This is an implementation of the popular clustering algorithm K-Means++. K-Means is a popular clustering algorithm used for partitioning a dataset into distinct groups, called clusters. The algorithm's effectiveness often depends on the initial placement of cluster centroids. Traditional K-Means starts with randomly selected centroids, which may result in suboptimal convergence.
K-Means++ addresses this limitation by employing a smarter initialization strategy. Instead of randomly selecting the first centroid, K-Means++ chooses it with a higher probability based on the distance from data points. Subsequent centroids are chosen with a similar approach, emphasizing points farther from existing centroids.
The algorithm only works for two dimensional points. You can check the format of the input file in the uploaded examples(normal.txt and unbalanced.txt).
First you would need to have a python environment with the packages numpy and matplotlip installed in it.
The python script should be run with the proper arguments.
python kmeans++.py <path_to_file> <k_clusters> <number_of_restarts>
The last argument being optional, where the default value is 0 if not added.
Example:
python kmeans++.py normal/normal.txt 3
Output:
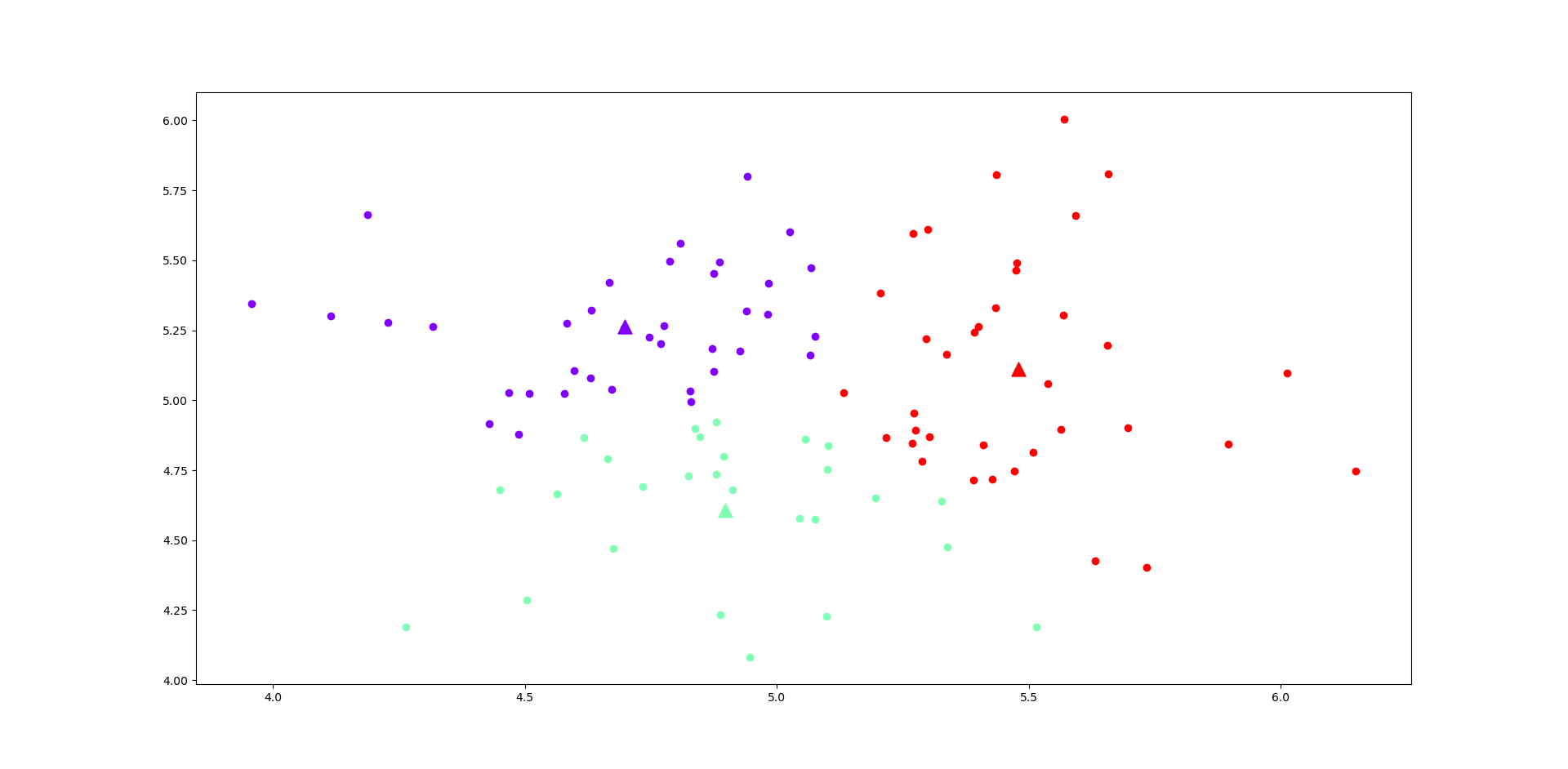
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Thank you for checking out my K-Means++ clustering algorithm!