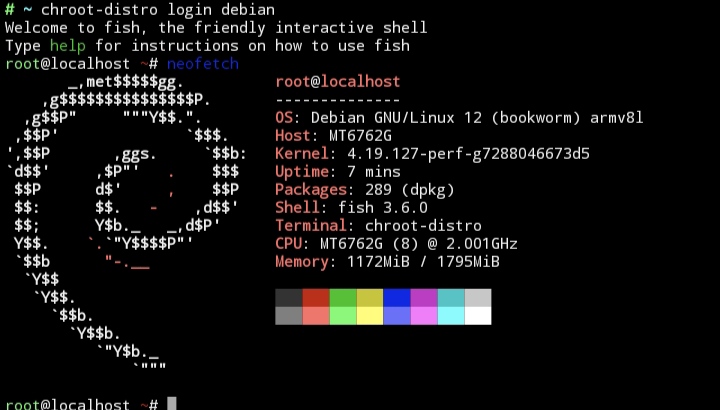
chroot-distro : Install linux distributions on android
- chroot-distro path : /data/local/chroot-distro/
Reasonably new Busybox-ndk magisk module version installed (1.36.1 is known to work, 1.32.1 is known to not work). If new enough version is not installed it may lead to problems with downloading rootfs.
- /dev
- /sys
- /proc
- /dev/pts
- /sdcard
- /system (NOTE: not used by default)
- /storage
- /data (NOTE: not used by default)
Be aware that as the chroot-distro needs to be running as a root to function there is a possibility that some corner case may have been missed where it is possible to accidentally removed more files than intended. The developers strive to ensure that this will not happen but before using the software you should backup your files/firmware just in case. Please also note that this is not specific to only this software but should be used as a general caution when ever using a rooted device.
As they say: With great power comes great responsibility.
- help
chroot-distro help
- list of available linux distributions
chroot-distro list
- download rootfs
chroot-distro download <distro>
- re-download rootfs
chroot-distro redownload <distro>
- delete rootfs
chroot-distro delete <distro>
- install distro
- By default does not mount
/dataor/systemfolder, use-aor--androidto mount it
- By default does not mount
chroot-distro install [-a|--android] <distro>
- reinstall distro
- By default does not mount
/dataor/systemfolder, use-aor--androidto mount it
- By default does not mount
chroot-distro reinstall [-a|--android] <distro>
- uninstall distro
chroot-distro uninstall <distro>
- backup distro
- If path given, then backup saved at that path
chroot-distro backup <distro> [<path>]
- delete default backup
chroot-distro unbackup <distro>
- restore distro
- By default restores as is, use
-dor--defaultto reset to default settings (note: only those set during install) - If path given, then backup restored from that path
- If using old format backups you may need to use
--forceto restore the backup but please be aware that you should review the backup before restoring said backup as there could be unintended side effects (for example system mounts shadowing restored files or internal storage running out)
- By default restores as is, use
chroot-distro restore [-d|--default] [--force] <distro> [<path>]
- unmount system mount points
chroot-distro unmount <distro>
- run command
- If command is quoted then can pass parameters to command, for example
"ping 127.0.0.1"
- If command is quoted then can pass parameters to command, for example
chroot-distro command <distro> <command>
- login to distro
chroot-distro login <distro>
chroot-distro download ubuntu
chroot-distro install ubuntu
chroot-distro login ubuntu
Note: right side is used as distro identifier, and it needs to be lowercase for it to be properly identified.
- Kali Linux : kali
- Parrot OS : parrot
- Alpine Linux : alpine
- Arch Linux : archlinux
- BackBox : backbox
- Centos : centos
- Centos Stream : centos_stream
- Artix Linux : artix
- Debian : debian
- Deepin : deepin
- Fedora 39 : fedora
- Manjaro : manjaro
- OpenKylin : openkylin
- OpenSUSE : opensuse
- Pardus : pardus
- Ubuntu : ubuntu
- Void Linux : void
You can use chroot-distro on any terminal, for example MT Manager, Termux, TWRP or Android terminal emulator (ADB Shell)...
your can use any vnc app , tutorial (tested on ubuntu and debian)
apt update
apt upgrade
apt install tightvncserver nano dbus-x11 xfce4 xfce4-goodies xfce4-terminal
update-alternatives --config x-terminal-emulator
vncserver
vncserver -kill :1
echo 'startxfce4 &' >> ~/.vnc/xstartup
start server :
vncserver
stop server :
vncserver -kill :1
Be default Android prevents suid usage under /data folder. This will prevent using sudo inside the rootfs. There is a few alternatives how this can be solved:
- remount
/datafor the current process with needed capabilities (needs to be run once for every session)
su -c mount -o remount,dev,suid /data- create an image to be mounted at
/data/local/chroot-distro
# use whatever size you want
su -c truncate -S 15G /data/local/distros.img
su -c mke2fs -t ext4 /data/local/distros.img
# following command needs to be run every time device is rebooted
su -c mount /data/local/distros.img /data/local/chroot-distro- Format SD card with ext4
- Follow the instructions on how to mount ext4 SD card
- Mount point should be
/data/local/chroot-distroinstead of/storage/sdcard1mentioned in the post - Mounting will need to be done every time device is rebooted
From security perspective the second and third one are the better as there is less of chance to accidentally running something which you did not intend. The third one (and second one if the image is created to SD card) helps preventing the internal storage from running out and also helps lessen the amount of writes done to internal storage (thus prolonging the use of the device). Note that when using third alternative you can't use it for android stuff (at least by default).
If you want to help with development, or if developers have requested you to check a bug report against latest development version, you can create development version with the help of this command:
zip chroot-distro.zip config.sh module.prop META-INF/com/google/android/* system/bin/chroot-distroAlternative way to do the development is to enable ssh with one of the distros and then remotely update the script to a separate location, and then invoke the development script against some other distro. This way there is no need to reboot the device, thus making the development quicker. Or even, doing the development directly on the device (either physically, or by remote connection), if that is your preferred way.
For any non-trivial change, you should verify that the change works, not only from Termux (or some other on-device terminals) but also with Android terminal emulator (ADB Shell). This is because ADB Shell will only have Busybox and Android Toybox commands available, and they may not behave the same way as the more full blown counterparts available for example in Termux.
During the development you should use shellcheck to ensure that the changes you make to the script will be POSIX compliant, and that they do not introduce new shellcheck warnings (either fix the code or document why the warning is ok with # shellcheck disable=SCXXXX and accompanied comment). And if you are not familiar with shell scripts (or even if you are familiar), you should peruse tutorial made by Grymoire as he explains the POSIX shell basics (and some not so basic stuff) very well.
chroot-distro uses semantic versioning for version numbers. Versioning uses three levels: major, minor and patch. Major version will change if there is breaking changes in API. Minor version will change for new features (or otherwise significant changes which does not break backwards compatibility). Patch version is reserved only for bug fixes, or really small changes (note: no breaking changes).