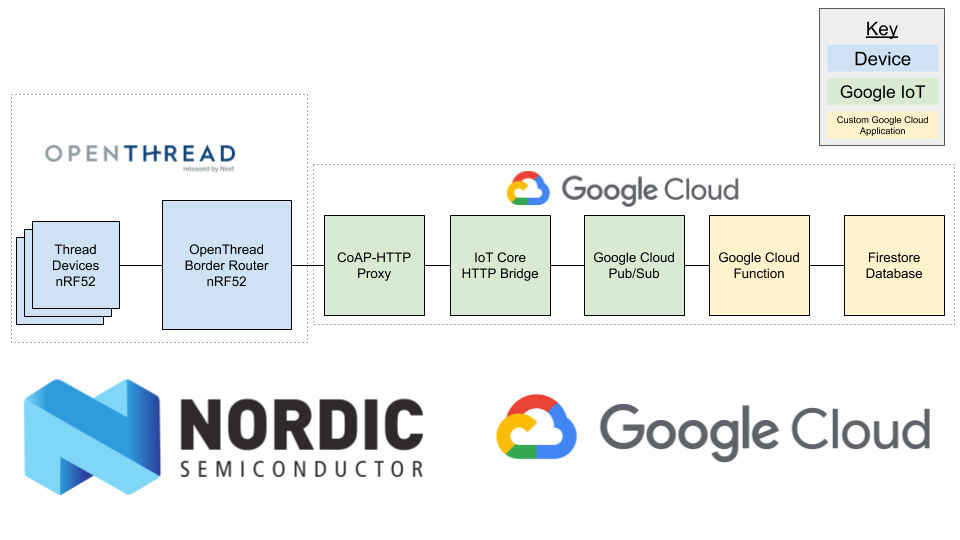
This repository contains an example of Google Cloud IoT interaction with the Thread-enabled devices over CoAP and CoAPs.
Thread is an emerging low-power and constraint-friendly IP-based networking protocol with tremendous potential. This demo shows the potential of Thread and the potential of Google IoT Core as a point of connectivity for all IoT devices.
This example is an addition to the nRF5 SDK for Thread and Zigbee v2.0.0 released by Nordic Semiconductor.
Additionally, the new set of updated OpenThread libraries has been generated from the following commit. Since the latest SDK does not include new OpenThread features, such as SNTP client or CoAP extensions, this example uses new libraries archived in the openthread_1253becb.zip file.
The firmware precommissions a Thread device with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Network Name | GCP Demo |
| PAN ID | 0xabcd |
| Network Key | 00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff |
| Extended PAN ID | dead00beef00cafe |
| Channel | 11 |
| On-Mesh Prefix | fd11:22:: |
The above default values are configurable from the main.c file of the example.
In order for a device to connect, it must first be registered with Cloud IoT Core. Registration consists of adding a device to a collection (the registry) and defining some essential properties. You can register a device with Cloud Platform Console or gcloud commands.
Cloud IoT Core uses public key (or asymmetric) authentication:
- The device uses a private key to sign a JSON Web Token (JWT). The token is passed to Cloud IoT Core as proof of the device's identity.
- The service uses the device public key (uploaded before the JWT is sent) to verify the device's identity. For details, see the sections on creating key pairs, using JWTs, and device security.
The first step to activate a new device is to create a “Device” keypair (see here for more info):
To generate an ES256 key pair using the Eliptic Curve algorithm, run the following commands:
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -noout -out ec_private.pem
openssl ec -in ec_private.pem -pubout -out ec_public.pemThese commands create the following public/private key pair:
- ec_private.pem: The private key that must be securely stored on the device. It is used to sign the authentication JWT.
- ec_public.pem: The public key that must be stored in Cloud IoT Core. It is used to verify the signature of the authentication JWT.
Next, go to your IOT Core registry, create a device via the Cloud Console or gcloud.
Provide a Device ID - it should match whatever is configured in the main.c file of the example (as GCP_COAP_IOT_CORE_DEVICE_ID). Select ES256 Public key format and copy the contents of ec_public.pem.
Run the following commands:
gcloud beta iot devices create SOMEDEVICEID --region us-central1 --project \
coap-iot-proxy --registry test-reg --public-key path=ec_public.pem,type=ES256A Thread Border Router connects a Thread network to other IP-based networks, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet. A Thread network uses Border Router to connect to other networks. This example uses IPv4 connectivity with Google IoT Cloud and therefore it is required in this demo.
Follow OpenThread Border Router guide in order to set up Raspberry Pi 3B with Nordic nRF52840 acting as NCP.
Make sure that Thread network parameters at OpenThread Border Router are aligned with those set in firmware side.
You must install a set of tools to complete the environment setup process. Because this repository contains a plugin of the regular nRF5 SDK for Thread and Zigbee, follow the Environment setup section.
Follow these instructions to build firmware for the nRF52840 device.
-
Download nRF5 SDK for Thread and Zigbee v2.0.0 from this website
-
Copy the content of the
thread/examples/google_iot_coapdirectory into a coresponding folder in the previously downloaded SDK. -
Unzip
openthread_1253becb.zipto thethread/examples/google_iot_coapdirectory. Note that you should see the following path structure:thread/examples/google_iot_coap/openthread_1253becb/lib -
Change the directory to the example's armgcc project.
cd thread/examples/google_iot_coap/pca10056/armgcc -
Make sure to provide correct credentials (Device ID and Private Key) by filling
GCP_COAP_IOT_CORE_DEVICE_IDandGCP_COAP_IOT_CORE_DEVICE_KEYdefines in thethread/examples/google_iot_coap/main.cfile.For example:
#define GCP_COAP_IOT_CORE_DEVICE_ID "nrf52-01" #define GCP_COAP_IOT_CORE_DEVICE_KEY "-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----\r\n" \ "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\r\n" \ "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\r\n" \ "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX==\r\n" \ "-----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----\r\n"
-
Build the example.
make
-
Flash the firmware to the nRF52840 DK.
make erase flash
In order to enable a DTLS session between the Thread device and Google IoT Cloud, modify the following line in the main.c file of the example:
#define GCP_COAP_SECURE_ENABLED 0and change it to:
#define GCP_COAP_SECURE_ENABLED 1You can interact with the development kit by using buttons and LEDs.
- Open Firestore database and choose your device.
- Turn on OpenThread Border Router.
- Turn on the Thread Device and wait few seconds to make sure that device joined a Thread Network.
- Observe LED status:
- LED1 blinking: Device is joining a Thread Network
- LED1 solid: Device joined a Thread Network
- Push
BUTTON 3to decrease the simulatedcountervalue. - Observe data received in Firestore database. https://console.cloud.google.com/firestore/data/devices/{DEVICE_ID}?project=coap-iot-proxy
- Push
BUTTON 4to increase the simulatedcountervalue. - Observe data received in Firestore database. https://console.cloud.google.com/firestore/data/devices/{DEVICE_ID}?project=coap-iot-proxy
- Push
BUTTON 1to obtain configuration of the device. Note that the device accepts only the following strings encoded in base64:- LED1
- LED2
- LED3
- LED4
- Observe that only the configured LED is turned on.
Follow this guide to test connectivity to public Google DNS server (64:ff9b::808:808) and Google Cloud IoT CoAP Proxy (64:ff9b::23c1:f84c).
How to verify that two nodes have joined the same network and my device communicates with Google IoT Cloud?
You can use the IEEE 802.15.4 sniffer project to sniff Thread packets. To decrypt them correctly, you need to set up Wireshark according to the points from 4 to 8 in the following guide.