KPhysics is an improved and extended version of Hayden Marshall's JPhysics. It is a 2D physics engine with zero third-party dependencies.
It is written in Kotlin and is intended to be easily used in games programmed with Kotlin or Java.
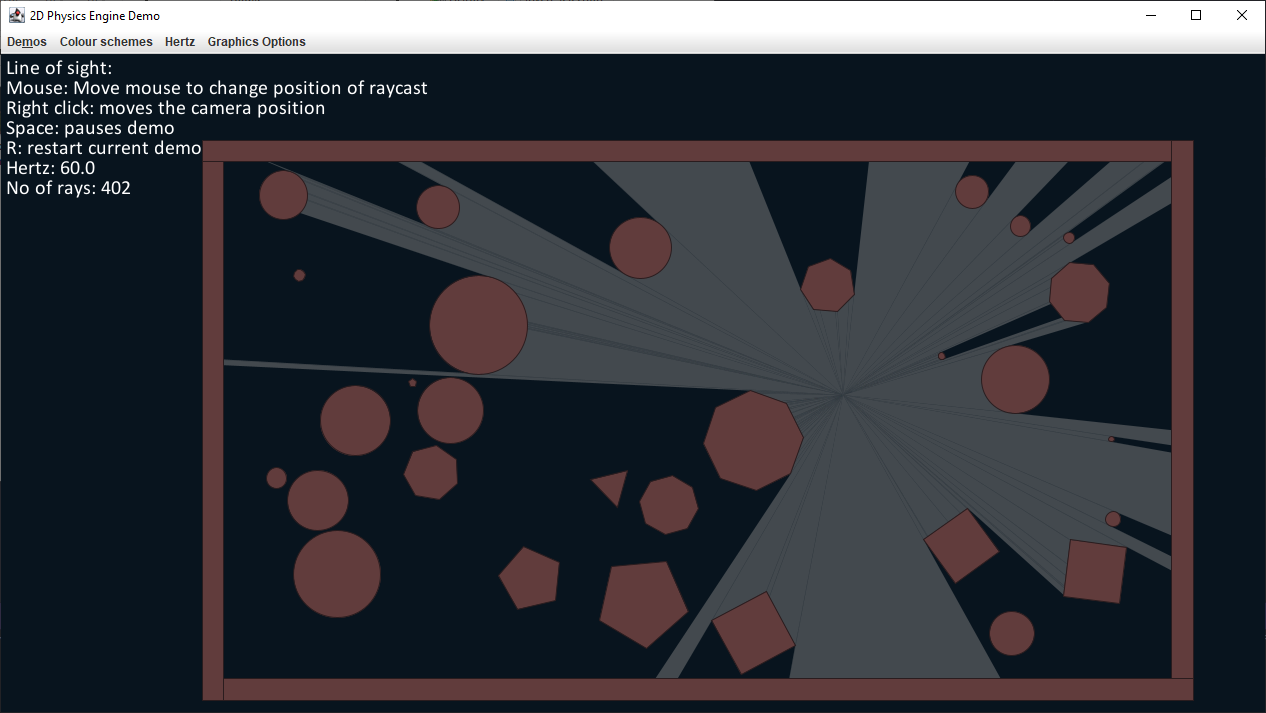
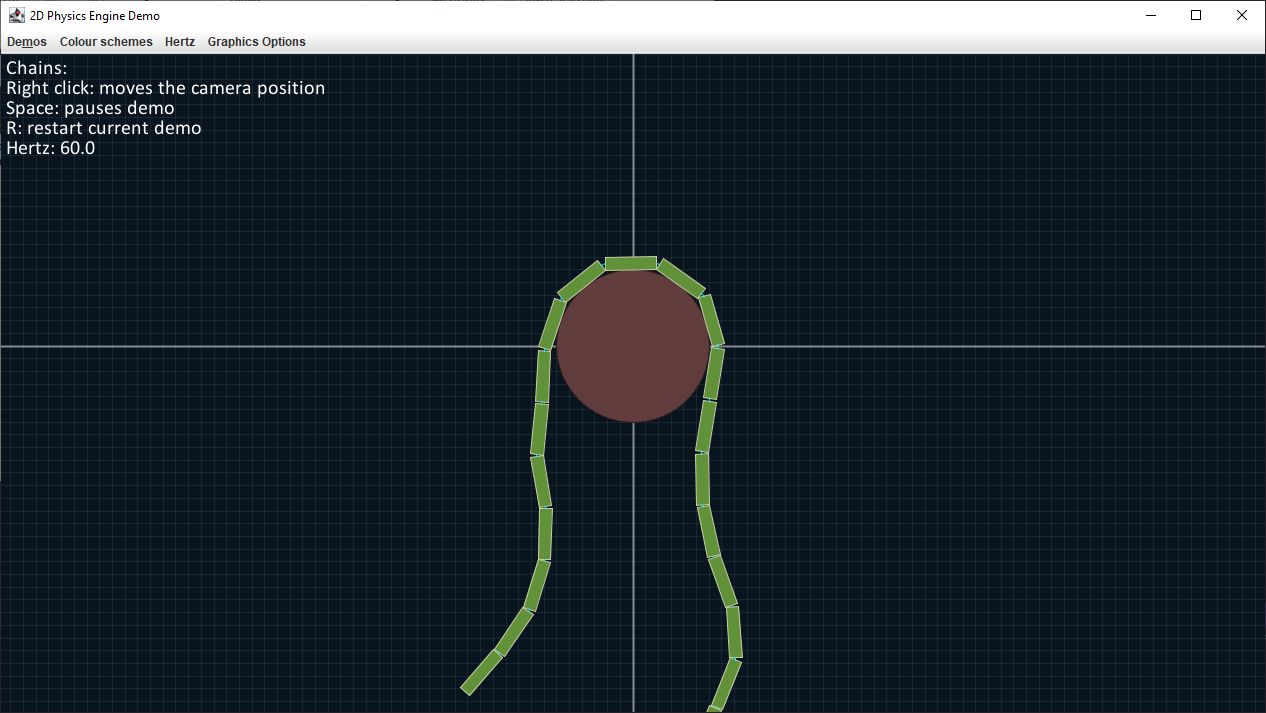
A tech demo can be found here and includes various examples to show what the engine is capable of.
To run the demos yourself simply clone the KPhysicsDemo repository and run the Main.java file.

- Rigid body dynamics
- Primitive joint constraints
- Momentum
- Friction
- Restitution
- Collision response (Sequential Impulses Solver)
- Stable object stacking
- Orbits
- Explosions
- Object slicing
- AABB queries (Broadphase)
- One-shot contact manifolds
- Discrete collision detection
- Convex polygon and circle collisions
- Ray casting
- Position resolution handling
- Proximity
- Ray casting
- Particle
- An appropriate IDE for example Intellij (with java 1.8+ JDK installed)
- Maven/Gradle or other dependency manager
Add KPhysics to your classpath by adding a Maven/Gradle dependency from Jitpack.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jitpack.io</id>
<url>https://jitpack.io</url>
</repository>
</repositories><dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.Chafficui</groupId>
<artifactId>KPhysics</artifactId>
<version>Tag</version>
</dependency>
</dependency>allprojects {
repositories {
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}
dependencies {
compile 'com.github.Chafficui:KPhysics:Tag'
}The world is an instance that exerts physical forces on all objects contained within it. It can be given a gravity vector, such as (0, -9.81). If this is not done, there is no gravity in the world.
val world = World(Vec(.0, -9.81))The next step is to create bodies. These are objects on which forces act, such as the player, or the ground, or even a bouncy ball (like it is in our example).
val bouncyBall = Body(Circle(20.0), .0, 200.0)A Body takes a shape (Polygon or Circle) and the position with x and y coordinates. We can also change some aspects of it, like the density, the drag and also the restitution (what we will do).
bouncyBall.restitution =1.0We will also add a plattform, where we set the density to zero, so that it does not move if the bouncy ball touches it.
val plattform = Body(Polygon(600.0, 20.0), .0, -300.0)
plattform.setDensity(.0)The last thing we need to add in this step is the bodies to the world. We do this as follows.
world.addBody(bouncyBall)
world.addBody(plattform)In your game loop or update method you should now run the world steps.
world.step(deltaTime)This takes the time passed between the last step and now.
KPhysics is very feature rich. For example, there is RayTracing, particle physics and explosion physics. To learn more about these things, it is worth taking a look at our dokka, or the javascripts.
Coming soon!
Everything in this project is based on the JPhysics.