Verif is a command-line tool that lets you verify the quality of weather forecasts for point locations. It can also compare forecasts from different forecasting systems (that have different models, post-processing methods, etc).
The program reads files with observations and forecasts in a specific format (see "Input files" below). The input files contain information about dates, forecast lead times, and locations such that statistics can be aggregated across different dimensions. To ensure a fair comparison among files, Verif will discard data points where one or more forecast systems have missing forecasts. Since Verif is a command-line tool, it can be used in scripts to automatically create verification figures.
Verif version 1.0 has been released (see "Installation Instruction" below). We welcome suggestions for improvements. Verif is developed by Thomas Nipen, David Siuta, and Tim Chui.
For more information on how to use Verif, check out the wiki at https://github.com/WFRT/verif/wiki.
- Deterministic metrics such as MAE, bias, correlation, RMSE (e.g.
-m mae) - Threshold-based metrics such as the false alarm rate, ETS, EDI, Yule's Q (e.g.
-m ets) - Probabilistic metrics such as brier score, PIT-histogram, reliability diagrams (e.g.
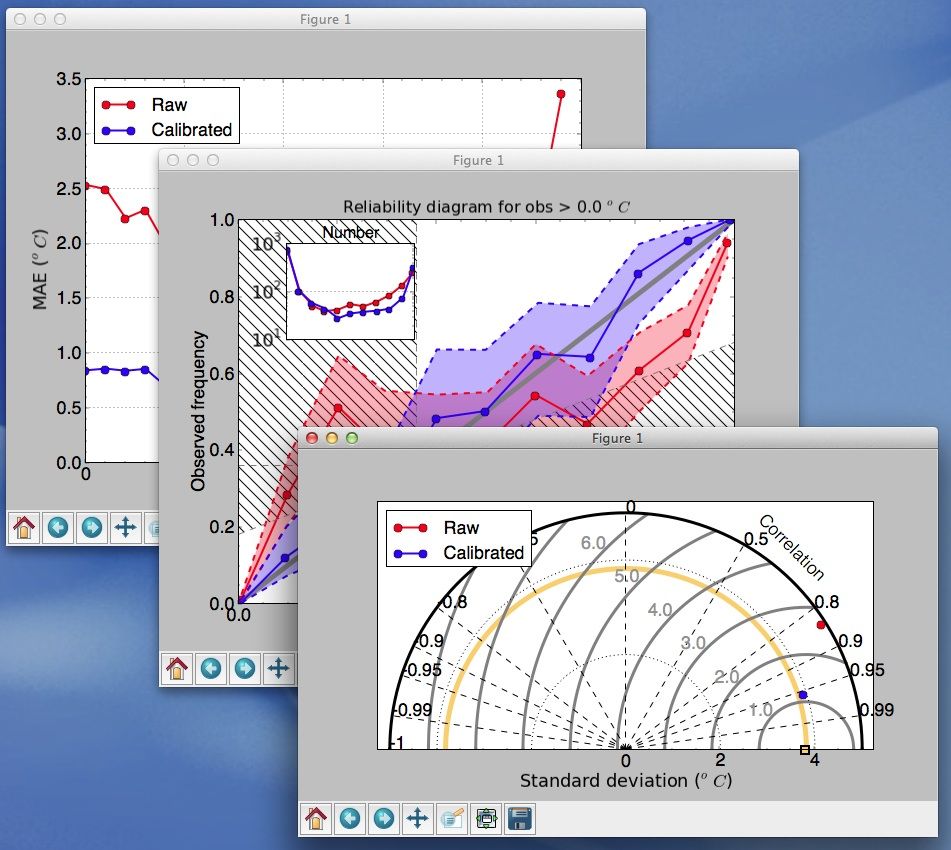
-m bs) - Special plots like Taylor diagrams (
-m taylor), quantile-quantile plots (-m qq). - Plot scores as a function of date, lead time, station altitude/lat/longitude (e.g.
-x date) - Show scores on maps (
-type map) - Subset the data by specifying a date range and lat/lon range (
-latrange 58,60) - Export to text (
-type text) - Options to adjust font sizes, label positions, tick marks, legends, etc (
-labfs 14) - Anomaly statistics relative to a baseline like climatology (
-c climfile.txt) - Output to png, jpeg, eps, etc and specify dimensions and resolution (
-f image.png -dpi 300)
Prerequisites
Verif requires NetCDF as well as the python packages numpy, scipy, and matplotlib. The python package mpltoolkits.basemap is optional, but provides a background map when verification scores are plotted on a map. Install the packages as follows:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install netcdf-bin libnetcdf-dev libhdf5-serial-dev
sudo apt-get install python-setuptools python-pip
sudo apt-get install python-numpy python-scipy python-matplotlib python-mpltoolkits.basemapInstalling using pip
After this, the easiest is to install the lastest version of Verif using pip:
sudo pip install verifVerif should then be accessible by typing verif on the command-line. If you do not have
sudo-rights, then install verif as follows:
pip install verif --userThis will create the executable ~/.local/bin/verif. Add this to your PATH environment
variable if necessary (i.e add export PATH=$PATH:~/.local/bin to ~/.bashrc).
To upgrade to a newer version of Verif, run the following:
pip install verif --upgradeInstalling from source
Alternatively, to install from source, download the source code of the latest version: https://github.com/WFRT/verif/releases/. Unzip the file and navigate into the extracted folder.
Then install Verif by executing the following inside the extracted folder:
sudo pip install -r requirements.txt
sudo python setup.py installThis will create the executable /usr/local/bin/verif. Add /usr/local/bin to your PATH environment
variable if necessary. If you do not have sudo privileges do:
pip install -r requirements.txt --user
python setup.py install --userThis will create the executable ~/.local/bin/verif. Add ~/.local/bin to your PATH environment
variable.
Follow the proceedure as for Ubuntu (either installing with pip or from source). If installing from source, then look for the line "Installing verif script to <some directory>", as this will indicate what folder Verif is installed into. Add the folder to your PATH environment variable if necessary.
A sample dataset for testing the program is found in ./examples/. There is one "raw" forecast file and
one "calibrated" forecast file (where statistical methods have been applied). For more information
about the dataset check out the wiki. Here are some example commands to test out:
# Shows mean absolute error as a function of lead-time
verif examples/raw.txt examples/kf.txt -m mae
# Shows average observed and forecasted values as a function on time
verif examples/raw.txt examples/kf.txt -m obsfcst -x time
# Shows equitable threat score as a function of threshold
verif examples/raw.txt examples/kf.txt -m ets
# Shows a reliability diagram for a threshold of 0 °C
verif examples/raw.txt examples/kf.txt -m reliability -r 0
# Shows Brier skill score as a function of threshold
verif examples/raw.txt examples/kf.txt -m bss -x thresholdCopyright © 2015-2019 UBC Weather Forecast Research Team. Verif is licensed under the 3-clause BSD license. See LICENSE file.