This notebook provides source code for solving discrete problems (i.e. with a discrete/finite number of states). The task is described as follows: There are 4 locations (labeled by different letters) and your job is to pick up the passenger at one location and drop him off in another. You receive +20 points for a successful dropoff, and lose 1 point for every timestep it takes. There is also a 10 point penalty for illegal pick-up and drop-off actions.
The task is solved by using a Q-table which associates for each state the reward the agent may expected for each action. The Q-table is simply a matrix of rows equal to the number of possible states and of columns equal to the number of possible actions. We update this the Bellman equation:
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + gamma * (reward + np.max(Q[next_state, ]) - Q[state, action])
It updates the previous estimation with the new incoming data/knowledge: it sets the new Q-value as the observed reward plus the maximum estimated future rewards. We update the table by playing the game and taking random action to explore all possible states. The random actions are taken less and less frequently, letting the agent "observe" the consequence of the decisions taken.
This notebook provides source code for solving continuous problems (i.e. with a infinite number of states). The task is described as follows: The system is controlled by applying a force of +1 or -1 to the cart. The pendulum starts upright, and the goal is to prevent it from falling over. A reward of +1 is provided for every timestep that the pole remains upright. The episode ends when the pole is more than 15 degrees from vertical, or the cart moves more than 2.4 units from the center.
The task is solved by discretizing the states and using a Q-table.
This notebook provides source code for solving discrete problems. The task is described as follows: If lander moves away from landing pad it loses reward back. Episode finishes if the lander crashes or comes to rest, receiving additional -100 or +100 points. Each leg ground contact is +10. Firing main engine is -0.3 points each frame. Solved is 200 points. Landing outside landing pad is possible. Fuel is infinite, so an agent can learn to fly and then land on its first attempt. Four discrete actions available: do nothing, fire left orientation engine, fire main engine, fire right orientation engine.
The task is solved by using Convolutional Neural Networks which approximate a Q-table.
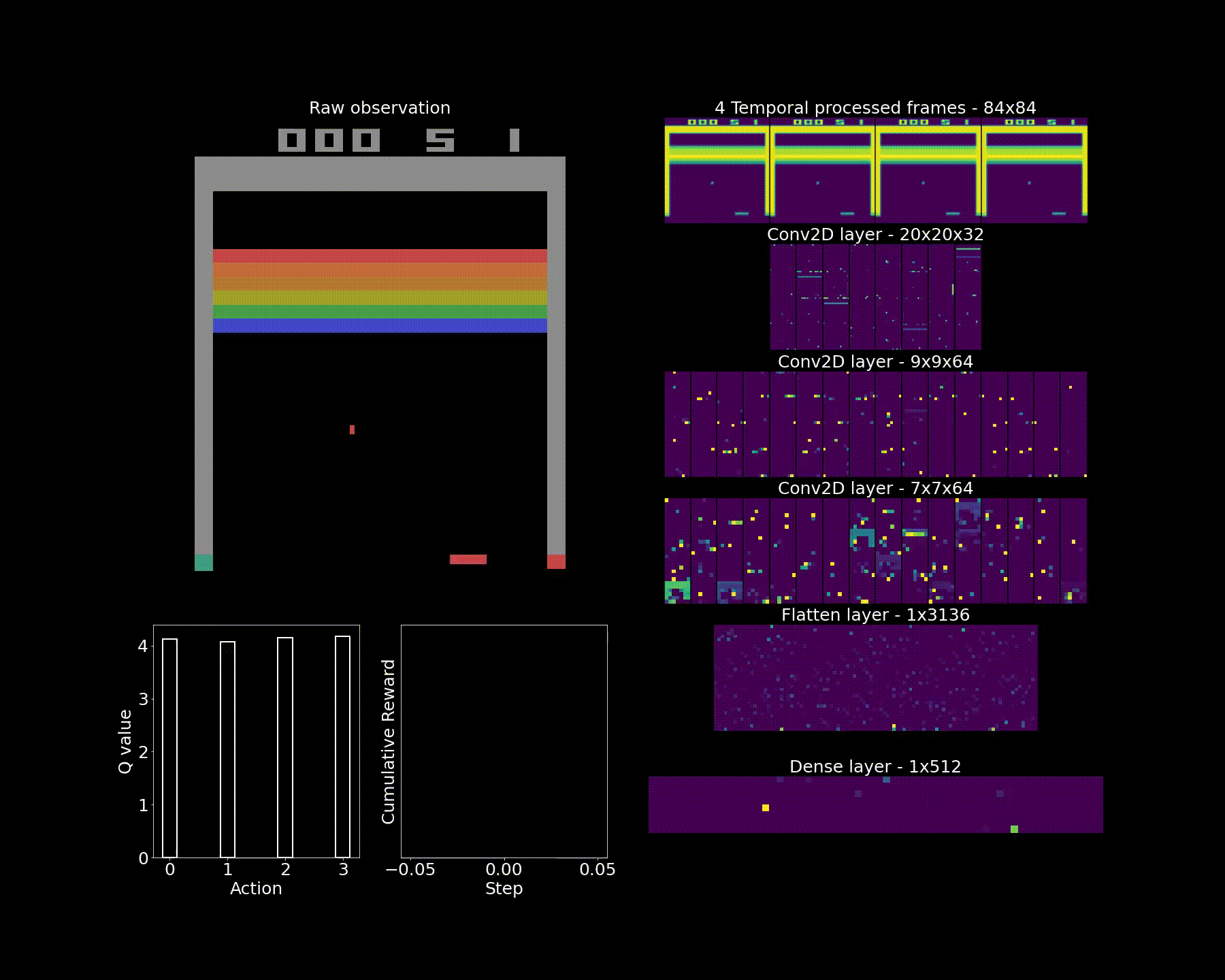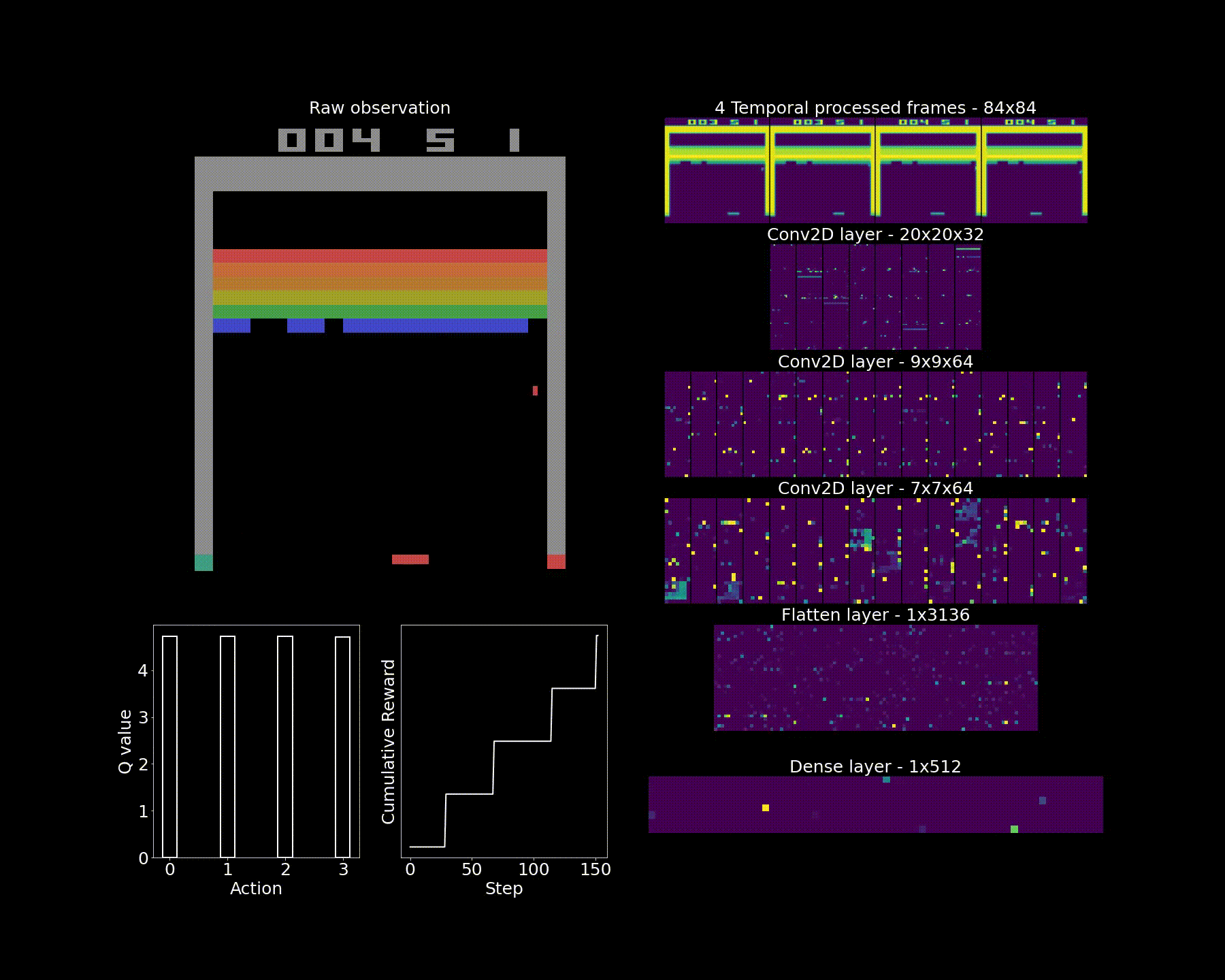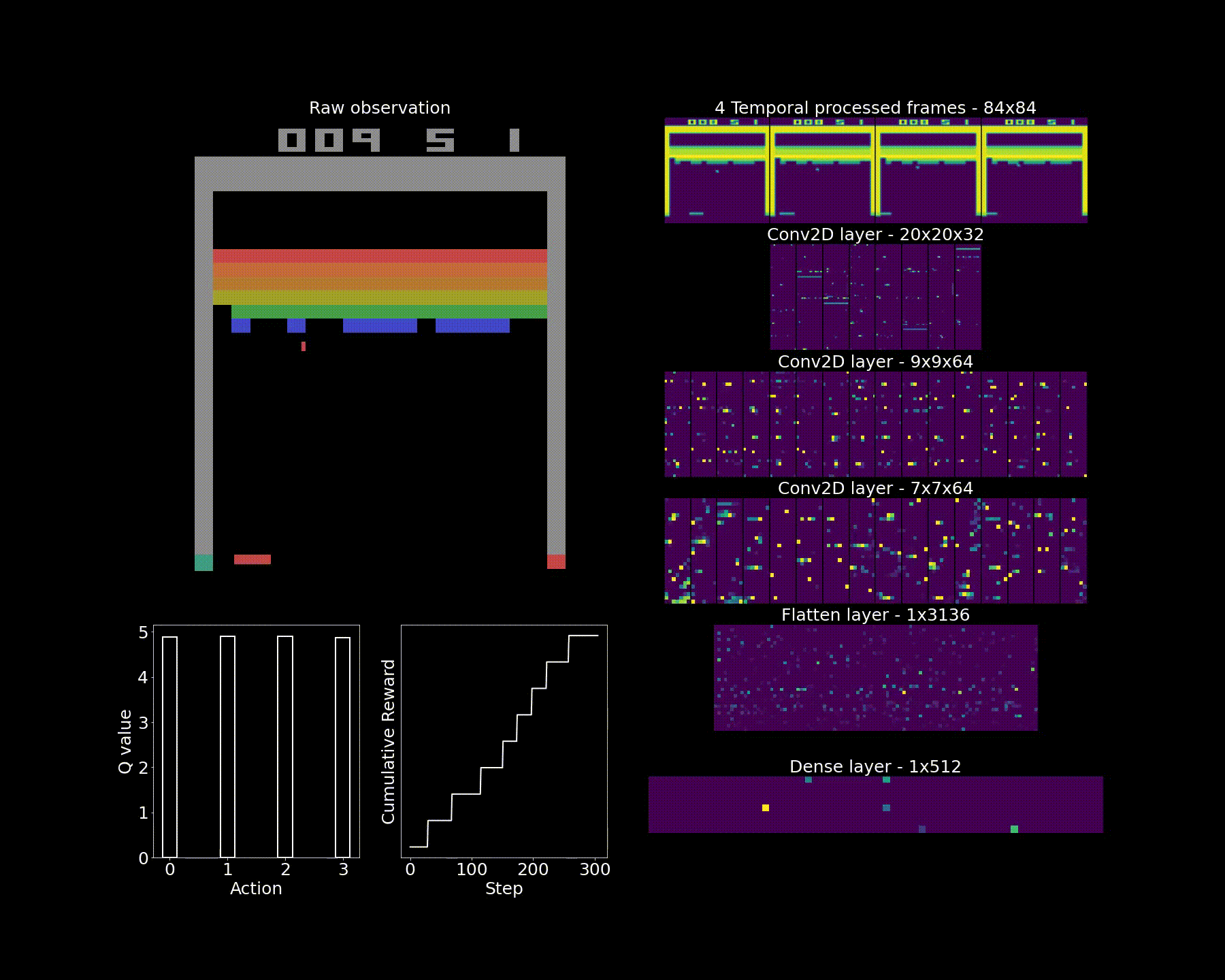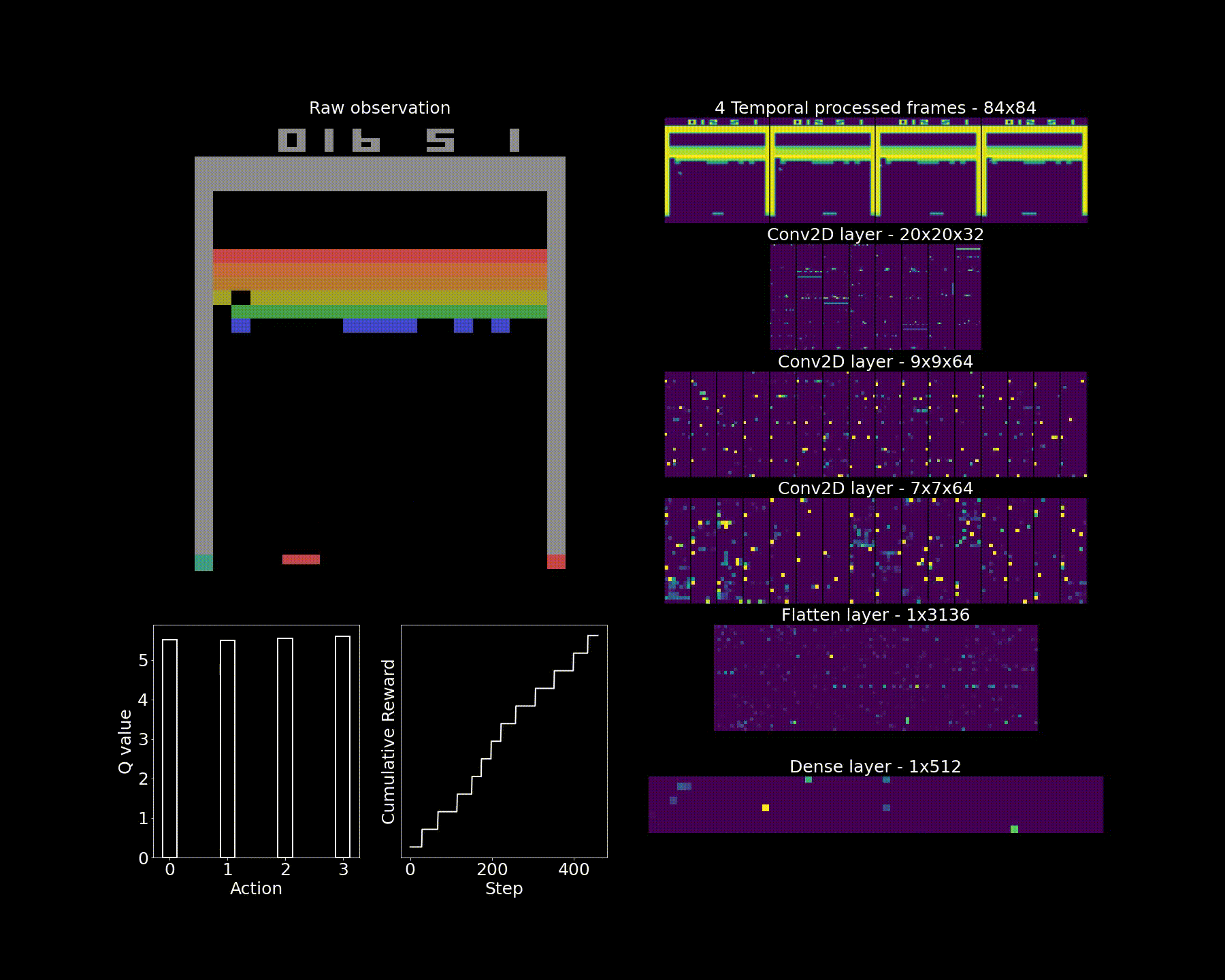
This notebook provides source code for solving continuous Computer Vision tasks. The task is described as follows: In this environment, the observation is an RGB image of the screen, which is an array of shape (210, 160, 3).
The task is solved by using Convolutional Neural Networks which approximate a Q-table.
Given the large state space (we are dealing with colored images), the images are downsampled and greyscaled. The frames are also stacked, which means that four consecutived greyscaled images are grouped together in a single array. This enables the image to capture motion of the ball and paddle.While previous tasks were solved by updating models on a step-by-step basis, we cannot follow this approach with CNNs. Indeed two consecutive frames are very similar (i.e. correlated) so any CNN would tend to overfit on the very few initial frames it is presented to. To avoid this, we create a replay memory where frames are pushed in a queue data structure at each step and frames are sampled randomly (with replacement) at regular intervals. This enables to simulate batches as well. An adjustment to the algorithm is reward shaping: they are clipped at [-1, 1]. This means that actions that lead to numerous bricks being broken will be levelled with those leading to only one but this will also avoid exploding gradients.