- Duke BME-590-02 Biomedical Machine Learning Final Project
- A practice to understand the effect of model compression under keras/tensorflow environment
- Original paper: DEEP COMPRESSION: COMPRESSING DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS WITH PRUNING, TRAINED QUANTIZATION AND HUFFMAN CODING click here
- In BME_Project_3_Model_Compression.ipynb click here, 3-stage model compression pipeline is implemented
- pruning
- quantization
- huffman coding
DenseNet100-12 from scratch
- number of convolutional layers: 100
- growth rate = 12
- used on Cifar10, Cifar100 and SVHN datasets click here to see densenet official git repo
- implemented using keras
- train, save and load pretrained weights densenet_100_12_pretrained.h5
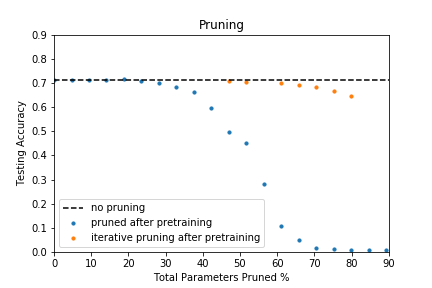
Results on direct pruning on the pretrained model all checkpoints are saved here

Results on iterative pruning on the pretrained model all checkpoints are saved here
Results on model compression rate after applying iterative pruning and quantization on the pretrained model

The results show that iteraitve pruning helps to slim the model while keep the model performance. For example, the pruned model with 70% sparsity can achieve 68% accuracy. The hyperparameters (epochs, learning rate, etc.) in the experiment are set the same for all sparsity levels. However, one can always tune those hyperparameters based on the sparsity level accordingly.
Direct pruning hurts the model performance but if retraining (i.e., fine-tuning) could be applied afterwards (only update the non-zero weights), the model performance evaluated in accuracy here will recover according to the paper.
As there is concern that the pruned model might have difficulty recovering from direct pruning, iterative pruning is commonly applied in real cases. Here tensorflow provides us with a ready-to-go package Magnitude-based weight pruning with Keras (click here) so that we can use directly to practice iterative pruning but with the caution that it is only compatible with tf 1.x version.
Quantization preserves the model performance using a technique called weight sharing. Weight sharing is implemented by K-means algorithm using sklearn package. Huffman coding will not affect the model performance and it is coded for each layer in the .ipynb file.
Duke ECE 590-10 Yiran Chen and Hai Li Lecture 13 slides on Model Compression
Duke BME 590-02 Ouwen Huang and Xiling Shen