This project aims to implement and compare two versions of the Support Vector Machine (SVM) model: a standard SVM model and a distributed SVM model using the Alternative Directions Multipliers Method (ADMM). The comparison focuses on examining their convergence and assessing whether the distributed version can match the performance of the centralized one using real data. The project also involves tuning model parameters, with a focus on understanding how ADMM parameters influence the convergence of the distributed model.
The project's parameters include:
- lambda: Regularization parameter used for fine-tuning the SVM model in the centralized version and reused in the distributed version.
- rho: Parameter indicating convergence within the distributed version, tested to determine the fastest convergence.
- Stopping Criteria (or Early Stopping): Option to stop the model when it reaches convergence instead of waiting for a predetermined iteration value.
General metrics used for comparing model performance include accuracy, confusion matrix, ROC and AUC scores, loss trend, and disagreement trend.
Two datasets are used: a synthetic dataset for verifying code implementation and a real dataset called Apple Quality obtained from Kaggle. The purpose of the project is not to implement a model for a specific task but to develop a framework for distributed optimization and compare implementations in terms of potential company infrastructure.
ADMM is a mathematical framework used to implement distributed versions of models. It involves dividing the loss function and regularization into separate steps to perform optimization procedures while maintaining consistency. The distributed SVM model using ADMM is explained, highlighting the convergence process and parameter tuning.
The project is implemented in Python using CVXPY, a modeling language for convex optimization problems. The Centralized SVM and Distributed SVM (by Samples) are presented, along with the implementation details of the ADMM framework.
The model selection process involves grid search for parameter tuning and examining convergence behavior. The results of the grid search for both centralized and distributed models are discussed, along with the impact of ADMM parameters on convergence.
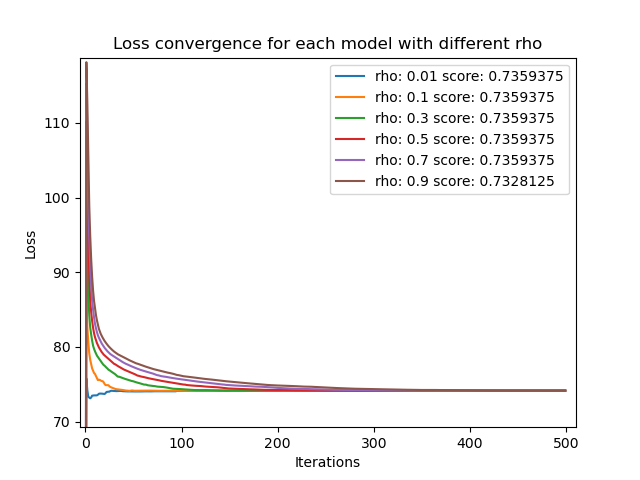
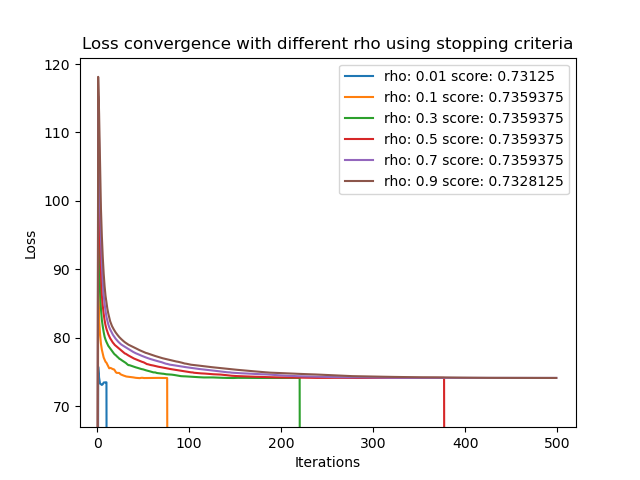
In these examples, we can observe the distributed version exhibiting different convergence behaviors using various step-size values and how applying a stopping criterion can influence their behavior.
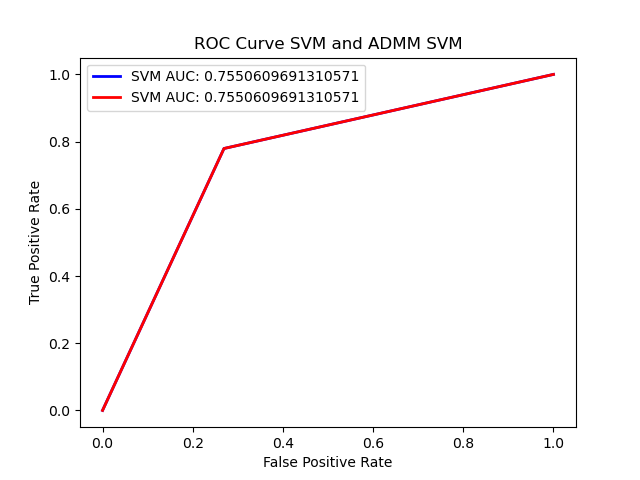
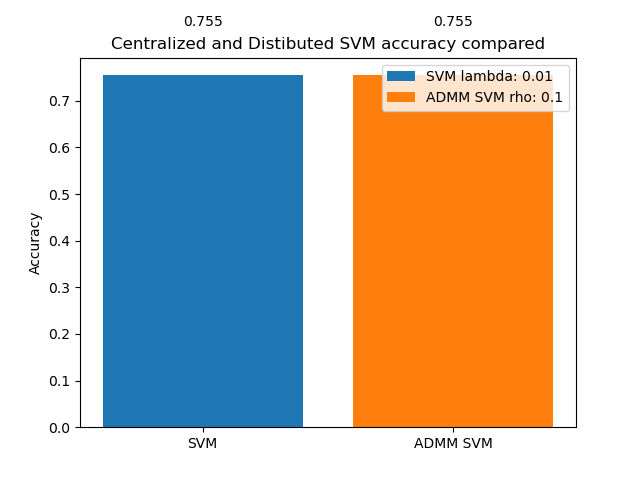
The performance of the centralized and distributed models is compared using various metrics, including accuracy, confusion matrix, ROC, and AUC scores. The project demonstrates how both finely-tuned models converge to the same performance level.
For further information check the complete guide here