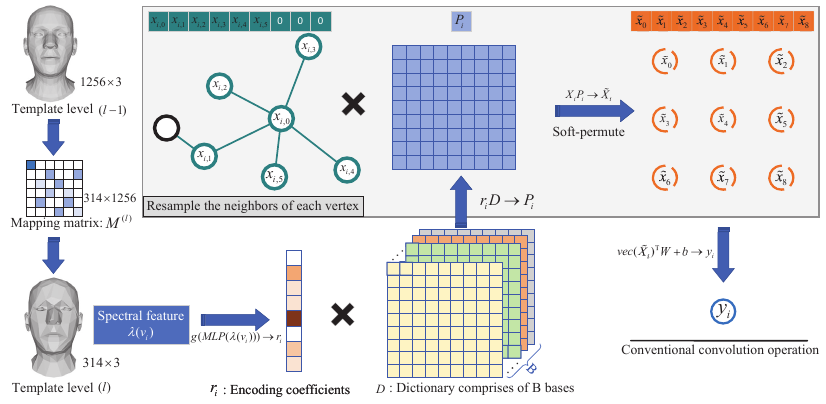
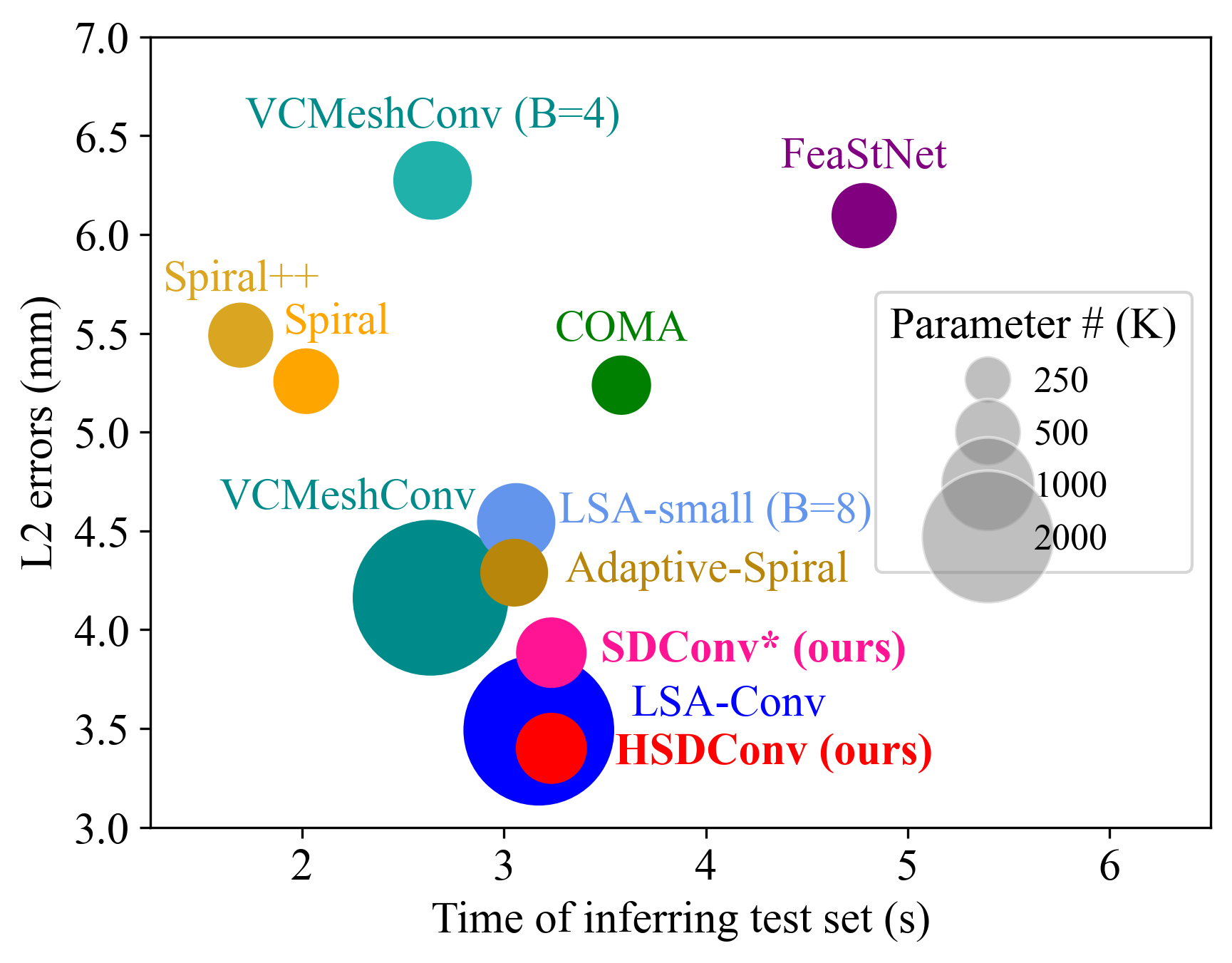
 This repository is the official implementation of my paper: "Learning Spectral Dictionary for Local Representation of Mesh"
This repository is the official implementation of my paper: "Learning Spectral Dictionary for Local Representation of Mesh"
Learning mesh representation is important for many 3D tasks. Conventional convolution for regular data (i.e., images) cannot directly be applied to meshes since each vertex's neighbors are unordered. Previous methods use isotropic filters or predefined local coordinate systems or learning weighting matrices for each template vertex to overcome the irregularity. Learning weighting matrices to resample the vertex's neighbors into an implicit canonical order is the most effective way to capture the local structure of each vertex. However, learning weighting matrices for each vertex increases the model size linearly with the vertex number. Thus, large parameters are required for high-resolution 3D shapes, which is not favorable for many applications. In this paper, we learn spectral dictionary (i.e., bases) for the weighting matrices such that the model size is independent of the resolution of 3D shapes. The coefficients of the weighting matrix bases are learned from the spectral features of the template and its hierarchical levels in a weight-sharing manner. Furthermore, we introduce an adaptive sampling method that learns the hierarchical mapping matrices directly to improve the performance without increasing the model size at the inference stage. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our model produces state-of-the-art results with much smaller model size.
This code was written in Pytorch 1.4. We use tensorboardX for the visualisation of the training metrics. We recommend setting up a virtual environment using Miniconda. To install Pytorch in a conda environment, simply run
$ conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch
Then the rest of the requirements can be installed with
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
Here are the pre-processed datasets on Google Drive: DFAUST-dataset.zip and COMA-dataset.zip.
Here are the trained models and logs on Google Drive DFAUST-Models.zip and COMA-Models.zip. Please put the models in the folder as the structure below.
In order to use a pytorch dataloader for training and testing, we split the data into seperate files by:
$ python data_generation.py --root_dir=/path/to/data_root_dir --dataset=DFAUST --num_valid=100
The following is the organization of the dataset directories expected by the code:
- data root_dir/
- dataset name/ (eg DFAUST-dataset)
- COMA_downsample
- downsampling_matrices.pkl (created by the code the first time you run it)
- pai_matrices.pkl
- Processed/
- sliced
- train.npy (number_meshes, number_vertices, 3) (no Faces because they all share topology)
- test.npy
- points_train/ (created by data_generation.py)
- points_val/ (created by data_generation.py)
- points_test/ (created by data_generation.py)
- paths_train.npy (created by data_generation.py)
- paths_val.npy (created by data_generation.py)
- paths_test.npy (created by data_generation.py)
- mean.tch
- std.tch
- sliced
- results
- HSDConvFinal-x (hierarchical SDConv result)
- checkpoints
- run.log
- SDConvFinal-x (SDConv result)
- checkpoints
- run.log
- HSDConvFinal-x (hierarchical SDConv result)
- template.obj
- COMA_downsample
- dataset name/ (eg DFAUST-dataset)
Config line 32-36 in pai3DMM.py
root_dir = 'dataset/COMA-dataset' ## 'COMA-dataset' or 'DFAUST-dataset' or 'MANO-dataset''
is_hierarchical = True ## 'True' or 'False' for learnable up/down sampling
is_same_param = 0 ## '0', '1', '2' where '1' for increaes channel and '2' for increase base
is_old_filter = False ## 'False' or 'True' to use different spectral filter
mode = 'test' ## 'test' or 'train' to train or test the models
python pai3DMM.py
- The code has compatibility with both mpi-mesh and trimesh packages (it can be chosen by setting the meshpackage variable pai3DMM.py).
The structure of this codebase is borrowed from Neural3DMM.
Please consider citing our work if you find it useful:
@inproceedings{ijcai2021-95,
title = {Learning Spectral Dictionary for Local Representation of Mesh},
author = {Gao, Zhongpai and Yan, Junchi and Zhai, Guangtao and Yang, Xiaokang},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Joint Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, {IJCAI-21}},
publisher = {International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization},
editor = {Zhi-Hua Zhou},
pages = {685--692},
year = {2021},
month = {8},
note = {Main Track}
doi = {10.24963/ijcai.2021/95},
url = {https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2021/95},
}