promptfoo helps you tune LLM prompts systematically across many relevant test cases.
With promptfoo, you can:
- Test multiple prompts against predefined test cases
- Evaluate quality and catch regressions by comparing LLM outputs side-by-side
- Speed up evaluations by running tests concurrently
- Flag bad outputs automatically by setting "expectations"
- Use as a command line tool, or integrate into your workflow as a library
- Use OpenAI models, open-source models like Llama and Vicuna, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API
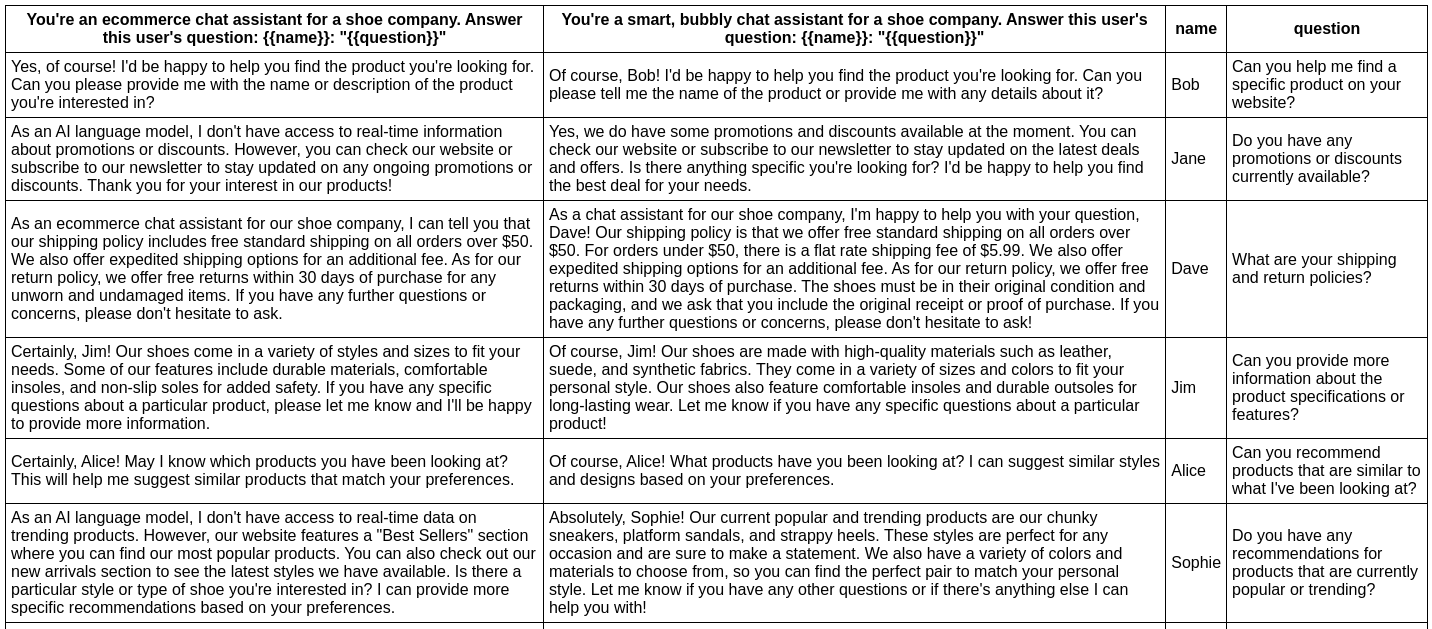
promptfoo produces matrix views that allow you to quickly review prompt outputs across many inputs. The goal: tune prompts systematically across all relevant test cases, instead of testing prompts by trial and error.
Here's an example of a side-by-side comparison of multiple prompts and inputs:
It works on the command line too:

To get started, run the following command:
npx promptfoo init
This will create some templates in your current directory: prompts.txt, vars.csv, and promptfooconfig.js.
After editing the prompts and variables to your liking, run the eval command to kick off an evaluation:
npx promptfoo eval
If you're looking to customize your usage, you have the full set of parameters at your disposal:
npx promptfoo eval -p <prompt_paths...> -o <output_path> -r <providers> [-v <vars_path>] [-j <max_concurrency] [-c <config_path>] [--grader <grading_provider>]<prompt_paths...>: Paths to prompt file(s)<output_path>: Path to output CSV, JSON, YAML, or HTML file. Defaults to terminal output<providers>: One or more of:openai:<model_name>, or filesystem path to custom API caller module<vars_path>(optional): Path to CSV, JSON, or YAML file with prompt variables<max_concurrency>(optional): Number of simultaneous API requests. Defaults to 4<config_path>(optional): Path to configuration file<grading_provider>: A provider that handles the grading process, if you are using LLM grading
After running an eval, you may optionally use the view command to open the web viewer:
npx promptfoo view
In this example, we evaluate whether adding adjectives to the personality of an assistant bot affects the responses:
npx promptfoo eval -p prompts.txt -v vars.csv -r openai:gpt-3.5-turboThis command will evaluate the prompts in prompts.txt, substituing the variable values from vars.csv, and output results in your terminal.
Have a look at the setup and full output here.
You can also output a nice spreadsheet, JSON, YAML, or an HTML file:
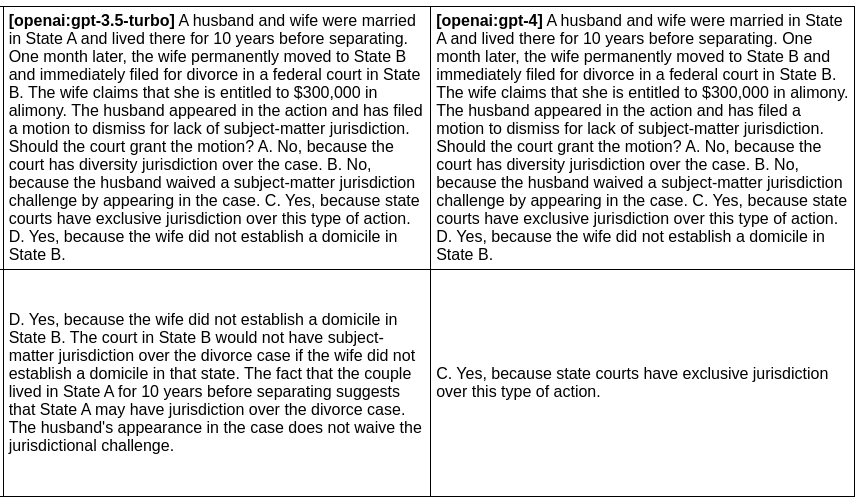
In this example, we evaluate the difference between GPT 3 and GPT 4 outputs for a given prompt:
npx promptfoo eval -p prompts.txt -r openai:gpt-3.5-turbo openai:gpt-4 -o output.htmlProduces this HTML table:
Full setup and output here.
You can also use promptfoo as a library in your project by importing the evaluate function. The function takes the following parameters:
-
providers: a list of provider strings orApiProviderobjects, or just a single string orApiProvider. -
options: the prompts and variables you want to test:{ prompts: string[]; vars?: Record<string, string>; }
promptfoo exports an evaluate function that you can use to run prompt evaluations.
import promptfoo from 'promptfoo';
const options = {
prompts: ['Rephrase this in French: {{body}}', 'Rephrase this like a pirate: {{body}}'],
vars: [{ body: 'Hello world' }, { body: "I'm hungry" }],
};
(async () => {
const summary = await promptfoo.evaluate('openai:gpt-3.5-turbo', options);
console.log(summary);
})();This code imports the promptfoo library, defines the evaluation options, and then calls the evaluate function with these options. The results are logged to the console:
{
"results": [
{
"prompt": {
"raw": "Rephrase this in French: Hello world",
"display": "Rephrase this in French: {{body}}"
},
"vars": {
"body": "Hello world"
},
"response": {
"output": "Bonjour le monde",
"tokenUsage": {
"total": 19,
"prompt": 16,
"completion": 3
}
}
},
// ...
],
"stats": {
"successes": 4,
"failures": 0,
"tokenUsage": {
"total": 120,
"prompt": 72,
"completion": 48
}
},
"table": [
// ...
]
}- Setting up an eval: Learn more about how to set up prompt files, vars file, output, etc.
- Configuring test cases: Learn more about how to configure expected outputs and test assertions.
We support OpenAI's API as well as a number of open-source models. It's also to set up your own custom API provider. See Provider documentation for more details.
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a pull request or open an issue.
promptfoo includes several npm scripts to make development easier and more efficient. To use these scripts, run npm run <script_name> in the project directory.
Here are some of the available scripts:
build: Transpile TypeScript files to JavaScriptbuild:watch: Continuously watch and transpile TypeScript files on changestest: Run test suitetest:watch: Continuously run test suite on changes