This repository contains the source code and data generated in the publication:
- Cristobal Galmez and Gaston Fermandois (2022). "Robust adaptive model-based compensator for the real-time hybrid simulation benchmark." (Submitted for publication in Structural Control and Health Monitoring.)
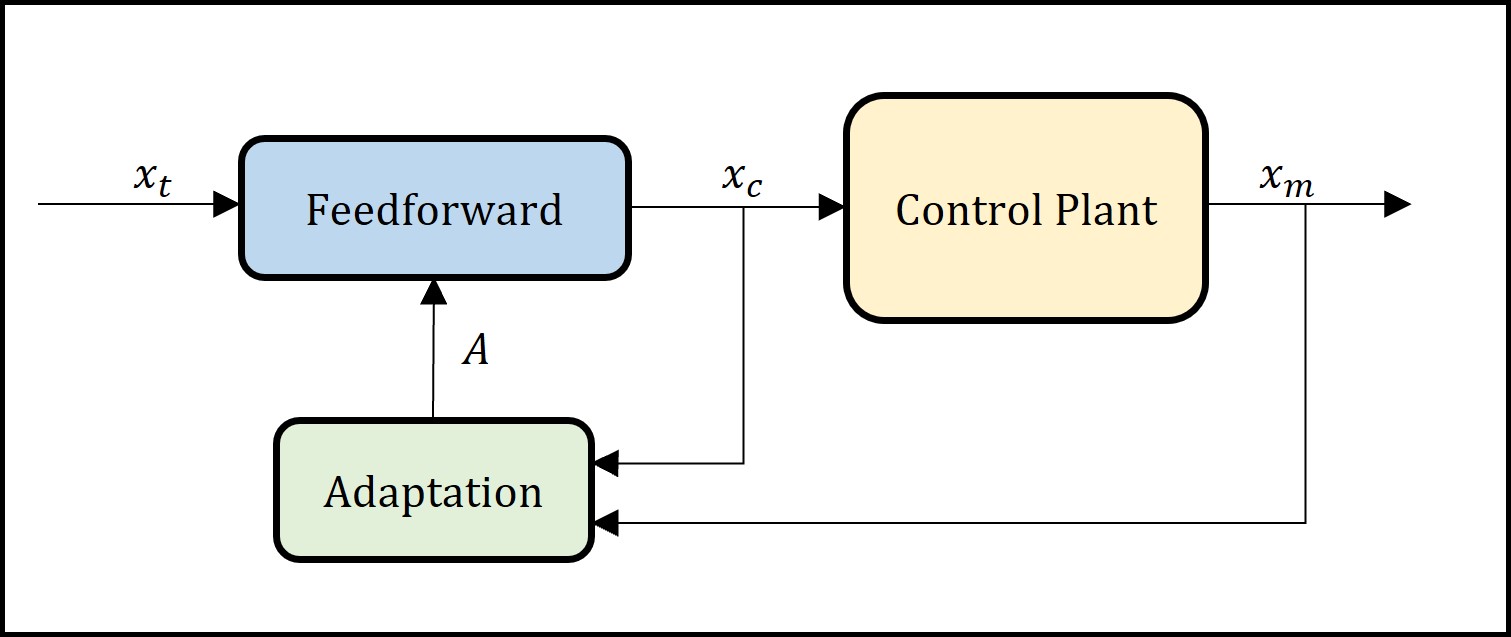
The Adaptive model-based compensator (AMB) consists in the inverse of the control plant in continuous form, but implemented with finite difference to achieve a causal controller. The AMB utilizes gradient adaptive law to identify the control plant model parameters and therefore requires the calibration of an adaptive gain matrix Gamma.
- Matlab R2021a or superior
A brief description of each application is presented and description of each file and instructions to execute are provided in the readme file inside the respective folders.
In this example the adaptive model-based compensator is designed, calibrated and applied to the RTHS benchmark. A calibrated gain matrix Gamma is provided to run several simulations with linear systems includding uncertainty. However, the adaptive gain matrix Gamma can be recalculated and analized using the calibration procedure.
In this example the adaptive mode-based compensator is applied to a modification of the RTHS benchmark, where the linear experimental substructure is replaced by non-linear models. Modified Bouc-Wen models are utilized to consider hysteretic models with degradation. This example does not include gains calibration since the goal is to prove the gains obtained for the linear case.