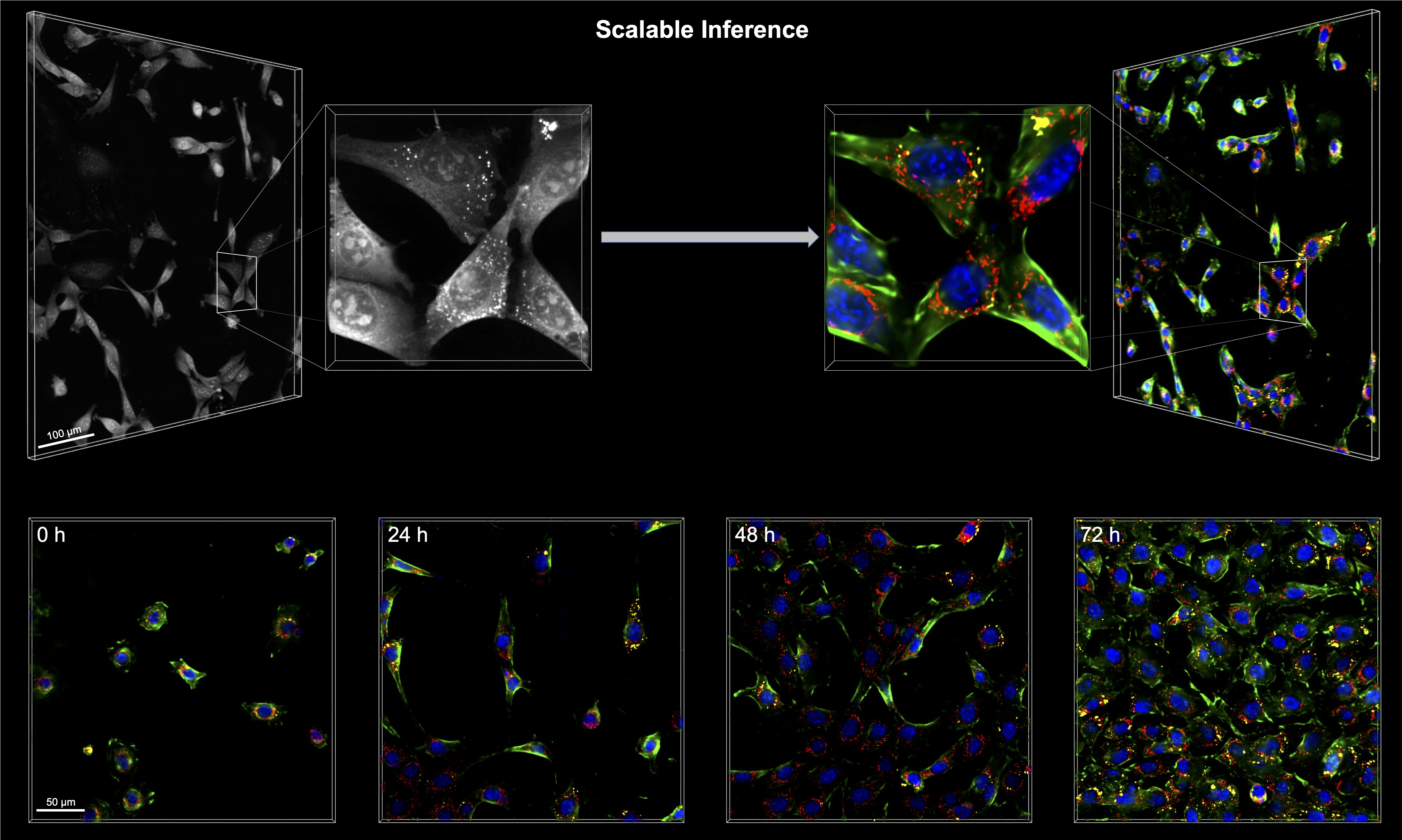
This repository contains PyTorch implementation of RI2FL.
Installation should be fairly quick (typically less than an hour). On a computer with CUDA-compatible GPUs and Linux operating system (e.g., Ubuntu 16.04), install CUDA/cuDNN and Python 3 (tested on 3.8) with the following command:
➜ pip install -r requirements.txtRI2FL class parses arguments from the yaml_file.
Exmaple of yaml_file:
# scripts/infer.yaml
path:
dataset: testset
model_path: models
save_path: result
setup:
fl_list: mem, nuc, oli
batch_size: 4
gpus: 0,1,2,3
cpus: 4
zoomed_size: [512, 512]
patch_size: 256
cropped_depth: 64
num_drop: 0
num_tta: 4# example.py
import argparse
from ri2fl import Ri2Fl
import torch.distributed as dist
argparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
argparser.add_argument("yaml")
argparser.add_argument("--local_rank", default=0, type=int)
cmd_args = argparser.parse_args()
ri2fl = Ri2Fl(f"{cmd_args.yaml}.yaml", cmd_args)
ri2fl.predict_all()
dist.destroy_process_group()Then, run the python script with the following command as bellow.
➜ python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 example.py inferThe demo data in the testset folder will output FL tomograms inferred from the input RI tomograms. In order to run RI2FL with your own data, organize your RI tomogram in this format and repeat the procedures above. Simple statistical analyses of the input/output tomograms could reproduce the results in the manuscript. Run time depends on data size and hardware; for a full-sized tomogram, it is expected to take less than a minute with a NVIDIA V100 GPU.
The samples for training a model are now available (Link).
You can build your own model and train it using samples.
➜ python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 train.py --data_root trainset --fl_type nuc --save_path outs/nuc