Empower the architects for analysing the relationship between structure & embodied carbon in early design stages!
Looking at all the new construction that is projected to take place between now and 2040, we see the critical role embodied carbon plays. The opportunity to change the embodied material decreases as the project progresses, since each change has a direct impact on the project cost.
Visit https://learncarbon.me/ to learn more details on the project.
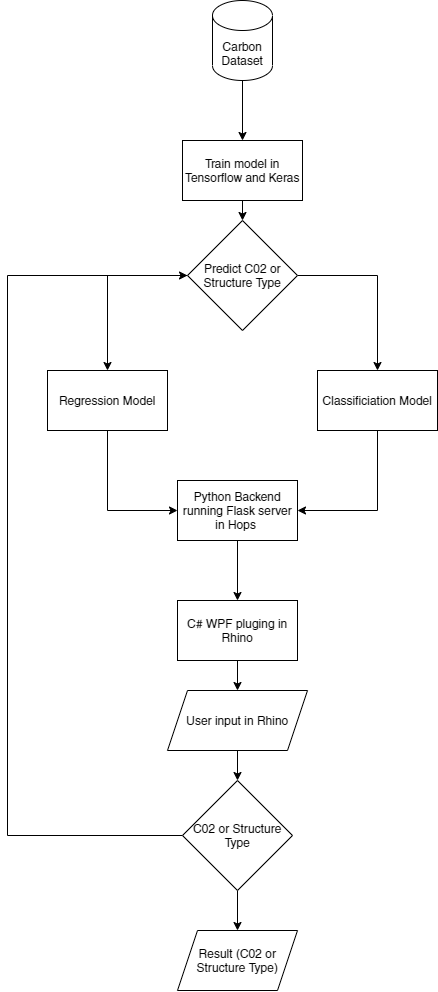
LearnCarbon is a Rhino plugin that integrates two machine learning models:
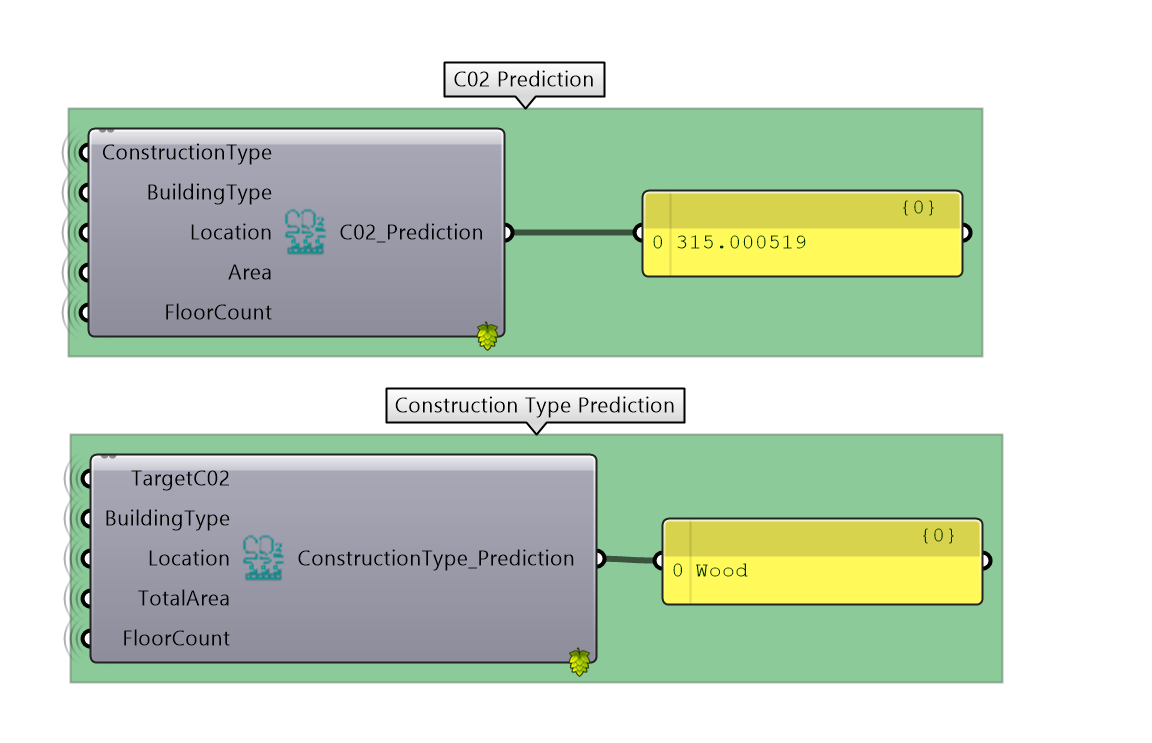
- Model A: inputs a conceptual massing model by just a click and gathers data on the area, total built-up, structure type and predicts the Global Warming Potential
- Model B: inputs area, total built-up, target GWP value and predicts the suitable structure.
Also check requirements.txt file in the src repository.
- pandas: required to read the library.
- numpy: required for the matrix calculations
- matplotlib: Required for the data visualization.
- seaborn: Statistical data visualization.
- tensorflow: An end-to-end open source machine learning platform.
- scikit-learn: Simple and efficient tools for predictive data analysis.
- joblib: A set of tools to provide lightweight pipelining in Python
- ghhops_server: Install ghhops_server
- flask: A Python module that lets you develop web applications easily.
- Altair: A declarative statistical visualization library for Python.
- CLF: Embodied Carbon Benchmark study is the initial dataset used in LearnCarbon
- Synthetic data: Data transformation (categorical to numerical) and data augmentation (add structure categorization depending on the CO2 emission, and building size.
- Model: Training on google collab with Tensorflow and Keras
- Validating the model: Plot learning curve
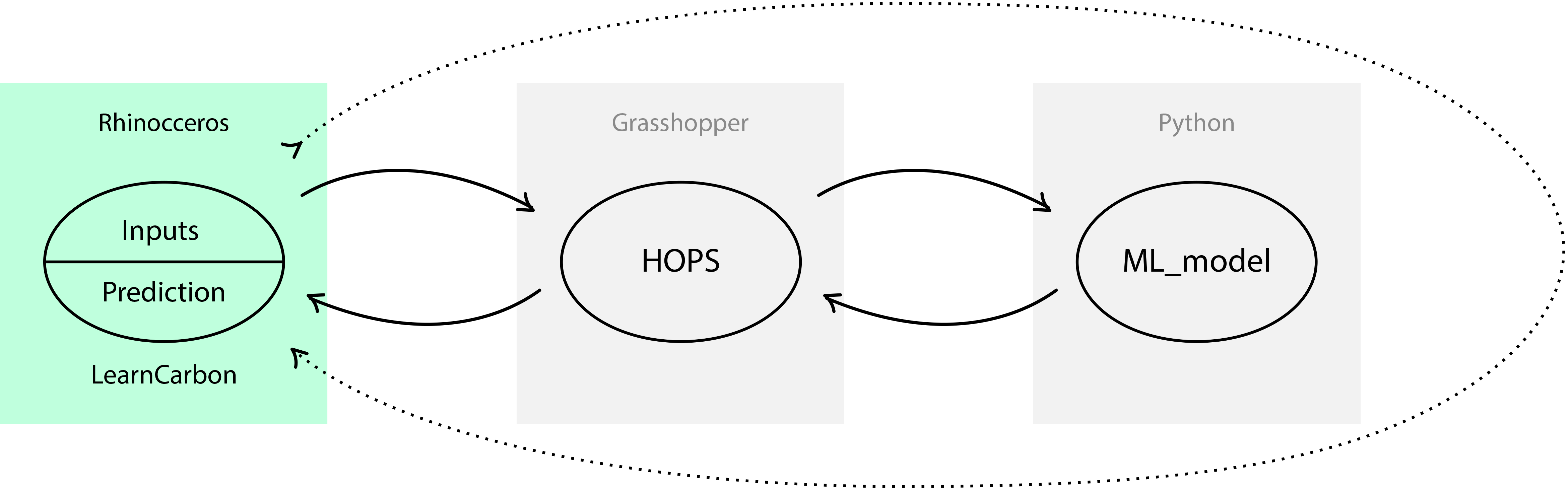
- Hops gets parameters from the 3D model designed in Rhino , and the users inputs.
- Hops is passing these values to the ML model and calling the ML model itself using a flask server
- After the prediction is calculated Hops returns the value to a Rhino .rhp plugin written in c# and WPF, which displays the result in LearnCarbon.
You would need a working Rhino 7 license and an IDE like Visual Studio where you can run the app.py file in src.