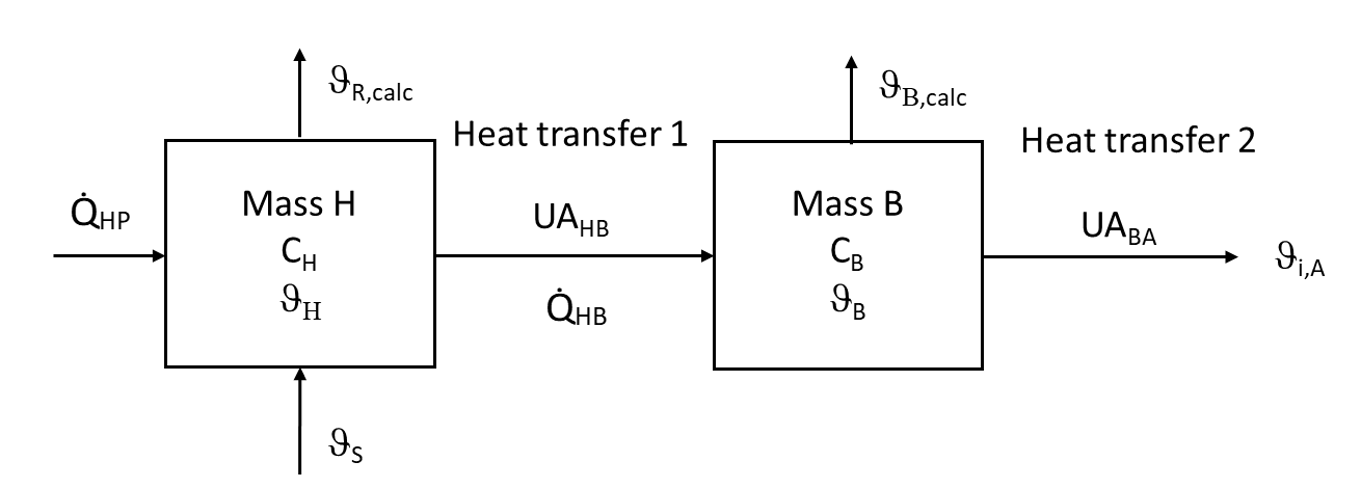
This repository consists of a simple two-mass building model for load-based testing of heat pumps. The model is used to define the inertial behavior of the heat sink.
LoadBasedTesting can be installed as a package. In order to use this package, you can either install it via pip install (see below) or simply download the Python files and use them in your own script. Installation steps are:
- Download or clone the repository via git:
git clone https://github.com/BAMresearch/bam-load-based-testing/ - Install the package via pip. Use conda prompt console or the terminal within pycharm:
pip install -e <local path to git repo>
The two-mass model consists of mass H, representing the heat transfer system, and mass B, representing the building envelope.
Each mass is characterized by a heat capacity MCp and an initial temperature
The heat output provided by the heat pump is delivered to mass H. Mass H is connected to mass B, so a heat exchange occurs between mass H and mass B.
Depending on the temperatures of the masses and the supply temperature
Mass B also exchanges heat with the environment.
The environment is represented by a constant ambient temperature
The associated energy balances of the subsystems determine the temperature changes of masses H and B:
The return temperature
The building model is defined in the class "TwoMassBuilding" in "twoMassModel.py" and consists of two objects of the class "ThermalMass".
To configure a new building model, the class "CalcParameters" can be used. A building model can be configured for a heat pump with constant mass flow or a constant temperature difference (t_flow - t_ret). In both cases, the nominal heating power and the nominal flow temperature of the heat pump must be specified. Additionally, the time constants tau_H and tau_B of the masses as well as the ambient temperature and the starting temperature of mass B are required. The function "createBuilding" determines all necessary parameters of the building model.
Parameterized building models for the BAM Round Robin Test can be found in the folder "BuildingModels".
All input parameters are in SI units.
q_design_e in Watt: - parameter has to be set, design heating power in PLC E
tau_b in seconds - constant, time constant of building envelope
tau_h in seconds - constant, time constant of transfer system
mass_flow in kg (or l) per second (since no fluid data is used, the water density is assumed as 1 kg per l), parameter, needed for design of 2-Mass-Model
t_b in °C
Models can be tested by using the scripts in the Example folder.